Exercise can improve sleep quality even when you don't perceive a difference
Researchers from the University of Tsukuba find that vigorous exercise causes imperceptible improvements in sleep quality
2021-03-25
(Press-News.org) Tsukuba, Japan - Physical exercise has long been prescribed as a way to improve the quality of sleep. But now, researchers from Japan have found that even when exercise causes objectively measured changes in sleep quality, these changes may not be subjectively perceptible.
In a study published this month in Scientific Reports, researchers from the University of Tsukuba have revealed that vigorous exercise was able to modulate various sleep parameters associated with improved sleep, without affecting subjective reports regarding sleep quality.
Exercise is known to improve overall sleep quality by reducing the amount of time it takes to fall asleep and increasing the power of brain waves during slow-wave sleep (SWS), also known as deep sleep. However, studies investigating the link between exercise and sleep have produced a range of contradictory results, likely due to limitations related to systems of classifying sleep stages. The researchers at the University of Tsukuba aimed to address this using the coefficient of variation of the envelope (CVE), which is a new computational method for analyzing brain signals like those collected in sleep research.
"CVE is a novel tool for quantifying sleep depth according to the characteristics of brain oscillations," says senior author of the study Professor Kaspar E. Vogt. "We wanted to use it to determine whether exercise would improve or decrease sleep quality, in addition to determining whether short bouts of exercise could exert a lasting effect on metabolic state."
To do this, the researchers recruited a group of healthy young men, and examined the effects of 60 minutes of vigorous exercise on sleep quality in terms of both subjective reports and polysomnography, in which data regarding physiological and neurological state are collected in a laboratory during sleep. They then used the CVE approach to assess the stability of SWS.
"The results were surprising," explain lead scientists of the study Insung Park and Javier Díaz. "We found that exercise improved the quality of sleep as measured using objective techniques, while the participants reported no change in the quality of their sleep."
The researchers speculated that the benefits of enhanced sleep quality might have been countered by an increase in stress and muscle soreness, because the participants were not accustomed to vigorous exercise.
"The results of the subjective evaluations of sleep quality indicate that regular moderate exercise may be more beneficial for perceived sleep quality than occasional vigorous exercise, which might not have a subjective effect despite objective improvements in sleep," says Professor Vogt.
Individuals who engage in vigorous exercise may perceive a decrease in the quality of their sleep compared with if they had not exercised at all. However, the findings of this study indicate that the sleep structure may indeed be improved by exercise and have potential application in developing new treatment recommendations for various sleep disorders.
INFORMATION:
The article, "Exercise improves the quality of slow?wave sleep by increasing slow?wave stability", was published in Scientific Reports at DOI:10.1038/s41598-021-83817-6
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-25
Lugano, Switzerland; Denver, CO, USA, 25 March 2021 - Clinical activity with a second drug inhibiting KRASG12C confirms its role as a therapeutic target in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) harbouring this mutation, according to results from a study with the KRASG12C inhibitor adagrasib reported at the European Lung Cancer Virtual Congress 2021. (1)
"As we strive to identify the oncogenic driver in more and more of our patients with NSCLC, it becomes critical that we develop therapies that can target these identified oncogenic drivers," said lead author Gregory Riely, from Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, ...
2021-03-25
For the first time, activation of nuclear receptor coactivator 3 (NCOA3) has been shown to promote the development of melanoma through regulation of ultraviolet radiation (UVR) sensitivity, cell cycle progression and circumvention of the DNA damage response. Results of a pre-clinical study led by Mohammed Kashani-Sabet, M.D., Medical Director of the Cancer Center at Sutter's California Pacific Medical Center (CPMC) in San Francisco, CA were published online today in Cancer Research, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research.
"Our research suggests a previously unreported mechanism by which NCOA3 regulates the DNA damage response and acts as a potential therapeutic target in melanoma, whereby activation ...
2021-03-25
Durham, NC - Depletion of a certain type of stem cell in the womb lining during pregnancy could be a significant factor behind miscarriage, according to a study released today in STEM CELLS. The study, by researchers at Warwick Medical School, University of Warwick, Coventry, England, reports on how recurrent pregnancy loss is a result of the loss of decidual precursor cells prior to conception.
"This raises the possibility that they can be harnessed to prevent pregnancy disorders," said corresponding author Jan J. Brosens, M.D., Ph.D., professor of obstetrics and gynecology at Warwick Medical School (WMS).
The womb lining - or endometrium - is a ...
2021-03-25
Perhaps the best hope for slowing climate change - capturing and storing carbon dioxide emissions underground - has remained elusive due in part to uncertainty about its economic feasibility.
In an effort to provide clarity on this point, researchers at Stanford University and Carnegie Mellon University have estimated the energy demands involved with a critical stage of the process. (Watch video here: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-ZPIwwQs9aM)
Their findings, published April 8 in Environmental Science & Technology, suggest that managing and ...
2021-03-25
Smoking cigarettes causes 480,000 premature deaths each year in the United States, due mainly to a two-fold risk of cardiovascular disease and a 20-fold risk of lung cancer. Although smoking rates have declined dramatically, there are currently 35 million smokers in the U.S.
In a commentary published in the Ochsner Medical Journal, Charles H. Hennekens, M.D., Dr.PH, senior author, the First Sir Richard Doll Professor, and senior academic advisor in the Schmidt College of Medicine at Florida Atlantic University, and colleagues, highlight how failure to institute smoking cessation in hospitalized patients is a missed opportunity to avoid many premature deaths.
Each year in the U.S., ...
2021-03-25
An international team led by scientists at the National Institutes of Health and the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, has found evidence that SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, infects cells in the mouth.
While it's well known that the upper airways and lungs are primary sites of SARS-CoV-2 infection, there are clues the virus can infect cells in other parts of the body, such as the digestive system, blood vessels, kidneys and, as this new study shows, the mouth. The potential of the virus to infect multiple areas of the body might help explain the wide-ranging symptoms experienced by COVID-19 patients, including oral symptoms such as taste loss, dry mouth and blistering.
Moreover, the findings ...
2021-03-25
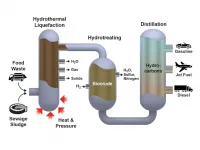
RICHLAND, WASH.--A large-scale demonstration converting biocrude to renewable diesel fuel has passed a significant test, operating for more than 2,000 hours continuously without losing effectiveness. Scientists and engineers led by the U.S. Department of Energy's Pacific Northwest National Laboratory conducted the research to show that the process is robust enough to handle many kinds of raw material without failing.
"The biocrude oil came from many different sources, including wastewater sludge from Detroit, and food waste collected from prison and an army base," said John Holladay, a PNNL scientist and co-director of the joint Bioproducts Institute, a collaboration between ...
2021-03-25
LA JOLLA--(March 25, 2021) The brush of an insect's wing is enough to trigger a Venus flytrap to snap shut, but the biology of how these plants sense and respond to touch is still poorly understood, especially at the molecular level. Now, a new study by Salk and Scripps Research scientists identifies what appears to be a key protein involved in touch sensitivity for flytraps and other carnivorous plants.
The findings, published March 16, 2021, in the journal eLife, help explain a critical process that has long puzzled botanists. This could help scientists better understand how plants of all kinds sense and respond to mechanical stimulation, and could also have a potential application in medical therapies that mechanically stimulate human cells such as neurons.
"We know that plants ...
2021-03-25
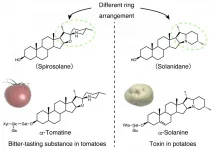
A multi-institutional collaboration has revealed that α-solanine, a toxic compound found in potato plants, is a divergent of the bitter-tasting α-tomatine, which is found in tomato plants. The research group included Associate Professor MIZUTANI Masaharu and Researcher AKIYAMA Ryota et al. of Kobe University's Graduate School of Agricultural Science, Assistant Professor WATANABE Bunta of Kyoto University's Institute for Chemical Research, Senior Research Scientist UMEMOTO Naoyuki of the RIKEN Center for Sustainable Resource Science, and Professor MURANAKA Toshiya of Osaka University's Graduate School of Engineering.
It ...
2021-03-25
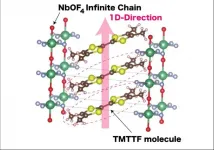
Salts are far more complicated than the food seasoning - they can even act as electrical conductors, shuttling current through systems. Extremely well studied and understood, the electrical properties of salts were first theorized in 1834. Now, nearly 200 years later, researchers based in Japan have uncovered a new kind of salt.
The results were published on March 17 in Inorganic Chemistry, a journal of the American Chemical Society.
The researchers were specifically investigating how one-dimensional versions of three-dimensional substances exhibit unique physical phenomena and functionality in a process called the ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Exercise can improve sleep quality even when you don't perceive a difference
Researchers from the University of Tsukuba find that vigorous exercise causes imperceptible improvements in sleep quality