(Press-News.org) A pilot human clinical trial conducted by researchers at Baylor College of Medicine reveals that supplementation with GlyNAC - a combination of glycine and N-acetylcysteine as precursors of the natural antioxidant glutathione - could improve many age-associated defects in older humans to improve muscle strength and cognition, and promote healthy aging.
Published in the journal Clinical and Translational Medicine, the results of this study show that older humans taking GlyNAC for 24 weeks saw improvements in many characteristic defects of aging, including glutathione deficiency, oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, inflammation, insulin resistance, endothelial dysfunction, body fat, genomic toxicity, muscle strength, gait speed, exercise capacity and cognitive function. The benefits declined after stopping supplementation for 12 weeks. GlyNAC supplementation was well tolerated during the study period.
"There is limited understanding as to why these defects occur in older humans, and effective interventions to reverse these defects are currently limited or lacking," said corresponding author endocrinologist Dr. Rajagopal Sekhar, associate professor of medicine in the Section of Endocrinology, Diabetes and Metabolism at Baylor.
For the last 20 years, Sekhar and his team have been studying natural aging in older humans and aged mice. Their work brings mitochondria, known as the batteries of the cell, as well as free radicals and glutathione to the table in discussions about why we age.
Mitochondrial dysfunction and aging
Mitochondria generate energy needed for supporting cellular functions by burning fat and sugar from foods, therefore mitochondrial health is critically important for life. Sekhar believes that improving the health of malfunctioning mitochondria in aging is the key.
As mitochondria generate energy, they produce waste products such as free radicals. These highly reactive molecules can damage cells, membranes, lipids, proteins and DNA. Cells depend on antioxidants, such as glutathione, the most abundant antioxidant in our cells, to neutralize these toxic free radicals. Failing to neutralize free radicals leads to harmful and damaging oxidative stress that can affect mitochondrial function.
Interestingly, glutathione levels in older people are much lower than those in younger people, and the levels of oxidative stress are much higher.
Animal studies conducted in the Sekhar lab have shown that restoring glutathione levels by providing GlyNAC reverses glutathione deficiency, reduces oxidative stress and fully restores mitochondrial function in aged mice.
"In previous work we showed that supplementing HIV patients with GlyNAC improved multiple deficits associated with premature aging observed in those patients," Sekhar said. "In this study, we wanted to understand the effects of GlyNAC supplementation on many age-associated defects in older adults."
GlyNAC improves several hallmark defects in aging
The world population of older humans is rapidly increasing and with it comes an increase in many age-related illnesses. To understand what causes unhealthy aging, scientific research has identified nine hallmark defects which are believed to contribute to the aging process.
"It is believed that correcting these aging hallmarks could improve or reverse many age-related disorders and help people age in a healthier way," Sekhar said. "However, we do not fully understand why these hallmark defects happen, and there are currently no solutions to fix even a single hallmark defect in aging."
This is where Sekhar's trial results become encouraging, because GlyNAC supplementation for 24 weeks appears to improve four of the nine aging hallmark defects.
To further understand whether GlyNAC holds the keys to mitochondrial recovery and more, Sekhar and his team conducted this pilot clinical trial.
"We worked with eight older adults 70 to 80 years of age, comparing them with gender-matched younger adults between 21 and 30 years old," Sekhar said. "We measured glutathione in red-blood cells, mitochondrial fuel-oxidation, plasma biomarkers of oxidative stress and oxidant damage, inflammation, endothelial function, glucose and insulin, gait-speed, muscle strength, exercise capacity, cognitive tests, gene-damage, glucose-production and muscle-protein breakdown rates and body composition. Before taking GlyNAC, all these measurements were abnormal in older adults when compared with those in younger people."
The older participants took GlyNAC for 24 weeks, and then stopped it for 12 weeks. Sekhar and his colleagues repeated the above measurements at the halfway point at 12 weeks, after 24 weeks of taking GlyNAC, and again after stopping GlyNAC for 12 weeks.
"We are very excited by the results," Sekhar said. "After taking GlyNAC for 24 weeks, all these defects in older adults improved and some reversed to the levels found in young adults." The researchers also determined that older adults tolerated GlyNAC well for 24 weeks. The benefits, however, declined after stopping GlyNAC supplementation for 12 weeks.
"I am particularly encouraged by the improvements in cognition and muscle strength," Sekhar said. "Alzheimer's disease and mild cognitive impairment (MCI) are serious medical conditions affecting memory in older people and leading to dementia, and there are no effective solutions for these disorders. We are exploring the possibility that GlyNAC could help with these conditions by conducting two pilot randomized clinical trials to test whether GlyNAC supplementation could improve defects linked to cognitive decline in Alzheimer's disease and in MCI, and possibly improve cognitive function."
"The overall findings of the current study are highly encouraging," Sekhar said. "They suggest that GlyNAC supplementation could be a simple and viable method to promote and improve healthy aging in older adults. We call this the 'Power of 3' because we believe that it takes the combined benefits of glycine, NAC and glutathione to reach this far reaching and widespread improvement. We also have completed a randomized clinical trial on supplementing GlyNAC vs. placebo in older adults and those results will be forthcoming soon."
INFORMATION:
Premranjan Kumar, Chun Liu, Jean Hsu, Shaji Chacko, Charles Minard and Farook Jahoor, all at Baylor College of Medicine, contributed to this work. This work was supported by a philanthropic gift from the McNair Medical Institute at the Robert and Janice McNair Foundation in Houston, TX.
Baylor College of Medicine holds a patent on GlyNAC, which has been licensed to Nestlé Health Science. GlyNAC is marketed in the United States by Nestlé Health Science under the name CelltrientTM Cellular Protect. Nestlé has not provided any funding or financial support for this research work.
In the Arctic, climate change and pollution are the biggest threats to top predators like narwals. Studying the animals' tusks reveals that diet and exposure to pollution have shifted over the past half century in response to sea-ice decline. Human emissions have also led to a sharp rise in the presence of mercury in recent years, according to an international team of researchers.
"Our research shows that climate change is having substantial impacts on Arctic ecosystems, with consequences for exposure to toxic pollutants like mercury," says co-author Jean-Pierre Desforges, a Postdoctoral Fellow at McGill University under the supervision ...
Alexandria, Va., USA -- Asymptomatic carriage of SARS-CoV-2 is a potentially significant source of transmission, yet remains relatively poorly understood. The study "SARS-CoV-2 Positivity in Asymptomatic-screened Dental Patients" published in the Journal of Dental Research (JDR), investigated SARS-CoV-2 infection in asymptomatic dental patients to inform community surveillance and improve understanding of risks in the dental setting.
Thirty-one dental care centers across Scotland invited asymptomatic screened patients over the age of five to participate. During the patient visit, trained ...
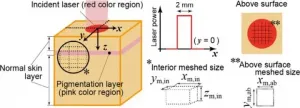
Laser treatment is now commonplace across various fields of medicine including dermatology, where it is commonly used to remove scars, wrinkles, and freckles. The technology, however, has a major downside: despite continued improvements, medical accidents related to laser treatment has been on the rise, with studies revealing excessively high laser energy as the major cause of such accidents.
Assistant Professor Takahiro Kono from Shibaura Institute of Technology (SIT), Japan, whose research is focused on the mechanism of heat transfer involved in the interaction of laser light with biological tissue explains, "The difficulty lies in adjusting the laser conditions for each patient ...
A team of researchers led by UCL Great Ormond Street Institute of Child Health (ICH) and Great Ormond Street Hospital (GOSH) has found that metformin - a drug commonly used to treat Type 2 diabetes - can successfully reduce symptoms associated with tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC), including reduction in the frequency of seizures and the size of brain tumours.
The study, which also included teams from Royal United Hospitals Bath NHS Foundation Trust (RUH) and University Hospitals Bristol and Weston NHS Foundation Trust, recruited 51 patients with TSC who were randomly assigned a placebo or metformin for one year on a dose similar to that given for Type 2 diabetes.
TSC is a genetic disorder characterised ...
In order to develop more effective drugs against a range of cancers, researchers have been investigating the molecular structure of many diseased-linked enzymes in the body. An intriguing case in point is Taspase 1, a type of enzyme known as a protease. The primary duty of proteases is to break down proteins into smaller peptide snippets or single amino acids.
Taspase 1 appears to play a vital role in a range of physiological processes, including cell metabolism, proliferation, migration and termination. The normal functioning of Taspase 1 can go awry however, leading to a range of diseases, including leukemia, colon and breast cancers, as well as glioblastoma, a particularly lethal and incurable malignancy in the brain.
Because Taspase 1 dysregulation is increasingly ...
Use of vouchers and coupons offered by pharmaceutical companies to defray patients' out-of-pocket drug costs is concentrated among a small number of drugs. While these offsets significantly reduce patient costs, they are not targeted to patients who most need the price reduction, according to a study from researchers at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health.
The researchers, in what is thought to be the largest study of its kind to date, analyzed tens of millions of pharmacy transactions by more than 600,000 people in the U.S. during 2017-19, in order to get a better sense of how vouchers and other point-of-sale copayment "offsets" are used. These coupons and vouchers come in many forms--some are offered online directly to customers, others by pharmacy ...
When you bump into someone in the workplace or at your local coffee shop, you might call that an "encounter." That's the scientific term for it, too. As part of urgent efforts to fight COVID-19, a science is rapidly developing for measuring the number of encounters and the different levels of interaction in a group.
At the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), researchers are applying that science to a concept they have created called "encounter metrics." They have developed an encrypted method that can be applied to a device such as your phone to help with the ultimate goal of slowing down or preventing future pandemics. The method is also applicable to the COVID-19 pandemic.
Their research ...
A drop of food coloring slowly spreading in a glass of water is driven by a process known as diffusion. While the mathematics of diffusion have been known for many years, how this process works in living organisms is not as well understood.
Now, a study published in Nature Communications provides new insights on the process of diffusion in complex systems. The result of a collaboration between physicists at Penn, the University of Chile, and Heinrich Heine University Düsseldorf, this new theoretical framework has broad implications for active surfaces, such as ones found in biofilms, active coatings, and even mechanisms for pathogen clearance.
Diffusion is described ...
BUFFALO, N.Y. - Bullying at boarding schools has a negative impact on students' emotional health, but for male students, having a school staff member to rely on for support may mute the harmful effects of bullying, according to a new University at Buffalo study. Support networks did not have the same effect for female students, the researchers say.
The study, recently published in School Psychology Review, is one of few to examine the impact of bullying at boarding schools, which provide a unique environment where most students live on school grounds, away from their families. It is also one of the first studies to observe the effects ...
Climate labels informing us of a meat product's carbon footprint cause many people to opt for climate-friendlier alternatives. This applies to people who are curious about a product's carbon footprint, as well as to those who actively avoid wanting to know more. The finding is published in a new study from, among others, the University of Copenhagen. As such, climate labeling food products can be a good way of reducing our climate footprint. But according to the researcher behind the study, labels must be obligatory for them to be effective.
Certain situations exist where we humans strategically avoid greater knowledge and more information - a phenomenon known as "active information avoidance". ...