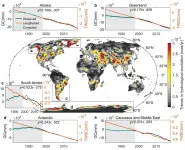
(Press-News.org) A joint research study by the Pacific Water Research Centre at Simon Fraser University and the Fraser Basin Council points to the use of certified, nature-based solutions for protecting salmon and aquatic habitats in the Lower Mainland.
Salmon face various threats in the Lower Fraser Watershed (where the Fraser River passes through the Metro Vancouver geographical area), including habitat loss due to urban development and toxic stormwater runoff, which is projected to worsen due to climate change-driven extreme rain events.
The END
Urban design standards needed to protect Fraser River salmon, SFU report finds
2021-04-23
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
'Like a metronome': Stalagmite growth found to be surprisingly constant
2021-04-23
Like tree rings, cave stalagmites are a portal to a prehistoric Earth, and now scientists from UNSW Sydney have found they are consistently reliable as time trackers the world over.
In a global investigation into the growth properties of stalagmites distributed across the world, the scientists found that while growth fluctuations due to climate events are evident in the shorter period, stalagmite growth over the longer periods - tens of thousands of years - are surprisingly linear.
"Our new global analysis shows that we can consider stalagmite growth as being like a metronome and very ...
Climate has shifted the axis of the Earth
2021-04-23
WASHINGTON-- Glacial melting due to global warming is likely the cause of a shift in the movement of the poles that occurred in the 1990s.
The locations of the North and South poles aren't static, unchanging spots on our planet. The axis Earth spins around--or more specifically the surface that invisible line emerges from--is always moving due to processes scientists don't completely understand. The way water is distributed on Earth's surface is one factor that drives the drift.
Melting glaciers redistributed enough water to cause the direction of polar wander to turn and accelerate eastward during the mid-1990s, according to a new study in Geophysical Research Letters, AGU's journal for high-impact, ...
COVID-19 mobility restrictions effective for short duration, study finds
2021-04-23
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. -- Attempts at restricting people's mobility to control the spread of COVID-19 may be effective only for a short period, researchers said. A new study examines people's mobility for seven months during the pandemic in the United States using publicly available, anonymized mobile phone data.
Reported in the Journal of Transport Geography, the study alerts authorities to the need for more manageable travel restrictions and policies that reduce COVID-19 exposure risk to essential workers - who, because they are required to be physically present at their workplaces, remained highly mobile during the pandemic.
The longitudinal study is one of the first to compare mobility data using a broad ...
Ankle exoskeleton enables faster walking
2021-04-23
Being unable to walk quickly can be frustrating and problematic, but it is a common issue, especially as people age. Noting the pervasiveness of slower-than-desired walking, engineers at Stanford University have tested how well a prototype exoskeleton system they have developed - which attaches around the shin and into a running shoe - increased the self-selected walking speed of people in an experimental setting.
The exoskeleton is externally powered by motors and controlled by an algorithm. When the researchers optimized it for speed, participants walked, on average, 42 percent faster than when they were wearing normal shoes and no exoskeleton. The results of this study were ...
TPU scientists first study composition of pore waters in methane cold seep of eastern Arctic seas
2021-04-23
Young scientists of Tomsk Polytechnic University as a part of the team of Arctic researchers have studied pore waters in three areas of methane release on the surface. They first managed to define in details the composition of pore waters in the cold methane seeps of the Eastern Arctic seas. The research findings are published in the Water academic journal.
The research was based on the samples obtained during the Arctic expedition aboard the research vessel "Akademik Mstislav Keldysh" in 2019. The scientists and students from 12 scientific institutions, including Tomsk Polytechnic University, Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology, Lomonosov Moscow State University, the Research Center of Biotechnology ...
US asbestos sites made risky by some remediation strategies
2021-04-23
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) largely remedies Superfund sites containing asbestos by capping them with soil to lock the buried toxin in place. But new research suggests that this may actually increase the likelihood of human exposure to the cancer-causing mineral.
"People have this idea that asbestos is all covered up and taken care of," said Jane Willenbring, who is an associate professor of geological sciences at Stanford University's School of Earth, Energy & Environmental Sciences (Stanford Earth). "But this is still a lingering legacy pollutant ...
Bacteria and viruses infect our cells through sugars: Now researchers want to know how they do it
2021-04-23
Sugar is not just something we eat. On the contrary. Sugar is one of the most naturally occurring molecules, and all cells in the body are covered by a thick layer of sugar that protects the cells from bacteria and virus attacks. In fact, close to 80 per cent of all viruses and bacteria bind to the sugars on the outside of our cells.
Sugar is such an important element that scientists refer to it as the third building block of life - after DNA and protein. And last autumn, a group of researchers found that the spike protein in corona virus needs a particular sugar to bind to our cells efficiently.
Now the same group of researchers have completed a new study that further digs into the cell receptors to which sugars and thus bacteria and virus ...
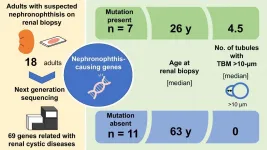
Finding clues to nephronophthisis in adults
2021-04-23
Researchers at Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) in a pioneering study identify clinical, genetic and histopathological characteristics that may help confirm the diagnosis when nephronophthisis occurs in adults
Tokyo, Japan - Nephronophthisis (NPH) is a kidney disease affecting mainly children. Now, for the first time, researchers at Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) have studied a number of adults with NPH and highlighted clinical, genetic and pathological characteristics that could help in confirming this challenging diagnosis.
NPH is inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern and, though rare, is the commonest genetic cause of kidney failure in children. The ...
Red Sea is no longer a baby ocean
2021-04-23
It is 2,250 kilometers long, but only 355 kilometers wide at its widest point - on a world map, the Red Sea hardly resembles an ocean. But this is deceptive. A new, albeit still narrow, ocean basin is actually forming between Africa and the Arabian Peninsula. Exactly how young it is and whether it can really be compared with other young oceans in Earth's history has been a matter of dispute in the geosciences for decades. The problem is that the newly formed oceanic crust along the narrow, north-south aligned rift is widely buried under a thick blanket of salt and sediments. This complicates direct investigations.
In the international journal Nature Communications, scientists from GEOMAR Helmholtz Centre for Ocean Research Kiel, ...
The type of blood vessel damage determines its path to regeneration
2021-04-23
Tsukuba, Japan - Blood vessels can be injured by the build-up of atherosclerosis and long-standing hypertension, among other conditions. As a consequence, blood vessels may undergo a process called remodeling, whereby their walls thicken and cause blockages (known as occlusion). In a new study, researchers from the University of Tsukuba discovered how cells marked by platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha (PDGFRa+) residing predominantly in the most outer layer of blood vessels contribute to their remodeling.
Blood vessels comprise three layers, each of which fulfills a unique role ...