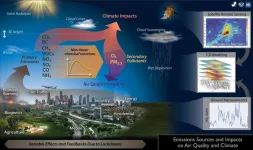
Impacts of coronavirus lockdowns: New study collects data on pollutants in the atmosphere
2021-04-14
(Press-News.org) One consequence of the coronavirus pandemic has been global restrictions on mobility. This, in turn, has had an effect on pollution levels in the atmosphere. Researchers from across the world are using this unique opportunity to take measurements, collect data, and publish studies. An international team led by Forschungszentrum Jülich's Institute of Climate and Energy Research - Troposphere has now published a comprehensive review providing an overview of results up to September 2020. The study also has its own dedicated website, where additional measurement data can be added to supplement and refine existing research results. At the same time, this collection of data allows scientifically substantiated predictions to be made about the pollution levels of future mobility scenarios.
The meta-analysis was coordinated by Prof. Astrid Kiendler-Scharr, director at Jülich's Institute of Climate and Energy Research - Troposphere. The analysis covers the measurement data of around 200 studies from the first seven months following the onset of the pandemic. It focuses on the following air pollutants: nitrogen dioxide, particulate matter, ozone, ammonia, sulfur dioxide, black carbon, volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and carbon monoxide. A third of the studies take into account the prevailing meteorological situation when calculating the influence of lockdowns on the air composition. The Government Stringency Index (SI) - summarizing the severity of local shutdown measures in a number that can be compared at international level - acted as a reference value.
A key finding of the analysis is that lockdowns, which have the sole aim of slowing down the infection rate, are also reducing the global pollution of the atmosphere with nitrogen dioxide and particulate matter - the higher the SI, the greater this impact. However, this only applies to pollutants that primarily have an anthropogenic origin, i.e. are directly emitted by humans, especially in the field of mobility. In contrast, ozone levels increased. This increase was a result of atmospheric chemical processes caused by reduced nitrogen oxide levels in the air.
The study also highlights current gaps in the data collection and the need for further research. The authors are therefore of the opinion that the period of analysis should be extended to cover the entire year of 2020. The scientists place a particular emphasis on hydrocarbons, which have so far only been examined sporadically in studies, and on extended analyses looking at the impact of emission changes on the climate.
An important addition to the meta-analysis is a database that can be accessed via a website (COVID-19 Air Quality Data Collection). It contains all data from the study on pollution levels, including data on pollutions levels in individual countries. Researchers can also find a list of publications to date and thus obtain a quick overview of previous studies.
The website also invites scientists to present data from their new studies and to thus become part of the reference system. It therefore acts as a "living version", with the presentation of collected results being constantly refined. Similarly, there are plans to further develop the data collection to include measurement results and the analysis of other pollutants that are not part of the current canon, for example hydrocarbons.
The important data could also form the basis for better assessments of the impacts on atmospheric chemistry in future scenarios. This includes a considerable, long-term reduction in pollution levels for a comprehensive transition to electromobility.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-04-14
By combining the 'chassis' of an oil-producing microalgae with genes from a Cuphea plant, scientists from the Single-Cell Center, Qingdao Institute of BioEnergy and Bioprocess Technology (QIBEBT) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), can turn the algae into a microbial cell factory that can produce various oils with different properties.
The study was published in Metabolic Engineering on April 3.
Oils are composed of fatty acids, and fatty acids are composed in part of chains of carbon atoms. The length of these carbon chains can impact the physical properties of the fatty acid and thus the ...
2021-04-14
While people may expect suicide rates to rise during a worldwide crisis such as the COVID-19 pandemic, a University of Michigan study suggests the onset of the pandemic and state of emergency executive orders likely did not increase suicide-related behavior in the early months of the outbreak.
The report, led by U-M researchers Rachel Bergmans and Peter Larson, found that emergency room visits related to suicide attempt and self-harm decreased by 40% during the first eight months of Michigan's lockdown. Their results are published in the Journal of Epidemiology and Community Health.
The study compared emergency room reports of suicide attempt and intentional self-harm at a hospital in Michigan's Washtenaw County during the first 8 months of the ...
2021-04-14
The COVID-19 pandemic has cast a harsh light on the urgent need for quick and easy techniques to sanitize and disinfect everyday high-touch objects such as doorknobs, pens, pencils, and personal protective gear worn to keep infections from spreading. Now scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy's (DOE) Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory and the New Jersey Institute of Technology (NJIT) have demonstrated the first flexible, hand-held, device based on low-temperature plasma -- a gas that consists of atoms, molecules, and free-floating electrons ...
2021-04-14
Birds have been shaped by evolution in many ways that have made them distinct from their vertebrate cousins. Over millions of years of evolution, our feathered friends have taken to the skies, accompanied by unique changes to their skeleton, musculature, respiration, and even reproductive systems. Recent genomic analyses have identified another unique aspect of the avian lineage: streamlined genomes. Although bird genomes contain roughly the same number of protein-coding genes as other vertebrates, their genomes are smaller, containing less noncoding DNA. Scientists are still exploring the potential consequences of this genome reduction on bird biology. In a new ...
2021-04-14
UPTON, NY--Scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy's (DOE) Brookhaven National Laboratory and the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign (UIUC) have developed a new mathematical model for predicting how COVID-19 spreads. This model not only accounts for individuals' varying biological susceptibility to infection but also their levels of social activity, which naturally change over time. Using their model, the team showed that a temporary state of collective immunity--what they coined "transient collective immunity"--emerged during early, fast-paced stages of the epidemic. However, subsequent "waves," ...
2021-04-14
An alloy is typically a metal that has a few per cent of at least one other element added. Some aluminium alloys have a seemingly strange property.
"We've known that aluminium alloys can become stronger by being stored at room temperature - that's not new information," says Adrian Lervik, a physicist at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU).
The German metallurgist Alfred Wilm discovered this property way back in 1906. But why does it happen? So far the phenomenon has been poorly understood, but now Lervik and his colleagues from NTNU and SINTEF, the largest independent research institute in Scandinavia, have tackled that question.
Lervik recently completed his doctorate at NTNU's Department of Physics. His work explains an important part of this ...
2021-04-14
Patients who have preexisting respiratory conditions such as asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and live in areas with high levels of air pollution have a greater chance of hospitalization if they contract COVID-19, says a University of Cincinnati researcher.
Angelico Mendy, MD, PhD, assistant professor of environmental and public health sciences, at the UC College of Medicine, looked at the health outcomes and backgrounds of 1,128 COVID-19 patients at UC Health, the UC-affiliated health care system in Greater Cincinnati.
Mendy led a team of researchers in an individual-level study which used a statistical model to evaluate the association between long-term exposure to particulate matter less or equal to 2.5 micrometers -- it refers to a mixture of tiny particles and ...
2021-04-14
Researchers have found a long-sought enzyme that prevents cancer by enabling the breakdown of proteins that drive cell growth, and that causes cancer when disabled.
Publishing online in Nature on April 14, the new study revolves around the ability of each human cell to divide in two, with this process repeating itself until a single cell (the fertilized egg) becomes a body with trillions of cells. For each division, a cell must follow certain steps, most of which are promoted by proteins called cyclins.
Led by researchers at NYU Grossman School of Medicine, the work revealed that an enzyme called AMBRA1 labels a key class of cyclins for destruction by cellular machines that break down proteins. The work finds that the enzyme's control of cyclins is essential ...
2021-04-14
ITHACA, N.Y. - Eurasian Blackcaps are spunky and widespread warblers that breed across much of Europe. Many of them migrate south to the Mediterranean region and Africa after the breeding season. But thanks to a changing climate and an abundance of food resources offered by people across the United Kingdom and Ireland, some populations of Blackcaps have recently been heading north for the winter, spending the colder months in backyard gardens of the British Isles.
New research published this week in Global Change Biology shows some of the ways that bird feeders, fruit-bearing plants, and a warming world are changing both the movements and the physiology of the Blackcaps that spend the winter in Great Britain and Ireland.
"Many migratory birds are ...
2021-04-14
COLUMBUS, Ohio - Most young women already know that tanning is dangerous and sunbathe anyway, so a campaign informing them of the risk should take into account their potential resistance to the message, according to a new study.
Word choice and targeting a specific audience are part of messaging strategy, but there is also psychology at play, researchers say - especially when the message is telling people something they don't really want to hear.
"A lot of thought goes into the content, but possibly less thought goes into the style," said Hillary Shulman, senior author of the study and an assistant ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Impacts of coronavirus lockdowns: New study collects data on pollutants in the atmosphere