Signal transduction without signal -- receptor clusters can direct cell movement
Clustering of receptors can have the same effect as binding a signaling molecule -- receptor clusters can direct cell movement
2021-02-25
(Press-News.org) Our body consists of 100 trillion cells that communicate with each other, receive signals from the outside world and react to them. A central role in this communication network is attributed to receiver proteins, called receptors, which are anchored at the cell membrane. There, they receive and transmit signals to the inside of the cell, where a cell reaction is triggered.
In humans, G protein-coupled receptors (GPC receptors) represent the largest group of these receptor molecules, with around 700 different types. The research of the Frankfurt and Leipzig scientists focused on a GPC receptor that serves as a receptor for the neuropeptide Y in cells and is accordingly called the Y2 receptor. Neuropeptide Y is a messenger substance that primarily mediates signals between nerve cells, which is why Y2 receptors are mainly present in nerve cells and among other activities trigger the formation of new cell connections.
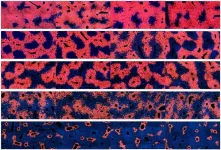
In the laboratory, the researchers engineered cells, which had approx. 300,000 Y2 receptors on their surface and were grown on specifically developed, light-sensitive matrices. Each of the Y2 receptors was provided with a small molecular "label". Once the scientists created a spot of light with a fine laser beam on the cell surface, the Y2 receptor under this spot were trapped via the molecular label to the exposed matrix in such a way that the Y2 receptors moved closely together to form an assembly known as a cluster. The whole reaction could be immediately observed at the defined spot and within a few seconds.
Professor Robert Tampé from the Institute of Biochemistry at Goethe University Frankfurt explains: "The serendipity about this experiment is that the clustering of receptors triggers a signal that is similar to that of neuropeptide Y. Solely by the clustering, we were able to trigger cell movement as a reaction of the cell. The laser spots even allowed us to control the direction of the cell movement." As the light-sensitive lock-and-key pairs utilized are very small compared to the receptors, the organization of the receptors in the cell membrane can be controlled with high precision using the laser spot. "This non-invasive method is thus particularly well suited to study the effects of receptor clustering in living cells," Tampé continues. "Our method can be used to investigate exciting scientific questions, such as how receptors are organized in networks and how new circuits are formed in the brain."
INFORMATION:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-02-25
Timothy Callaghan, PhD, and Alva Ferdinand, DrPH, JD, from the Southwest Rural Health Research Center at Texas A&M University School of Public Health, joined colleagues in the first national study of how often people in urban and rural areas in the United States follow COVID-19 guidelines. These include public health best practices like wearing masks in public, sanitizing homes and work areas, maintaining physical distancing, working from home and avoiding dining in restaurants or bars.
The research team used a survey of 5,009 U.S. adults that closely matched the makeup of the country's population as a whole. The survey asked how often participants followed COVID-19 prevention recommendations and collected data on political ideology, perceived risk ...
2021-02-25
ITHACA, N.Y. - A team from Cornell University's Environmental Systems Lab, led by recent graduate Allison Bernett, has put forth a new framework for injecting as much information as possible into the pre-design and early design phases of a project, potentially saving architects and design teams time and money down the road.
"(Our framework) allows designers to understand the full environmental impact of their building," said Bernett, corresponding author of "Sustainability Evaluation for Early Design (SEED) Framework for Energy Use, Embodied Carbon, Cost, and Daylighting Assessment" which published Jan. 10 in the Journal of ...
2021-02-25
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. -- Doppler radar improves lives by peeking inside air masses to predict the weather. A Purdue University team is using similar technology to look inside living cells, introducing a method to detect pathogens and treat infections in ways that scientists never have before.
In a new study, the team used Doppler to sneak a peek inside cells and track their metabolic activity in real time, without having to wait for cultures to grow. Using this ability, the researchers can test microbes found in food, water, and other environments to see if they are pathogens, or help them identify the right medicine to treat antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
David Nolte, Purdue's Edward ...
2021-02-25
HOUSTON - (Feb. 25, 2021) - Low-income livestock farmers in developing countries are often faced with a difficult dilemma: protect their animals from endangered predators, or spare the threatened species at the expense of their livestock and livelihood.
A new paper by Rice University economist Ted Loch-Temzelides examines such circumstances faced by farmers in Pakistan. "Conservation, risk aversion, and livestock insurance: The case of the snow leopard" outlines a plan under which farmers can protect themselves from crippling financial losses while ...
2021-02-25
While the amazing regenerative power of the liver has been known since ancient times, the cells responsible for maintaining and replenishing the liver have remained a mystery. Now, research from the Children's Medical Center Research Institute at UT Southwestern (CRI) has identified the cells responsible for liver maintenance and regeneration while also pinpointing where they reside in the liver.
These findings, reported today in Science, could help scientists answer important questions about liver maintenance, liver damage (such as from fatty liver or alcoholic liver disease), and liver cancer.
The liver performs vital functions, including chemical detoxification, blood protein production, bile excretion, and regulation of energy metabolism. Structurally, the liver ...
2021-02-25
Paleo-ecologists from The University of New Mexico and at the University of Nebraska-Lincoln have demonstrated that the offspring of enormous carnivorous dinosaurs, such as Tyrannosaurus rex may have fundamentally re-shaped their communities by out-competing smaller rival species.
The study, released this week in the journal Science, is the first to examine community-scale dinosaur diversity while treating juveniles as their own ecological entity.
"Dinosaur communities were like shopping malls on a Saturday afternoon ? jam-packed with teenagers" explained Kat Schroeder, a graduate student in the UNM Department of Biology who led the study. "They made up a significant portion of the individuals in a species and would have had a very real impact ...
2021-02-25
An international team of scientists has developed a system that can generate random numbers over a hundred times faster than current technologies, paving the way towards faster, cheaper, and more secure data encryption in today's digitally connected world.
The random generator system was jointly developed by researchers from Nanyang Technological University, Singapore (NTU Singapore), Yale University, and Trinity College Dublin, and made in NTU.
Random numbers are used for a variety of purposes, such as generating data encryption keys and one-time ...
2021-02-25
As Covid-19 impacts lives around the world- a new skeleton study is reconstructing ancient pandemics to assess human's evolutionary ability to fight off leprosy, tuberculosis and treponematoses with help from declining rates of transmission when the germs became widespread.
The researchers state the germs mutated to infect ancient humans so they could replicate- hopping across to as many new hosts as possible- but the severity of the diseases reduced as a result.
The analysis by Adjunct Professor in Archaeology Maciej Henneberg and Dr Teghan Lucas at Flinders ...
2021-02-25
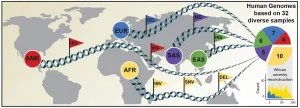
In 2001, the International Human Genome Sequencing Consortium announced the first draft of the human genome reference sequence. The Human Genome Project, as it was called, had taken more than eleven years of work and involved more than 1000 scientists from 40 countries. This reference, however, did not represent a single individual but instead is a composite of humans that could not accurately capture the complexity of human genetic variation.
Building on this, scientists have carried out many sequencing projects over the last 20 years to identify and catalog genetic differences between an individual and the reference genome. Those differences usually ...
2021-02-25
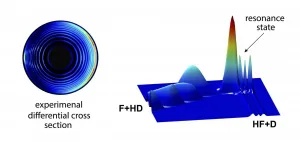
A chemical reaction can be understood in detail at the quantum state-resolved level, through a combined study of molecular crossed beam experiments and theoretical quantum molecular reaction dynamics simulations.
At a single collision condition, the molecular crossed beam apparatus is able to detect the scattering angle-resolved product with rotational state-resolution. Whereas, with accurate global potential energy surface, quantum reactive scattering theory is able to predict the corresponding reactive scattering information.
In previous studies, the chemical reaction dynamics was revealed only with the product rotational state-resolution. And the investigation of a reaction ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Signal transduction without signal -- receptor clusters can direct cell movement
Clustering of receptors can have the same effect as binding a signaling molecule -- receptor clusters can direct cell movement