Only 41% of people would sign up for COVID-19 trials says new report
2021-05-06
(Press-News.org) Research conducted by the University of Birmingham shows in order to have an effective Covid-19 vaccination rollout it has to be widely accepted by the entire population.
The study, conducted in collaboration with the NIHR Clinical Research Network West Midlands and The Royal Wolverhampton NHS Trust was published in the journal Trials involved an anonymous cross-sectional online survey across the UK involving 4884 participants of which 9.44% were Black Asian Minority Ethnic (BAME). Overall, 2020 (41.4%) respondents were interested in participating in vaccine trials, while 27.6% of the respondents were not interested and 31.1% were unsure. The most interested groups were male, graduates the 40-49 and 50-59 age groups and those with no health issues. The least interested groups were BAME those from villages and small towns and those aged 70 and above.
Currently, the UK registry has a very low trial participant uptake on the elderly and BAME participants which are two high-risk priority groups. The study concludes there is a need to design interventional and public health strategies to engage and encourage trial participation from these specific demographic groups as the research data provides unique insights into participation interest geographically and can be used to target ongoing and future campaigns in rural and core inner city populations.
Dr Anandadeep Mandal, lecturer in finance from the Birmingham Business School and one the lead authors who carried out the research design involving enhanced text mining and non-linear estimations said: "This study has key importance with COVID-19 mutant (VOC) B117 acquiring mutant E484 and the need for continual trials. The study examines the various factors affecting participation in trials, including geographical locations in England. The results indicate the lack of interest in trial participation among the BAME community even though they score high on importance of vaccine trials. Further, respondents from small town and villages fail to address the need for vaccine trials. Therefore, a joint effort is required engage various ethnic communities and people from different geographical locations to participate in vaccine trials to help the society in need."
Even though 50% of the UK population has the first dose of the vaccination current COVID-19 vaccination trials are not adequately representing a diverse participant population in terms of age, ethnicity and backgrounds which is becoming a challenge in clinical trial management. The study highlights how it is crucial to recruit patients which are representative of the target population which can help in drug development. The aim of this study was to provide possible interventions to increase the uptake for COVID-19 vaccine trial participations with the overall goal to acquire a safe and effective vaccine. This can provide useful in future trials that will continue on for 2021, such as human challenge trials, phase 3 trials and non-inferiority COVID-19 vaccine studies.
The study could not ascertain the reasons to why people did not want to partake in vaccination trials but they were to deduce their general perception towards COVID-19 and vaccines, as well as extracting demographic and geographical data. Being able to understand the key reasons would be beneficial in targeting educational campaigns to tackle specific barriers to trial recruitment.
INFORMATION:
Notes to Editors:
About the University of Birmingham
The University of Birmingham is ranked amongst the world's top 100 institutions, its work brings people from across the world to Birmingham, including researchers and teachers and more than 6,500 international students from over 150 countries.
About the National Institute for Health Research
The National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) is the nation's largest funder of health and care research. The NIHR:
* Funds, supports and delivers high quality research that benefits the NHS, public health and social care
* Engages and involves patients, carers and the public in order to improve the reach, quality and impact of research
* Attracts, trains and supports the best researchers to tackle the complex health and care challenges of the future
* Invests in world-class infrastructure and a skilled delivery workforce to translate discoveries into improved treatments and services
* Partners with other public funders, charities and industry to maximise the value of research to patients and the economy
Sethi et al (2021), 'The UPTAKE study: implications for the future of COVID-19 vaccination trial recruitment in UK and beyond'.' TRIALS.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-05-06
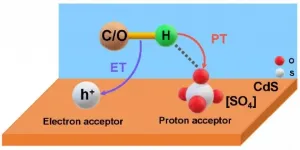
a Photocatalytic biomass conversion is an ideal way of generating syngas (H2 and CO) via C-C bond cleavage, which is initiated by hydrogen abstraction of O/C-H bond. However, the lack of efficient electron-proton transfer limits its efficiency. Conversional gasification of biomass into syngas needs to be operated at high temperature (400-700 °C).
Recently, a group led by Prof. WANG Feng from the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics (DICP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), in collaboration with Prof. WANG Min from Dalian University of Technology, proposed a new method to realize photocatalytic conversion of biopolyols to syngas at room temperature with high efficiency.
This study was published in Journal of the American Chemical ...
2021-05-06
The Korea Institute of Civil Engineering and Building Technology (KICT) has announced the development of a fully-automated peak-picking method for cable monitoring. The developed method will improve reliability of the method. Such as Incheon Bridge in South Korea, Cable-stayed bridges have received significant attention as efficient structural systems worldwide. In this regard, newly developed cable monitoring systems have become an essential and efficient maintenance approach for cable-stayed bridges. As structural integrity for stay-cables, tension force and damping ratio have been widely utilized as efficient metrics.
A research team in KICT, led by Dr. Seung-Seop Jin, has developed a fully-automated peak-picking ...
2021-05-06
Moderate alcohol intake--defined as no more than one alcoholic drink for women and two for men per day--has been associated with a lower risk of dying from cardiovascular disease when compared with individuals who abstain from drinking or partake in excessive drinking, according to a new study being presented at the American College of Cardiology's 70th Annual Scientific Session. It's also the first study to show that drinking moderate amounts of alcohol may be heart protective, in part, by reducing stress-related brain signals based on a subset of patients who underwent brain imaging.
"We found that stress-related activity in the brain was higher in non-drinkers ...
2021-05-06
Nearly 1 in 5 adults with high blood pressure, a leading risk factor for heart disease and stroke, also take a medicine that could be elevating their blood pressure, according to new research presented at the American College of Cardiology's 70th Annual Scientific Session. The results underscore the need for patients to routinely review all of the medications they take with their care team, including those available over the counter, to make sure none could be interfering with blood pressure lowering efforts.
Which are the most likely culprits? Based on the study findings, the three most common classes of medications were antidepressants; nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) that include ibuprofen and naproxen; and oral ...
2021-05-06
Among younger adults visiting the emergency department for chest pain, women may be getting the short end of the stick. Compared with men of similar age, women were triaged less urgently, waited longer to be seen, and were less likely to undergo basic tests or be hospitalized or admitted for observation to diagnose a heart attack, according to new research being presented at the American College of Cardiology's 70th Annual Scientific Session.
The study is the first to examine emergency room management of chest pain specifically among younger adults (age 18-55 years). Heart disease is the leading cause of death in women and is becoming more common in younger adults. About one-third of women who were hospitalized ...
2021-05-06
Young and middle-aged adults who reported severe psychological distress--such as depression or anxiety--after suffering a heart attack were more than twice as likely to suffer a second cardiac event within five years compared with those experiencing only mild distress, according to a study presented at the American College of Cardiology's 70th Annual Scientific Session.
The study is the first to comprehensively assess how mental health influences the outlook for younger heart attack survivors, according to the researchers. The researchers also tracked ...
2021-05-06
Social factors such as education, financial stability, food security and the neighborhood where someone resides were strongly correlated with whether or not individuals with heart disease adopted measures to prevent the spread of COVID-19, including wearing masks and working from home, according to a study presented at the American College of Cardiology's 70th Annual Scientific Session. The researchers say the findings draw attention to longstanding challenges related to social determinants of health.
"Unless we look at COVID-19 through the lens of social determinants of health, we may not optimize our yield from interventions, and we might not be reaching ...
2021-05-06
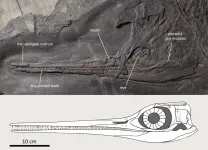
Middle Triassic ichthyosaurs are rare, and mostly small in size. The new Besanosaurus specimens described in the peer-reviewed journal PeerJ - the Journal of Life and Environmental Sciences - by Italian, Swiss, Dutch and Polish paleontologists provide new information on the anatomy of this fish-like ancient reptile, revealing its diet and exceptionally large adult size: up to 8 meters, a real record among all marine predators of this geological epoch. In fact, Besanosaurus is the earliest large-sized marine diapsid - the group to which lizards, snakes, crocodiles, and their extinct cousins belong to - with a long and narrow snout.
Besanosaurus leptorhynchus was originally discovered near Besano (Italy) three decades ago, during systematic excavations led by the Natural ...
2021-05-06
LUGANO, 6 May, 2021- Researchers have discovered a novel biomarker to identify male COVID-19 patients most at risk for ICU admission. The findings presented today at EADV's 2021 Spring Symposium, suggest that men with genetic characteristics (phenotypes) sensitive to the male sex hormone androgen, are more likely to experience severe COVID-19 disease.
Researchers were driven to study the association between the androgen receptor (AR) gene and COVID-19, after observing the disproportionate number of men hospitalised with COVID-19 presenting with androgenetic alopecia (a common form of hair-loss) compared to the expected number in a similar age-matched population (79% vs. 31-53%).
Androgenetic alopecia is known to be controlled by variations ...
2021-05-06
LUGANO, 6 May, 2021- New research investigating for the first time the effects of modified intermittent fasting (MIF) on the skin of people with psoriasis has yielded promising results. Preliminary study findings presented today at the EADV Spring Symposium, show a significant reduction in scaling and thickness in patients with mild psoriasis after following a MIF 5:2 diet (eating normally for 5 days and restricting calorie intake on 2 non-consecutive days).
Psoriasis is a chronic, systemic immune-mediated inflammatory disease that causes raised plaques and ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Only 41% of people would sign up for COVID-19 trials says new report