Excess nitrogen puts butterflies at risk
2021-06-17
(Press-News.org) Nitrogen from agriculture, vehicle emissions and industry is endangering butterflies in Switzerland. The element is deposited in the soil via the air and has an impact on vegetation - to the detriment of the butterflies, as researchers at the University of Basel have discovered.
More than half of butterfly species in Switzerland are considered to be at risk or potentially at risk. Usually, the search for causes focuses on intensive agriculture, pesticide use and climate change. A research team led by Professor Valentin Amrhein from the University of Basel, however, has been investigating another factor - the depositing of nitrogen from agriculture and exhaust fumes from industry and traffic in soils via the air. In the journal Conservation Biology, the research team reports a connection between this unintentional fertilization and the low diversity of butterflies in Switzerland.
It was already known from previous studies that too much nitrogen leads to denser vegetation, but with a smaller selection of plant species. Nitrogen stimulates the growth of less demanding plants in particular, with more specialized species being displaced. "We wanted to find out whether a nitrogen surplus also indirectly affects the diversity of butterflies via this change in vegetation," explains Dr. Tobias Roth, lead author of the study.
The team analyzed data from Biodiversity Monitoring Switzerland on the diversity and prevalence of plants and butterflies on 383 plots throughout Switzerland. The result was clear: the more nitrogen introduced via the air to the areas studied, the less diverse the vegetation and hence the butterfly species.
"As caterpillars, some butterfly species need certain plant species as food, or are dependent on a certain microclimate," Roth explains. Over-fertilization results in open, warm and dry places becoming cooler, shadier and damper due to stronger plant growth.
The nitrogen surplus impacts the prevalence of a large number of butterfly species in Switzerland, such as those that prefer open and dry sites. The researchers saw the clearest effect in rare and endangered species. "Nitrogen from the air is likely to be an important factor in the reason why these species are endangered," Roth remarks.
Existing literature on the diversity of butterflies explains the presence or absence of species primarily in terms of habitat quality or climate. A literature review by the research team revealed that plant diversity and vegetation density have so far received less attention. "We believe that the impact of nitrogen enrichment on butterflies has been underestimated," says Amrhein. Nitrogen appears to play a similarly extensive role as climate change when it comes to butterfly diversity.
While the researchers do not see a simple approach for improving the situation, technical improvements continue to offer a certain potential. "In the past, slurry was sprayed on farmland, for example, and some of this was transferred to other areas of land by the wind," Roth explains. Today, he says, drag hoses are used increasingly to apply the slurry directly to the soil. This reduces nitrogen input via the air to other areas where it is not wanted.
In addition, buffer zones and adapted landscape management can also help to partially mitigate the negative impact on sensitive habitats: this includes measures to prevent scrub encroachment, such as grazing or more frequent mowing. This is beneficial not only for demanding plant species, but also for butterflies. According to the researchers, however, there is ultimately no way around environmentally friendly consumer behavior when it comes to reducing unwanted nitrogen input, for example through the reduction of vehicle emissions and livestock farming. Around two thirds of nitrogen input into sensitive ecosystems in Switzerland today originate from ammonia emissions from livestock farming.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-17
Living beings are continuously exposed to harmful agents, both exogenous (ultraviolet radiation, polluting gases, etc.) and endogenous (secondary products of cellular metabolism) that can affect DNA integrity. That's why cells are endowed with a series of molecular mechanisms whose purpose is to identify and signpost possible damage to the genetic material for speedy repair. These mechanisms are precisely regulated because they are key to cell survival. In extreme situations of massive and irreparable damage, cells enter a phase of controlled dismantling called "programmed cell death". Among the events that take place during this process is the massive delivery to the cytoplasm of a mitochondrial protein called cytochrome C. Under homeostatic conditions, this protein plays a role in energy ...
2021-06-17
The 2018 Nobel Prize in Physics was shared by researchers who pioneered a technique to create ultrashort, yet extremely high-energy laser pulses at the University of Rochester.
Now researchers at the University's Institute of Optics have produced those same high-powered pulses--known as chirped pulses--in a way that works even with relatively low-quality, inexpensive equipment. The new work could pave the way for:
Better high-capacity telecommunication systems
Improved astrophysical calibrations used to find exoplanets
Even more accurate atomic clocks
Precise devices for measuring chemical contaminants in the atmosphere
In a paper in Optica, the researchers describe the first demonstration ...
2021-06-17
Peatlands are an important ecosystem that contribute to the regulation of the atmospheric carbon cycle. A multidisciplinary group of researchers, led by the University of Helsinki, investigated the climate response of a permafrost peatland located in Russia during the past 3,000 years. Unexpectedly, the group found that a cool climate period, which resulted in the formation of permafrost in northern peatlands, had a positive, or warming, effect on the climate.
The period studied, which began 3,000 years ago, is known as a climate period of cooling temperatures. The climate-related effect of permafrost formation brought about by the cooling was investigated particularly by analysing the ancient plant communities of the peatland, using similarly analysed peatland data from elsewhere in ...
2021-06-17
An international survey by the University of Münster's Cluster of Excellence "Religion and Politics" provides the first empirical evidence of an identity-related political cleavage of European societies that has resulted in the emergence of two entrenched camps of substantial size. "We see two distinct groups with opposing positions, which we call 'Defenders' and 'Explorers'", says psychologist Mitja Back, spokesperson of the interdisciplinary research team that conducted the most comprehensive survey of identity conflicts in Europe to date. "Who belongs to our country, who threatens whom, who is disadvantaged? Across all such questions of identity, the initial analyses of the survey reveal a new line of conflict between the two groups, which have almost diametrically opposite ...
2021-06-17
RUDN University doctors found alterations in serum amino acid profile in children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). The findings will help to understand the mechanism of the disorder and develop new treatment strategies. The study is published in the journal Biomedical Reports.
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder that manifests itself in childhood. Children with ADHD find it difficult to concentrate and manage their impulsivity. It is known that ADHD is also manifested at the neurochemical level -- for example, the work of dopamine and norepinephrine is disrupted. However, there is still no definitive data ...
2021-06-17
The death of a mother is a traumatic event for immature offspring in species in which mothers provide prolonged maternal care, such as in long-lived mammals, including humans. Orphan mammals die earlier and have less offspring compared with non-orphans, but how these losses arise remains under debate. Clinical studies on humans and captive studies on animals show that infants whose mothers die when they are young are exposed to chronic stress throughout their lives. However, such chronic stress, which has deleterious consequences on health, can be reduced or even cancelled if human orphans are placed in foster families young enough. How stressed orphans are in the wild and whether ...
2021-06-17
Testicular cancer is the most common cancer among men under 40 in Europe and the USA. National statistics from the Cancer League indicate 471 new cases and 12 deaths in Switzerland. In general, the prospects for successful treatment of testicular cancer are good over time and, especially with early diagnosis, even further improved. Even if metastases are already present, testicular cancer can be successfully treated with appropriate therapy in the majority of cases.
New classification enables even more targeted treatment
The primary treatment for testicular cancer is the removal of the affected testicle. However, the disease is often only discovered at a stage where metastases are already present and then, after the primary surgical procedure, ...
2021-06-17
Modelling the financial system as a network is a precondition to understanding and managing challenges of great relevance for society, including the containment of financial crises and the transition to a low-carbon economy.
Financial Networks is the scientific discipline that deals with these issues. An article published in the scientific journal Nature Review Physics carries out the first comprehensive review of this exciting interdisciplinary field. By covering over 250 studies across domains, the paper is also a call for researchers in all scientific disciplines to consider the insights from the financial network models, because of their implications for citizens, public agencies and governments. Professor Guido Caldarelli from Ca' Foscari University of Venice coordinated ...
2021-06-17
In the mid-14th century Europe was devastated by a major pandemic - the Black Death - which killed between 40 and 60 per cent of the population. Later waves of plague then continued to strike regularly over several centuries.
Plague kills so rapidly it leaves no visible traces on the skeleton, so archaeologists have previously been unable to identify individuals who died of plague unless they were buried in mass graves.
Whilst it has long been suspected that most plague victims received individual burial, this has been impossible to confirm until now. ...
2021-06-17
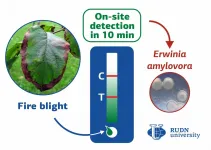
RUDN University biotechnologists have created a method for detection of bacterial infection in apple, pear, hawthorn and other plants of the Rosaceae family. The test does not require laboratory equipment, the result is ready in 10 minutes. This will allow detecting the disease quickly and prevent the spread of infection. The results are published in Physiological and Molecular Pathology of Plants.
Erwinia amylovora bacteria causes a dangerous infectious disease in plants -- a fire blight. Most plants of the Rosaceae family are vulnerable to it, for example, hawthorn, apple, pear. The bacteria causes the blossom to wither, the leaves dry up and curl, the bark develop necrotic lesions. The disease can spread through infected plants, garden tools, and with the wind, which ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Excess nitrogen puts butterflies at risk