(Press-News.org) CORVALLIS, Ore. - A quarter-century-old harvesting restriction intended to last one year has served as an obstacle to returning eastern Oregon national forests to the healthier, more fire-resilient conditions they embodied in the late 1800s, research by the Oregon State University College of Forestry shows.
The findings, published in Ecosphere, are both important and timely because the U.S. Forest Service recently revised what has widely become known as the "21-inch rule" - a prohibition against cutting trees greater than 21 inches in diameter at breast height on Forest Service land in eastern Oregon.
"Under the old policy, live trees more than 21 inches in diameter couldn't be cut," said the study's lead author, James Johnston. "The simulations we conducted show that a quarter of mixed conifer stands east of the Cascades couldn't be restored to historical forest density or basal area under this 21-inch rule."
A stand's basal area is the total surface area of all the stumps that would be created if every tree in the stand were cut at 4.5 feet.
Johnston, College of Forestry colleagues Skye Greenler and Chris Dunn and collaborators from the U.S. Forest Service looked at hundreds of long-term research plots within a 2.5-million-acre study area in eastern Oregon to summarize historical and current forest structure and composition.
The scientists then ran a range of simulations to learn the degree to which thinning under different diameter limits restored mixed conifer stands to late-1800s conditions: less dense, less basal area and a lower proportion of shade-tolerant species than are currently found within stands.
"Historical conditions were much better suited for old growth trees," said Johnston. "Since we began to suppress fires that maintained open stands of widely spaced old trees, competition from young trees, including fairly large fir that established in the absence of fire, is killing old growth trees faster than they can be replaced."
Diameter limits were widely adopted by Forest Service managers throughout the 1990s, Johnston said, in the face of social and legal pressure to conserve old growth habitat. Eastern Oregon's diameter rule was supposed to be temporary as the Forest Service put together a comprehensive ecosystem management plan, but that process stalled, meaning the 21-inch rule is now 25 years past its original sunset date.
"With the Forest Service's 21-inch rule for eastern Oregon, even stands that could be restored to their historical basal areas still had a lot more shade-tolerant trees than they did historically," Greenler said. "But allowing the larger shade-tolerant trees to be removed helps reduce competition around old growth trees and improves their chances in the face of future stress."
The Forest Service, Johnston added, recently completed a National Environmental Policy Act planning effort to reflect the best available science regarding diameter limits' effects on restoration efforts.
"The cutting of big trees is controversial, especially in mixed conifer stands that have complex structures and a wide range of species and age classes," he said. "But collaborative research like ours has the potential to build social license for that type of cutting when it makes sense in the big picture of restoring forests."
Assisting with this study were the Blue Mountains Forest Partners and the Malheur National Forest. The study makes use of data collected in the field over the last six years as part of a partnership between the Blue Mountains Forest Partners, the Forest Service and Oregon State University.
"We used data from real trees we measured in real forests," said Greenler, "but instead of thinning hundreds of thousands of acres and remeasuring those stands, we wrote a computer program that simulates years worth of thinning in seconds. It's exciting to develop these tools with managers and stakeholders and to be able to use these results to inform policy change."
INFORMATION:
The Forest Service and the Blue Mountains Forest Partners provided funding.
Johnston and his co-authors have two other articles pending on the 21-inch rule. A paper to be published in the Journal of Forestry argues that a big-data approach is necessary to monitor the health of old growth trees in eastern Oregon. The other, to appear in Frontiers in Forests and Global Change, describes the implications of the 21-inch rule on carbon storage.
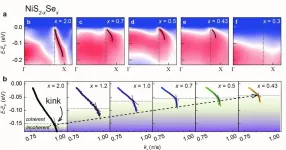
Strongly correlated systems are materials that exhibit strong interactions between electrons, a property unseen in ordinary conductors or insulators. Typical examples include metal-insulator transitions or unconventional high-temperature superconductivity where the resistance becomes zero at high temperatures.
There have been studies to explain this strong interaction between electrons and their characteristic energy scales, but no direct observation on such energy scales through theory or experiments has been reported. To this, the POSTECH-IBS joint research team has succeeded in directly observing the evolution of coherence energy ...
WASHINGTON--Illegal use of anabolic steroids not only has dangerous side effects during use but also can harm of men's testicular function years after they stop abusing steroids, according to a study published in the Endocrine Society's Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.
Anabolic steroids are synthetic forms of testosterone, and their abuse is prevalent among athletes worldwide. Some people use these steroids without a prescription to improve athletic performance or get a more muscular look. Known side effects of these drugs in men include breast growth, hair loss, shrunken testicles and lower testosterone levels. Also called hypogonadism, low testosterone can cause decreased sex drive, poor erections and a low sperm count.
"It is still debated whether illicit ...
A worryingly high number of Asian bamboo longhorn beetles (Chlorophorus annularis) turn out to have been emerging across Europe for about a century already, finds an international research team, headed by researchers from the Center of Natural History, University of Hamburg, Germany. Curiously, the recent records of the invasive, non-native to the Old Continent species are mostly sourced from citizen scientists and online platforms, which proves the power of involving the public in species monitoring. The study is published in the open-access, peer-reviewed ...
A two-week course of high doses of CBD helps restore the function of two proteins key to reducing the accumulation of beta-amyloid plaque, a hallmark of Alzheimer's disease, and improves cognition in an experimental model of early onset familial Alzheimer's, investigators report.
The proteins TREM2 and IL-33 are important to the ability of the brain's immune cells to literally consume dead cells and other debris like the beta-amyloid plaque that piles up in patients' brains, and levels of both are decreased in Alzheimer's.
The investigators report ...
An analysis of SARS-CoV-2 genome diversity in more than 1,000 people in the United Kingdom suggests that if viral mutations do arise, they can be transmitted in some cases but they rarely persist in subsequent transmissions. "Our observations indicate the within-host emergence of vaccine- and therapeutic-escape mutations is likely to be relatively rare," say the authors, "at least during early infection when viral loads are high." However, because mutations that can escape therapies like antibodies were identified, including in higher viral load samples, the authors encourage continued monitoring and vigilance, particularly as vaccines and therapeutics that put "pressure" on viruses to adapt are rolled out more widely. ...
While receiving just one dose of a two-dose SARS-CoV-2 vaccine tends to decrease infections in the short-term if it produces a strong immune response, it may increase the potential for the virus to "escape" therapies in the longer-term if one-dose vaccinal immunity is weak, reports a new modeling study "[O]ur work emphasizes that the impact of vaccine dosing regimes are strongly dependent on the relative robustness of immunity conferred by a single dose," the authors write. As COVID-19 vaccines have been distributed internationally, several countries including the United Kingdom and Canada have chosen to delay the second dose to increase the number of individuals ...
Amid the COVID-19 pandemic, children's hospitals across the United States have seen signification reductions in the number of children being treated for common pediatric illnesses like asthma and pneumonia, according to a new multicenter study led by Monroe Carell Jr. Children's Hospital at Vanderbilt.
Researchers at Children's Hospital found that 42% fewer children were being seen and hospitalized at 44 children's hospital across the U.S. for both respiratory and non-respiratory illnesses, with the most significant reduction seen in children under age 12. Hospitals saw a decline in the number of children seen or hospitalized for respiratory illness by 62%, while there was 38% reduction for non-respiratory illnesses.
The trend, ...
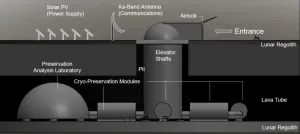
University of Arizona researcher Jekan Thanga is taking scientific inspiration from an unlikely source: the biblical tale of Noah's Ark. Rather than two of every animal, however, his solar-powered ark on the moon would store cryogenically frozen seed, spore, sperm and egg samples from 6.7 million Earth species.
Thanga and a group of his undergraduate and graduate students outline the lunar ark concept, which they call a "modern global insurance policy," in a paper presented over the weekend during the IEEE Aerospace Conference.
"Earth is naturally a volatile environment," said Thanga, a professor of aerospace and mechanical engineering in the UArizona College ...
Neuroendocrine tumours are cancers that begin in specialised cells called neuroendocrine cells. These cells have traits similar to those of nerve cells and hormone-producing cells. Neuroendocrine tumours, while rare, can occur anywhere in the body. Most affect the cardiothoracic region, eg lungs, appendix, small intestine, pancreas as well as the rectum. There are many types of neuroendocrine tumours: some grow slowly while others develop very rapidly.
Neuroendocrine tumors are characterised by abundant production of somatostatin receptor 2, a naturally circulating hormone that is an important target for scientists studying new treatment approaches.
Peptide Receptor Radionuclide Therapy (PRRT) is the most commonly used treatment for refractive ...
Home delivery of HIV medicines in South Africa significantly increased viral suppression compared to those who received clinical care, according to a study by researchers at the University of Washington School of Medicine.
The study, conducted with Amazon.com guidance during COVID-19 restrictions in South Africa, showed that among study participants, paying a fee for home delivery and monitoring of antiretroviral therapy (ART) was highly acceptable in the context of low income and high unemployment, and improved health outcomes as a result.
The researching findings were ...