Citizen scientists help expose presence of invasive Asian bamboo longhorn beetle in Europe
2021-03-09
(Press-News.org) A worryingly high number of Asian bamboo longhorn beetles (Chlorophorus annularis) turn out to have been emerging across Europe for about a century already, finds an international research team, headed by researchers from the Center of Natural History, University of Hamburg, Germany. Curiously, the recent records of the invasive, non-native to the Old Continent species are mostly sourced from citizen scientists and online platforms, which proves the power of involving the public in species monitoring. The study is published in the open-access, peer-reviewed scientific journal BioRisk.
In our globalised world, which has already become victim to climate change and biodiversity loss, non-native species present a further threat to our ecosystems. Thus, the rising accounts of newly recorded alien species are of serious concern to both scientists and (inter)national institutions. However, surveying non-native species remains limited to a small fraction of species: those known to be particularly invasive and harmful.
One of the multitude of non-native species that are currently lacking efficient and coordinated surveying efforts is the Asian bamboo longhorn beetle (Chlorophorus annularis). Naturally occurring in temperate and tropical Southeast Asia, the insect feeds on a variety of plants, but prefers bamboo. Thus, due to the international trade of bamboo and the insects 'travelling' with the wood, the species has continuously been expanding its distribution around the world. Its first appearance in Europe was recorded back in 1924, when it was identified in England.
Back to our days, during a fieldwork practice for students at the University of Hamburg, held within the city because of the COVID-19 travelling restrictions, the team stumbled across a longhorn beetle, later identified by scientists as the Asian bamboo borer. Furthermore, it became clear that there were even more recent records published across different citizen science platforms, such as iNaturalist, iRecord and Waarneming.nl. Having taken the contacts of the citizen scientists from there, the researchers approached them to ask for additional collection details and images, which were readily provided. As a result, the researchers formally confirmed the presence of the Asian bamboo borer in Belgium and the Netherlands. In total, they reported thirteen new introductions of the species in Europe, which translates to a 42% increase of the records of the species for the continent.
"In light of the warming climate and a growing abundance of ornamental bamboo plants in Europe, the beetle might get permanently established. Not only could it become a garden pest, but it could also incur significant costs to the bamboo-processing industry," comments Dr Matthias Seidel, lead author of the study.
Having realised the potential of citizen science for bridging the gaps in invasive species monitoring, the researchers now propose for specialised platforms to be established with the aim to familiarise non-professional scientists with non-native species of interest and provide them with more sophisticated reporting tools. The aim is to speed up the identification of important alien species by collating records of specific species of interest, which are flagged and regularly exported from other citizen science databases and platforms.
INFORMATION:
Original source:
Seidel M, Lüttke M, Cocquempot C, Potts K, Heeney WJ, Husemann M (2021) Citizen scientists significantly improve our knowledge on the non-native longhorn beetle Chlorophorus annularis (Fabricius, 1787) (Coleoptera, Cerambycidae) in Europe. BioRisk 16: 1-13. https://doi.org/10.3897/biorisk.16.61099
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-09
A two-week course of high doses of CBD helps restore the function of two proteins key to reducing the accumulation of beta-amyloid plaque, a hallmark of Alzheimer's disease, and improves cognition in an experimental model of early onset familial Alzheimer's, investigators report.
The proteins TREM2 and IL-33 are important to the ability of the brain's immune cells to literally consume dead cells and other debris like the beta-amyloid plaque that piles up in patients' brains, and levels of both are decreased in Alzheimer's.
The investigators report ...
2021-03-09
An analysis of SARS-CoV-2 genome diversity in more than 1,000 people in the United Kingdom suggests that if viral mutations do arise, they can be transmitted in some cases but they rarely persist in subsequent transmissions. "Our observations indicate the within-host emergence of vaccine- and therapeutic-escape mutations is likely to be relatively rare," say the authors, "at least during early infection when viral loads are high." However, because mutations that can escape therapies like antibodies were identified, including in higher viral load samples, the authors encourage continued monitoring and vigilance, particularly as vaccines and therapeutics that put "pressure" on viruses to adapt are rolled out more widely. ...
2021-03-09
While receiving just one dose of a two-dose SARS-CoV-2 vaccine tends to decrease infections in the short-term if it produces a strong immune response, it may increase the potential for the virus to "escape" therapies in the longer-term if one-dose vaccinal immunity is weak, reports a new modeling study "[O]ur work emphasizes that the impact of vaccine dosing regimes are strongly dependent on the relative robustness of immunity conferred by a single dose," the authors write. As COVID-19 vaccines have been distributed internationally, several countries including the United Kingdom and Canada have chosen to delay the second dose to increase the number of individuals ...
2021-03-09
Amid the COVID-19 pandemic, children's hospitals across the United States have seen signification reductions in the number of children being treated for common pediatric illnesses like asthma and pneumonia, according to a new multicenter study led by Monroe Carell Jr. Children's Hospital at Vanderbilt.
Researchers at Children's Hospital found that 42% fewer children were being seen and hospitalized at 44 children's hospital across the U.S. for both respiratory and non-respiratory illnesses, with the most significant reduction seen in children under age 12. Hospitals saw a decline in the number of children seen or hospitalized for respiratory illness by 62%, while there was 38% reduction for non-respiratory illnesses.
The trend, ...
2021-03-09
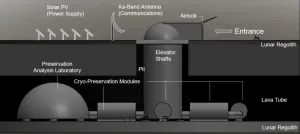
University of Arizona researcher Jekan Thanga is taking scientific inspiration from an unlikely source: the biblical tale of Noah's Ark. Rather than two of every animal, however, his solar-powered ark on the moon would store cryogenically frozen seed, spore, sperm and egg samples from 6.7 million Earth species.
Thanga and a group of his undergraduate and graduate students outline the lunar ark concept, which they call a "modern global insurance policy," in a paper presented over the weekend during the IEEE Aerospace Conference.
"Earth is naturally a volatile environment," said Thanga, a professor of aerospace and mechanical engineering in the UArizona College ...
2021-03-09
Neuroendocrine tumours are cancers that begin in specialised cells called neuroendocrine cells. These cells have traits similar to those of nerve cells and hormone-producing cells. Neuroendocrine tumours, while rare, can occur anywhere in the body. Most affect the cardiothoracic region, eg lungs, appendix, small intestine, pancreas as well as the rectum. There are many types of neuroendocrine tumours: some grow slowly while others develop very rapidly.
Neuroendocrine tumors are characterised by abundant production of somatostatin receptor 2, a naturally circulating hormone that is an important target for scientists studying new treatment approaches.
Peptide Receptor Radionuclide Therapy (PRRT) is the most commonly used treatment for refractive ...
2021-03-09
Home delivery of HIV medicines in South Africa significantly increased viral suppression compared to those who received clinical care, according to a study by researchers at the University of Washington School of Medicine.
The study, conducted with Amazon.com guidance during COVID-19 restrictions in South Africa, showed that among study participants, paying a fee for home delivery and monitoring of antiretroviral therapy (ART) was highly acceptable in the context of low income and high unemployment, and improved health outcomes as a result.
The researching findings were ...
2021-03-09
Researchers at the Buck Institute analyzed data from the COVID-19 Symptom Tracker app used by 3 million people in the United Kingdom, adding the use of immunosuppressant medication, use of a mobility aid, shortness of breath, fever, and fatigue to the list of symptoms and comorbidities that increase the risk for severe COVID-19. Results are published in the Journal of Medical Internet Research.
"Even though there are established risk factors for severe COVID-19 there are no good predictors that enable healthcare providers, or even those who have tested positive, to assess who should seek advanced medical care," says Buck Institute ...
2021-03-09
TAMPA, Fla. (March 8, 2021) -- Preterm birth is a END ...
2021-03-09
Recently, Prof. CHEN Gao from Institute of Geometry and Physics of the University of Science and Technology of China has made breakthrough in the field of complex differential geometry. Using mathematical invention, he buildt a new bridge between the relativity of Einstein and quantum mechanics. This work was published in Inventiones Mathematicae.
In the field of complex differential geometry, there are two crucial physical equations: the Hermitian-Yang-Mills equation, which became the standard model of quantum mechanics, and the Kähler-Einstein equation, which is closely related to relativity. To stably solve these two equations ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Citizen scientists help expose presence of invasive Asian bamboo longhorn beetle in Europe