RUDN University medics detect alterations in amino acid profiles in children with ADHD
2021-06-17
(Press-News.org) RUDN University doctors found alterations in serum amino acid profile in children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). The findings will help to understand the mechanism of the disorder and develop new treatment strategies. The study is published in the journal Biomedical Reports.
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder that manifests itself in childhood. Children with ADHD find it difficult to concentrate and manage their impulsivity. It is known that ADHD is also manifested at the neurochemical level -- for example, the work of dopamine and norepinephrine is disrupted. However, there is still no definitive data on how the responsible for brain function amino acids profile changes in ADHD. Although drugs consisting of amino acids are often used for the treatment of ADHD. Scientists of the RUDN University detected the alterations of the amino acid profile in blood serum in children with ADHD.
"Amino acids serve a significant role in brain development and functioning. In particular, certain amino acids or their precursors are well-established to be involved in neuronal signaling as neurotransmitters. Correspondingly, disruption of amino acid metabolism results in significant neurological disorders, particularly in children. Therefore, unraveling the potential underlying mechanisms implicated in ADHD pathogenesis is essential for improving our understanding of the disorder and further development of management strategies", Anatoly Skalny, DSc, Head of RUDN Department of medical elements studies
102 children aged 7 to 14 years were involved in the study. 71 of them were diagnosed with ADHD, the rest of the participants were neurotypical (without diagnosed disorders). The level of amino acids in the blood serum was measured using liquid chromatography. Then scientists compared the data obtained in children with ADHD and neurotypical children using statistical methods.
It turned out that the serum amino acid profile in children with ADHD differs from neurotypical children. Histidine, glutamine, and proline levels were found to be 29%, 10%, and 20% lower, respectively. Aspartic acid and glutamate were found to be 7% higher, and hydroxyproline-42% higher. Accordingly, the ratio of glutamine to glutamate in children with ADHD is 28% lower than normal, and the ratio of proline to hydroxyproline is 29% lower. The first ratio is one of the indicators of the transmission of nerve impulses, and the second can be a marker of disorders of collagen metabolism and connective tissue. Related diseases are sometimes considered to be associated with ADHD.
«The observed alterations in Pro/Hypro and Gln/Glu levels and ratios are likely associated with the coexisting connective tissue pathology and alterations in glutamatergic neurotransmission in ADHD, respectively. However, further in vivo and in vitro studies are required in order to investigate the detailed mechanisms linking amino acid metabolism with ADHD", Anatoly Skalny, DSc, Head of RUDN Department of medical elements studies
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-17
The death of a mother is a traumatic event for immature offspring in species in which mothers provide prolonged maternal care, such as in long-lived mammals, including humans. Orphan mammals die earlier and have less offspring compared with non-orphans, but how these losses arise remains under debate. Clinical studies on humans and captive studies on animals show that infants whose mothers die when they are young are exposed to chronic stress throughout their lives. However, such chronic stress, which has deleterious consequences on health, can be reduced or even cancelled if human orphans are placed in foster families young enough. How stressed orphans are in the wild and whether ...
2021-06-17
Testicular cancer is the most common cancer among men under 40 in Europe and the USA. National statistics from the Cancer League indicate 471 new cases and 12 deaths in Switzerland. In general, the prospects for successful treatment of testicular cancer are good over time and, especially with early diagnosis, even further improved. Even if metastases are already present, testicular cancer can be successfully treated with appropriate therapy in the majority of cases.
New classification enables even more targeted treatment
The primary treatment for testicular cancer is the removal of the affected testicle. However, the disease is often only discovered at a stage where metastases are already present and then, after the primary surgical procedure, ...
2021-06-17
Modelling the financial system as a network is a precondition to understanding and managing challenges of great relevance for society, including the containment of financial crises and the transition to a low-carbon economy.
Financial Networks is the scientific discipline that deals with these issues. An article published in the scientific journal Nature Review Physics carries out the first comprehensive review of this exciting interdisciplinary field. By covering over 250 studies across domains, the paper is also a call for researchers in all scientific disciplines to consider the insights from the financial network models, because of their implications for citizens, public agencies and governments. Professor Guido Caldarelli from Ca' Foscari University of Venice coordinated ...
2021-06-17
In the mid-14th century Europe was devastated by a major pandemic - the Black Death - which killed between 40 and 60 per cent of the population. Later waves of plague then continued to strike regularly over several centuries.
Plague kills so rapidly it leaves no visible traces on the skeleton, so archaeologists have previously been unable to identify individuals who died of plague unless they were buried in mass graves.
Whilst it has long been suspected that most plague victims received individual burial, this has been impossible to confirm until now. ...
2021-06-17
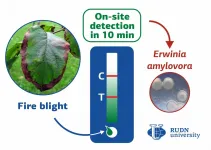
RUDN University biotechnologists have created a method for detection of bacterial infection in apple, pear, hawthorn and other plants of the Rosaceae family. The test does not require laboratory equipment, the result is ready in 10 minutes. This will allow detecting the disease quickly and prevent the spread of infection. The results are published in Physiological and Molecular Pathology of Plants.
Erwinia amylovora bacteria causes a dangerous infectious disease in plants -- a fire blight. Most plants of the Rosaceae family are vulnerable to it, for example, hawthorn, apple, pear. The bacteria causes the blossom to wither, the leaves dry up and curl, the bark develop necrotic lesions. The disease can spread through infected plants, garden tools, and with the wind, which ...
2021-06-17
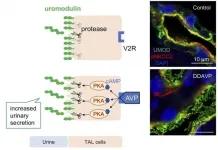
Researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) find that the secretion of uromodulin protein into urine can be induced by treatments that may protect against urinary tract infections and kidney stones, among other diseases
Tokyo, Japan - The normal function of uromodulin, a protein that is made in the kidney and secreted into the urine, remains largely unknown. However, higher levels of uromodulin in the urine are related to lower rates of urinary tract infections and kidney stones, while higher levels of this protein in kidney cells are associated with higher rates of hypertension and chronic kidney disease. Researchers from Japan have now uncovered how uromodulin secretion into the urine can be increased by the hormone vasopressin--a finding that may ...
2021-06-17
A study performed by researchers at the Institute for Advanced Chemistry of Catalonia (IQAC-CSIC) from the Spanish National Research Council (CSIC) in collaboration with Stony Brook University (USA) proposes a new strategy for the development of new drugs based on the inhibition of tyrosine kinase enzymes, molecules that activate and trigger many cellular processes. The results have been published in the Chemistry - A European Journal.
The new approach is based on the regulation of the signaling cascade of tyrosine kinases, and could lead to the development ...
2021-06-17
Today as they did 100 years ago, doctors diagnose cancer by taking tissue samples from patients, which they usually fix in formalin for microscopic examination. In the past 20 years, genetic methods have also been established that make it possible to characterize mutations in tumors in greater detail, thus helping clinicians select the best treatment strategy.
Even tiny tissue samples can be used to detect proteins
Now, a group of researchers from the Berlin-based Max Delbrück Center for Molecular Medicine in the Helmholtz Association (MDC), the Berlin Institute of Health (BIH), Charité - Universitätsmedizin ...
2021-06-17
The German National Academy of Sciences Leopoldina and the German Council for Sustainable Development (RNE) have published a joint position paper presenting paths to climate neutrality by 2050. In it, the Leopoldina and the RNE highlight options for action to effect the changes needed within society, at political level and in the business world, in view especially of the urgency and the historic dimensions of the transformation we face. With the paper, the Leopoldina and the RNE are consciously not seeking to engage in a race to set the most ambitious target. They are instead offering an options paper for setting the right course and covering the key implementation steps. ...
2021-06-17
Abu Dhabi, UAE: Trans-Neptunian Objects (TNOs), small objects that orbit the sun beyond Neptune, are fossils from the early days of the solar system which can tell us a lot about its formation and evolution.
A new study led by Mohamad Ali-Dib, a research scientist at the NYU Abu Dhabi END ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] RUDN University medics detect alterations in amino acid profiles in children with ADHD