(Press-News.org) TAMPA, Fla. -- Chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy, or CAR T, is a relatively new type of therapy approved to treat several types of aggressive B cell leukemias and lymphomas. Many patients have strong responses to CAR T; however, some have only a short response and develop disease progression quickly. Unfortunately, it is not completely understood why these patients have progression. In an article published in Proceedings of the Royal Society B, Moffitt Cancer Center researchers use mathematical modeling to help explain why CAR T cells work in some patients and not in others.
CAR T is a type of personalized immunotherapy that uses a patient's own T cells to target cancer cells. T cells are harvested from a patient and genetically modified in a laboratory to add a specific receptor that targets cancer cells. The patient then undergoes lymphodepletion with chemotherapy to lower some of their existing normal immune cells to help with expansion of the CAR T cells that are infused back into the patient, where they can get to work and attack the tumor.
Mathematical modeling has been used to help predict how CAR T cells will behave after being infused back into patients; however, no studies have yet considered how interactions between the normal T cells and CAR T cells impact the dynamics of the therapy, in particular how the nonlinear T cell kinetics factor into the chances of therapy success. Moffitt researchers integrated clinical data with mathematical and statistical modeling to address these unknown factors.
The researchers demonstrate that CAR T cells are effective because they rapidly expand after being infused back into the patient; however, the modified T cells are shown to compete with existing normal T cells, which can limit their ability to expand.
"Treatment success critically depends on the ability of the CAR T cells to multiply in the patient, and this is directly dependent upon the effectiveness of lymphodepletion that reduces the normal T cells before CAR T infusion," said Frederick Locke, M.D., co-lead study author and vice chair of the Blood and Marrow Transplant and Cellular Immunotherapy Department at Moffitt.
In their model, the researchers discovered that tumor eradication is a random, yet potentially highly probable event. Despite this randomness of cure, the authors demonstrated that differences in the timing and probability of cures are determined largely by variability among patient and disease factors. The model confirmed that cures tend to happen early, within 20 to 80 days before CAR T cells decline in number, while disease progression tends to happen over a wider time range between 200 to 500 days after treatment.
The researchers' model could also be used to test new treatments or propose refined clinical trial designs. For example, the researchers used their model to demonstrate that another round of CAR T-cell therapy would require a second chemotherapy lymphodepletion to improve patient outcomes.
"Our model confirms the hypothesis that sufficient lymphodepletion is an important factor in determining durable response. Improving the adaptation of CAR T cells to expand more and survive longer in vivo could result in increased likelihood and duration of response," explained Philipp Altrock, Ph.D., lead study author and assistant member of the Integrated Mathematical Oncology Department at Moffitt.
INFORMATION:
This study was supported by the Richard O. Jacobson Foundation, Moffitt's Center of Excellence for Evolutionary Therapy, the William G. Bankhead, Jr. and David Coley Cancer Research Program (20B06), the National Cancer Institute (P30 CA076292, U54 CA193489) and the U.S. Army Medical Research Acquisition Activity Program (KC180036).
About Moffitt Cancer Center
Moffitt is dedicated to one lifesaving mission: to contribute to the prevention and cure of cancer. The Tampa-based facility is one of only 51 National Cancer Institute-designated Comprehensive Cancer Centers, a distinction that recognizes Moffitt's scientific excellence, multidisciplinary research, and robust training and education. Moffitt is the No. 11 cancer hospital and has been nationally ranked by U.S. News & World Report since 1999. Moffitt's expert nursing staff is recognized by the American Nurses Credentialing Center with Magnet® status, its highest distinction. With more than 7,000 team members, Moffitt has an economic impact in the state of $2.4 billion. For more information, call 1-888-MOFFITT (1-888-663-3488), visit MOFFITT.org, and follow the momentum on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.
ORLANDO, March 25, 2021 - Early screening can mean the difference between life and death in a cancer and disease diagnosis. That's why University of Central Florida researchers are working to develop a new screening technique that's more than 300 times as effective at detecting a biomarker for diseases like cancer than current methods.
The technique, which was detailed recently in the Journal of the American Chemical Society, uses nanoparticles with nickel-rich cores and platinum-rich shells to increase the sensitivity of an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA).
ELISA is a test ...
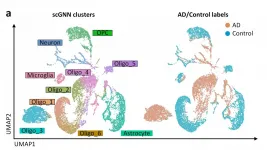
Studying genetic material on a cellular level, such as single-cell RNA-sequencing, can provide scientists with a detailed, high-resolution view of biological processes at work. This level of detail helps scientists determine the health of tissues and organs, and better understand the development of diseases such as Alzheimer's that impacts millions of people. However, a lot of data is also generated, and leads to the need for an efficient, easy-to-use way to analyze it.
Now, a team of engineers and scientists from the University of Missouri and the Ohio State University have created a new way to analyze data from single-cell RNA-sequencing ...
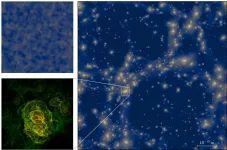
The very first moments of the Universe can be reconstructed mathematically even though they cannot be observed directly. Physicists from the Universities of Göttingen and Auckland (New Zealand) have greatly improved the ability of complex computer simulations to describe this early epoch. They discovered that a complex network of structures can form in the first trillionth of a second after the Big Bang. The behaviour of these objects mimics the distribution of galaxies in today's Universe. In contrast to today, however, these primordial structures are microscopically small. Typical clumps have masses of only a few grams and fit into volumes much smaller than present-day elementary particles. The results of the study have been published ...
One-third of the Earth's surface is covered by more than 11,000 grass species -- including crops like wheat, corn, rice and sugar cane that account for the bulk of the world's agricultural food production and important biofuels. But grass is so common that few people realize how diverse and important it really is.
Research published today in the journal Nature provides insights that scientists could use not only to improve crop design but also to more accurately model the effects of climate change. It also offers new clues that could help scientists use ...
Orthopaedic researchers are one step closer to preventing life-long arm and leg deformities from childhood fractures that do not heal properly.
A new study led by the University of South Australia and published in the journal Bone, sheds light on the role that a protein plays in this process.
Lead author Dr Michelle Su says that because children's bones are still growing, an injury to the growth plate can lead to a limb in a shortened position, compared to the unaffected side.
"Cartilage tissue near the ends of long bones is known as the growth plate that is responsible for bone growth in children and, unfortunately, 30 per cent of childhood and teen fractures involve this growth ...
Researchers have used the evidence of pumice from an underwater volcanic eruption to answer a long-standing mystery about a mass death of migrating seabirds.
New research into the mass death of millions of shearwater birds in 2013 suggests seabirds are eating non-food materials including floating pumice stones, because they are starving, potentially indicating broader health issues for the marine ecosystem.
The research which was led by CSIRO, Australia's national science agency, and QUT, was published in the journal Marine Ecology Progress Series, that examined a 2013 seabird "wreck" in which up to 3 million ...
A coordinated global effort to reduce the production of greenhouse gas emissions from industry and other sectors may not stop climate change, but Earth has a powerful ally that humans might partner with to achieve carbon neutrality: Mother Nature. An international team of researchers called for the use of natural climate solutions to help "cancel" produced emissions and remove existing emissions as part of a comprehensive plan to keep global warming below 1.5 degrees Celsius -- the point at which damage to human life and livelihoods could become catastrophic, according to the United Nations' Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change.
The researchers published their invited views on March 24 in ...
Recently, the team led by Professor WU Changzheng from School of Chemistry and Materials Science from University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) in cooperation with the team led by Prof. WU Hengan from School of Engineering Science, realized the homogenization of surface active sites of heterogeneous catalyst by dissolving the electrocatalytic active metal in molten gallium. The related results have been published on the Nature Catalysis on March 11th.
Due to the existence of various defects and crystal faces, the active components on the surface of heterogeneous catalysts are often in different ...
Tsukuba, Japan - Physical exercise has long been prescribed as a way to improve the quality of sleep. But now, researchers from Japan have found that even when exercise causes objectively measured changes in sleep quality, these changes may not be subjectively perceptible.
In a study published this month in Scientific Reports, researchers from the University of Tsukuba have revealed that vigorous exercise was able to modulate various sleep parameters associated with improved sleep, without affecting subjective reports regarding sleep quality.
Exercise is ...
Lugano, Switzerland; Denver, CO, USA, 25 March 2021 - Clinical activity with a second drug inhibiting KRASG12C confirms its role as a therapeutic target in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) harbouring this mutation, according to results from a study with the KRASG12C inhibitor adagrasib reported at the European Lung Cancer Virtual Congress 2021. (1)
"As we strive to identify the oncogenic driver in more and more of our patients with NSCLC, it becomes critical that we develop therapies that can target these identified oncogenic drivers," said lead author Gregory Riely, from Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, ...