INFORMATION:
Co-authors are Cynthia Wong of the University of Iowa and Alexander Friedman of Columbia University Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons.
Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health
Founded in 1922, the Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health pursues an agenda of research, education, and service to address the critical and complex public health issues affecting New Yorkers, the nation and the world. The Columbia Mailman School is the seventh largest recipient of NIH grants among schools of public health. Its nearly 300 multi-disciplinary faculty members work in more than 100 countries around the world, addressing such issues as preventing infectious and chronic diseases, environmental health, maternal and child health, health policy, climate change and health, and public health preparedness. It is a leader in public health education with more than 1,300 graduate students from 55 nations pursuing a variety of master's and doctoral degree programs. The Columbia Mailman School is also home to numerous world-renowned research centers, including ICAP and the Center for Infection and Immunity. For more information, please visit http://www.mailman.columbia.edu.
Failure to rescue a major driver of excess maternal mortality in Black women
Site of delivery represents a focal point for interventions to reduce racial and ethnic disparities
2021-04-09
(Press-News.org) In a study of over 73 million delivery hospitalizations during a 19-year period in the United States, researchers at Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health and Columbia University Irving Medical Center found that failure to rescue from severe maternal morbidity contributes more than a half of the 3-fold difference in maternal mortality between Black women and White women. Failure to rescue refers to death resulting from severe maternal morbidity such as eclampsia, acute heart failure, and sepsis. The findings are published in the journal Obstetrics and Gynecology.
"Despite the continuing decrease in failure to rescue over the entire study period, racial and ethnic disparities in failure to rescue persisted, underscoring the need to identify factors accounting for these disparities and to identify interventions to avoid potentially preventable deaths in racial and ethnic minority women," said Jean Guglielminotti, MD, PhD, in the Department of Anesthesiology, Columbia Medical Center, and lead author.
Using community hospital discharge records from the National Inpatient Sample of the Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project, the researcher analyzed data of delivery hospitalizations with severe maternal morbidity beginning in 1999-2017, identified using Centers for Disease Control and Prevention diagnosis codes and include 21 serious medical conditions during or immediately after childbirth.
Among the 993,864 women with severe maternal morbidity, 4,328 (0.4 percent) died, accounting for 88 percent of deaths during delivery. The severe maternal morbidity rate in Black women (2.2 percent) was higher than in Hispanic or White women, at 1.5 percent and 1.1 percent, respectively. Women with severe maternal morbidity who died were more likely to be older, and have nonprivate insurance, lower household income, and a higher obstetric comorbidity index. They also were more likely to be transferred from another acute care hospital, be admitted during a weekend, have a cesarean birth, or deliver in a large-bed size hospital or in an urban teaching hospital.
"Our study confirms that excess maternal mortality continues to be a serious public health problem and improving the quality of obstetric care, especially for Black and other minority women, could help substantially decrease maternal mortality and reduce racial and ethnic disparities in maternal mortality in the United States. " said Guohua Li, MD, DrPH, professor of Anesthesiology and Epidemiology at Columbia Mailman School of Public Health, and senior author.
Guglielminotti and Li make the point that hospital culture, team attitudes and behaviors toward patient safety and communication, and favorable nursing environments may be important determinants of maternal health outcomes.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Monuments that matter
2021-04-08
When most Americans imagine an archaeologist, they picture someone who looks like Indiana Jones. Or, perhaps, Lara Croft, from the Tomb Raider game. White, usually male but occasionally female, digging up the spoils of a vanished culture in colonized lands.
Depictions of archaeologists in popular culture mirror reality. Many scholars have noted the experts institutions recognize as authorities to discuss or represent the past are overwhelmingly white and mostly male. Archaeology has also been a tool colonizing countries use to consolidate and justify their domination. As a new open-access paper in American Antiquity points out, the first doctoral degree in archaeology was not granted to a Black woman until 1980.
First author Ayana Omilade Flewellen, ...
Lessons in equity from the frontlines of COVID-19 vaccination
2021-04-08
Cambridge, Mass. - When the first COVID-19 vaccines were approved for emergency use in December 2020, healthcare systems across the Unites States needed to rapidly design and implement their own approaches to distribute COVID-19 vaccines equitably and efficiently. This new role has required Beth Israel Lahey Health (BILH) to develop new strategies and build large operational teams to organize and successfully vaccinate more than 14,000 patients a week across Eastern Massachusetts. In an Insight article published in JAMA Health Forum, Leonor Fernandez, MD, Assistant Professor of Medicine in the Department of Medicine at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center (BIDMC) and Peter Shorett, MPP, Chief Integration Officer at ...
Surgery for stress urinary incontinence doesn't cause pelvic cancer
2021-04-08
April 8, 2021 - Women undergoing surgery to treat stress urinary incontinence (SUI) are not at increased risk of developing pelvic cancers, according to a large-scale, population-based study in The Journal of Urology®, Official Journal of the American Urological Association (AUA). The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
"In a very large population with extended follow-up, we found no increase in the risk of any pelvic malignancy in women who underwent stress urinary incontinence surgery," comments lead author Humberto ...
Configuring infrared spectroscopy tools to better detect breast cancer
2021-04-08
Detecting and analyzing breast cancer goes beyond the initial discovery of the cancer itself. If a patient has a tumor removed and it needs to be analyzed to determine further treatment, it might be OK for the results to take 24 hours. But if the patient is still on the operating table and clinicians are waiting to make sure no cancer cells are present along the edges of the removed tumor, results need to be nearly immediate.
A paper titled, "Breast cancer histopathology using infrared spectroscopic imaging: The impact of instrumental configurations," ...
Could Mario Kart teach us how to reduce world poverty and improve sustainability?
2021-04-08
Many Mario Kart enthusiasts are familiar with the rush of racing down Rainbow Road, barely squeaking around a corner, and catching a power-up from one of the floating square icons on the screen--or, less ideally, slipping on a banana peel laid by another racer and flying off the side of the road into oblivion. This heated competition between multiple players, who use a variety of game tokens and tools to speed ahead or thwart their competitors, is part of what makes the classic Nintendo racing game that has been around since the early 1990s so appealing.
"It's been fun since I was a kid, it's fun ...
Study: Scant evidence that 'wood overuse' at Cahokia caused collapse
2021-04-08
Whatever ultimately caused inhabitants to abandon Cahokia, it was not because they cut down too many trees, according to new research from Washington University in St. Louis.
Archaeologists from Arts & Sciences excavated around earthen mounds and analyzed sediment cores to test a persistent theory about the collapse of Cahokia, the pre-Columbian Native American city in southwestern Illinois that was once home to more than 15,000 people.
No one knows for sure why people left Cahokia, though many environmental and social explanations have been proposed. One oft-repeated theory is tied to resource exploitation: specifically, that Native Americans ...
Altering traumatic memories
2021-04-08
Scientists could be a step closer to finding a way to reduce the impact of traumatic memories, according to a Texas A&M University study published recently in the journal END ...
Leaking calcium in neurons an early sign of Alzheimer's pathology
2021-04-08
New Haven, Conn. -- Alzheimer's disease is known for its slow attack on neurons crucial to memory and cognition. But why are these particular neurons in aging brains so susceptible to the disease's ravages, while others remain resilient?
A new study led by researchers at the Yale School of Medicine has found that susceptible neurons in the prefrontal cortex develop a "leak" in calcium storage with advancing age, they report April 8 in the journal Alzheimer's & Dementia, The Journal of the Alzheimer's Association. This disruption of calcium storage in turns ...
COVID-19 causes 'unexpected' cellular response in the lungs, research finds
2021-04-08
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. - New insights into the immune response to SARS-CoV-2 infections could bring better treatments for COVID-19 cases.
An international team of researchers unexpectedly found that a biochemical pathway, known as the immune complement system, is triggered in lung cells by the virus, which might explain why the disease is so difficult to treat. The research is published this week in the journal Science Immunology.
The researchers propose that the pairing of antiviral drugs with drugs that inhibit this process may be more effective. Using an in vitro model using human lung ...
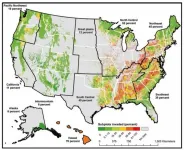
New Forest Service assessment delivers research on invasive species
2021-04-08
MADISON, WI, April 8, 2021 - USDA Forest Service scientists have delivered a new comprehensive assessment of the invasive species that confront America's forests and grasslands, from new arrivals to some that invaded so long ago that people are surprised to learn they are invasive.
The assessment, titled "Invasive Species in Forests and Rangelands of the United States: A Comprehensive Science Synthesis for the United States Forest Sector," serves as a one-stop resource for land managers who are looking for information on the invasive species that are already affecting the landscape, the species that may threaten the landscape, and what is known about control ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
COVID-19 vaccination during pregnancy may help prevent preeclampsia
Menopausal hormone therapy not linked to increased risk of death
Chronic shortage of family doctors in England, reveals BMJ analysis
Booster jabs reduce the risks of COVID-19 deaths, study finds
Screening increases survival rate for stage IV breast cancer by 60%
ACC announces inaugural fellow for the Thad and Gerry Waites Rural Cardiovascular Research Fellowship
University of Oklahoma researchers develop durable hybrid materials for faster radiation detection
Medicaid disenrollment spikes at age 19, study finds
Turning agricultural waste into advanced materials: Review highlights how torrefaction could power a sustainable carbon future
New study warns emerging pollutants in livestock and aquaculture waste may threaten ecosystems and public health
Integrated rice–aquatic farming systems may hold the key to smarter nitrogen use and lower agricultural emissions
Hope for global banana farming in genetic discovery
Mirror image pheromones help beetles swipe right
Prenatal lead exposure related to worse cognitive function in adults
Research alert: Understanding substance use across the full spectrum of sexual identity
Pekingese, Shih Tzu and Staffordshire Bull Terrier among twelve dog breeds at risk of serious breathing condition
Selected dog breeds with most breathing trouble identified in new study
Interplay of class and gender may influence social judgments differently between cultures
Pollen counts can be predicted by machine learning models using meteorological data with more than 80% accuracy even a week ahead, for both grass and birch tree pollen, which could be key in effective
Rewriting our understanding of early hominin dispersal to Eurasia
Rising simultaneous wildfire risk compromises international firefighting efforts
Honey bee "dance floors" can be accurately located with a new method, mapping where in the hive forager bees perform waggle dances to signal the location of pollen and nectar for their nestmates
Exercise and nutritional drinks can reduce the need for care in dementia
Michelson Medical Research Foundation awards $750,000 to rising immunology leaders
SfN announces Early Career Policy Ambassadors Class of 2026
Spiritual practices strongly associated with reduced risk for hazardous alcohol and drug use
Novel vaccine protects against C. diff disease and recurrence
An “electrical” circadian clock balances growth between shoots and roots
Largest study of rare skin cancer in Mexican patients shows its more complex than previously thought
Colonists dredged away Sydney’s natural oyster reefs. Now science knows how best to restore them.
[Press-News.org] Failure to rescue a major driver of excess maternal mortality in Black womenSite of delivery represents a focal point for interventions to reduce racial and ethnic disparities