Telemedicine improves access to high-quality sleep care
COVID-19 has revealed that the sleep medicine specialty is well-equipped to provide care remotely
2021-04-01
(Press-News.org) DARIEN, IL - The American Academy of Sleep Medicine recently published an update on the use of telemedicine for the diagnosis and treatment of sleep disorders to reflect lessons learned from the transition to telemedicine during the COVID-19 pandemic and the benefits of continuing to utilize remote care when appropriate.
While the technology to remotely connect doctor and patient has been in place for years, its use was limited until the spread of COVID-19. In 2020, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) lifted restrictions on telemedicine reimbursement, and private insurance companies followed suit. Telemedicine has been critical to ensuring safe, timely care for patients during the pandemic, and the field of sleep medicine has proven to be a specialty that can offer complete and quality care remotely.
"Delivering care during the pandemic has proven to providers and insurers that telemedicine offers patients safe, secure and effective sleep care," said Dr. Douglas Kirsch, chair of the AASM Telemedicine Presidential Committee, which wrote the update. "The AASM will continue to advocate for permanent coverage and reimbursement of telemedicine services with CMS and third-party payers."
Published online as an accepted paper in the Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine, the update addresses several key issues in the delivery of sleep care using telemedicine, including quality and value, privacy and safety, health advocacy, and future directions. The paper shares new evidence that telemedicine is effective in the diagnosis and management of obstructive sleep apnea and improves adherence to CPAP therapy. Telemedicine also has been widely used to provide care to patients with insomnia through cognitive behavioral therapy and brief behavioral therapy, with results similar to in-person treatment.
The paper also acknowledges opportunities for improvement in the adoption and use of telemedicine. Those include compliance with patient privacy laws, additional training for providers, and awareness of limited access among disadvantaged populations.
"Telemedicine improves access to care, but we need to be cautious that its use doesn't introduce new health inequities in underserved communities that may lack the necessary technologies," said Kirsch. "Improved connectivity and increased access to high-speed internet need to grow together with telehealth expansion."
INFORMATION:
Additional telemedicine resources for clinicians, including video discussions and coding guidance, are available on the telemedicine page of the AASM website.
To request a copy of the paper, "The use of telemedicine for the diagnosis and treatment of sleep disorders: an American Academy of Sleep Medicine update," or to arrange an interview with an AASM spokesperson, please contact the AASM at 630-737-9700 or media@aasm.org. Accepted papers, which are published online prior to their final inclusion in an issue, are not embargoed. The update is schedule to be published in the May 2021 issue of the journal.
Established in 1975, the American Academy of Sleep Medicine (AASM) is advancing sleep care and enhancing sleep health to improve lives. The AASM has a combined membership of 11,000 accredited member sleep centers and individual members, including physicians, scientists and other health care professionals (aasm.org).
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-04-01
When we watch a mime seemingly pull rope, climb steps or try to escape that infernal box, we don't struggle to recognize the implied objects -- our minds automatically "see" them, a new study concludes.
To explore how the mind processes the objects mimes seem to interact with, Johns Hopkins University cognitive scientists brought the art of miming into the lab, concluding that invisible, implied surfaces are represented rapidly and automatically. The work appears today in the journal Psychological Science.
"Most of the time, we know which objects are ...
2021-04-01
In the 1960s, a national focus on hunger was essential to address major problems of undernutrition after World War II. In the 1990s, the nation shifted away from hunger toward "food insecurity" to better capture and address the challenges of food access and affordability.
Now, a END ...
2021-04-01
Space scientists at the University of Bath in the UK have found a new way to probe the internal structure of neutron stars, giving nuclear physicists a novel tool for studying the structures that make up matter at an atomic level.
Neutron stars are dead stars that have been compressed by gravity to the size of small cities. They contain the most extreme matter in the universe, meaning they are the densest objects in existence (for comparison, if Earth were compressed to the density of a neutron star, it would measure just a few hundred meters in diameter, and all humans would fit in a teaspoon). This makes neutron stars unique natural laboratories ...
2021-04-01
Recent research from the University of Vaasa and the University of Jyväskyla shows that speculation and lottery-like behavior is a fundamental factor for the pricing of cryptocurrencies. Speculation could explain the enormous increase in the market capitalizations of cryptocurrencies.
Nowadays more than 8000 cryptocurrencies have been launched. Unlike traditional assets like stocks, research has shown that investments in cryptocurrencies are associated with a considerably higher level of uncertainty. The price of Bitcoin, which is the first traded cryptocurrency, increased by from $7,200.17 to $29,374.15 in January 1, 2020 ...
2021-04-01
A team of researchers at the University of Alberta has uncovered a long-sought link in the battle to control cholesterol and heart disease.
The protein that interferes with low-density lipoprotein (LDL) receptors that clear "bad" cholesterol from the blood was identified in END ...
2021-04-01
MADISON - Bipolar disorder affects millions of Americans, causing dramatic swings in mood and, in some people, additional effects such as memory problems.
While bipolar disorder is linked to many genes, each one making small contributions to the disease, scientists don't know just how those genes ultimately give rise to the disorder's effects.
However, in new research, scientists at the University of Wisconsin-Madison have found for the first time that disruptions to a particular protein called Akt can lead to the brain changes characteristic of bipolar disorder. The results offer a foundation for research into treating the often-overlooked cognitive impairments of bipolar disorder, ...
2021-04-01
NASA's OSIRIS-REx mission is on the brink of discovering the extent of the mess it made on asteroid Bennu's surface during last fall's sample collection event. On Apr. 7, the OSIRIS-REx spacecraft will get one last close encounter with Bennu as it performs a final flyover to capture images of the asteroid's surface. While performing the flyover, the spacecraft will observe Bennu from a distance of about 2.3 miles (3.7 km) - the closest it's been since the Touch-and-Go Sample Collection event on Oct. 20, 2020.
The OSIRIS-REx team decided to add this last flyover after Bennu's surface was significantly disturbed by the sample collection event. During touchdown, the spacecraft's ...
2021-04-01
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University and Providence Veterans Affairs Medical Center] -- Brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) are an emerging assistive technology, enabling people with paralysis to type on computer screens or manipulate robotic prostheses just by thinking about moving their own bodies. For years, investigational BCIs used in clinical trials have required cables to connect the sensing array in the brain to computers that decode the signals and use them to drive external devices.
Now, for the first time, BrainGate clinical trial participants with tetraplegia have demonstrated use of an intracortical wireless BCI with an external wireless transmitter. The system is capable of transmitting brain signals at single-neuron resolution and ...
2021-04-01
Few compounds are as important to industry and medicine today as titanium dioxide. Despite the variety and popularity of its applications, many issues related to the surface structure of materials made of this compound and the processes taking place therein remain unclear. Some of these secrets have just been revealed to scientists from the Institute of Nuclear Physics of the Polish Academy of Sciences. It was the first time they had used the SOLARIS synchrotron in their research.
It is found in many chemical reactions as a catalyst, as a pigment in plastics, paints or cosmetics and in medical implants it ...
2021-04-01
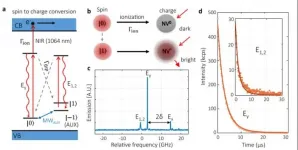
The team led by Professor DU Jiangfeng and Professor WANG Ya from the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) Key Laboratory of Microscale Magnetic Resonance of the University of Science and Technology of China put forward an innovative spin-to-charge conversion method to achieve high-fidelity readout of qubits, stepping closer towards fault-tolerant quantum computing.
Quantum supremacy over classical computers has been fully exhibited in some specific problems, yet the next milestone, fault-tolerant quantum computing, still requires the accumulated logic gate error and the spin readout fidelity to exceed the fault-tolerant threshold. DU's team has resolved the first requirement in the nitrogen-vacancy (NV) center system ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Telemedicine improves access to high-quality sleep care
COVID-19 has revealed that the sleep medicine specialty is well-equipped to provide care remotely