(Press-News.org) A rare parasitic infection imported from Europe continues to take root in Alberta, Canada. The province is now the North American hotspot for human alveolar echinococcosis (AE), which takes the form of a growth in the liver, causing serious and potentially deadly health complications.
A END
Incidents of serious parasitic disease on the rise in Alberta, Canada
The province is now the North American hotspot for a rare, potentially fatal disease, say researchers
2021-06-18
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Altered microstructure improves organic-based, solid state lithium EV battery
2021-06-18
Only 2% of vehicles are electrified to date, but that is projected to reach 30% in 2030. A key toward improving the commercialization of electric vehicles (EVs) is to heighten their gravimetric energy density - measured in watt hours per kilogram - using safer, easily recyclable materials that are abundant. Lithium-metal in anodes are considered the "holy grail" for improving energy density in EV batteries compared to incumbent options like graphite at 240 Wh/kg in the race to reach more competitive energy density at 500 Wh/kg.
Yan Yao, Cullen Professor of electrical ...
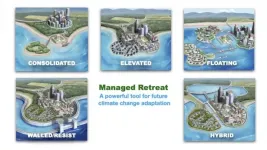
New analysis discusses role of managed retreat as a climate change response
2021-06-18
MIAMI--In a new analysis on managed retreat--the climate adaptation response of moving people and property out of harm's way--researchers explore what it would take for managed retreat to be supportive of people and their priorities. A key starting point is considering retreat alongside other responses like coastal armoring and not just as an option of last resort.
In a new paper in the journal Science, University of Miami (UM) Rosenstiel School of Marine and Atmospheric Science researcher Katharine Mach argues that managed retreat should be viewed as a proactive option that can support communities and livelihoods in the face of climate change.
"Managed retreat ...
Tailored laser fields reveal properties of transparent crystals
2021-06-18
The surface of a material often has properties that are very different from the properties within the material. For example, a non-conducting crystal, which actually exhibits no magnetism, can show magnetisation restricted to its surface because of the way the atoms are arranged there. These distinct properties at interfaces and surfaces of materials often play a key role in the development of new functional components such as optoelectronic chips or sensors and are therefore subject to extensive research. An international research team from the University of Göttingen, the Max Planck Institute for Biophysical Chemistry Göttingen and the National Research Council Canada has now succeeded in investigating the surfaces of transparent crystals using ...
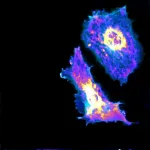
For the first time, researchers visualize metabolic process at the single-cell level
2021-06-18
Understanding cellular metabolism - how a cell uses energy- could be key to treating a wide array of diseases, including vascular diseases and cancer.
While many techniques can measure these processes among tens of thousands of cells, researchers have been unable to measure them at the single-cell level.
Researchers at the University of Chicago's Pritzker School of Molecular Engineering and Biological Sciences Division have developed a combined imaging and machine learning technique that can, for the first time, measure a metabolic process at both the cellular and sub-cellular levels.
Using a genetically encoded biosensor paired with artificial intelligence, ...
Tug-of-war receptors for sour taste in fruit flies sheds light on human taste biology
2021-06-18
PHILADELPHIA - Sour taste does not have the nearly universal appeal that sweet taste does. Slightly sour foods or drinks such as yogurt and lemon juice are yummy to many, but such highly sour foods as spoiled milk are yucky, even dangerous. Like humans, many other animals, including insects, prefer slightly acidic over very acidic foods.
Evolutionary biologists surmise that the need for sour detection to be finely tuned is a two-sided coin: slightly acidic foods can enhance digestion and stimulate saliva production; relative sour-to-sweet taste can signal optimal ripeness of fruit; and extremely sour food, as with bitter taste, is a warning to what not to ingest. However, despite this usefulness, how do animals discern different concentrations ...
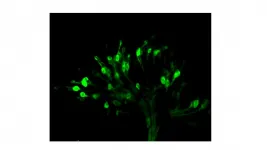
Controlling brain states with a ray of light
2021-06-18
The brain presents different states depending on the communication between billions of neurons, and this network is the basis of all our perceptions, memories, and behaviours. It is often considered a "black box", with difficult access for clinicians and researchers, as few limited tools are available to perform accurate and spaciotemporal studies on brain neuronal behaviour. Now, researchers from the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia (IBEC) in collaboration with August Pi i Sunyer Biomedical Research Institute (IDIBAPS) and have added some light to the subject: they succeeded for the first time in controlling neuronal activity in the brain using a molecule responsive to light.
The study included participants ...
Vaccination, previous infection, protect against gamma variant in animal model
2021-06-18
MADISON - In early January 2021, travelers returning to Tokyo, Japan, from Amazonas, Brazil, were screened for COVID-19 at the airport. A few days later, the National Institute of Infectious Disease of Japan announced that the travelers had returned with a new variant of the SARS-CoV-2 virus.
That variant, known as gamma, or P.1, led to a deadly surge in COVID-19 cases in Brazil this spring, and has now spread across the world. More than 200 cases have been detected in Wisconsin. Whether current vaccines are as effective against the gamma variant remains unknown.
In a new study using variant virus recovered from one of the original travelers, ...
Managed retreat: A must in the war against climate change
2021-06-18
University of Delaware disaster researcher A.R. Siders said it's time to put all the options on the table when it comes to discussing climate change adaptation.
Managed retreat -- the purposeful movement of people, buildings and other assets from areas vulnerable to hazards -- has often been considered a last resort. But Siders said it can be a powerful tool for expanding the range of possible solutions to cope with rising sea levels, flooding and other climate change effects when used proactively or in combination with other measures.
Siders, a core faculty member in UD's Disaster Research Center, and Katharine J. Mach, associate professor at the University ...
KIYATEC clinical study data shows test accurately predicts brain cancer patient response
2021-06-17
KIYATEC, Inc. announced today the publication of new peer-reviewed data that establishes clinically meaningful prediction of patient-specific responses to standard of care therapy, prior to treatment, in newly diagnosed glioblastoma (GBM) and other high-grade glioma (HGG) patients. The results, the interim data analysis of the company's 3D-PREDICT clinical study, were published June 16, 2021 in Neuro-Oncology Advances, an open access clinical journal.
A goal of the study, which continues to enroll, was for the test's prospective, patient-specific response prediction to achieve statistical significance for ...
Study explores how the elderly use smart speaker technology
2021-06-17
Researchers from Bentley University, in partnership with Waltham Council on Aging in Massachusetts, and as part of a study funded by the National Science Foundation, have been exploring how the elderly use smart speakers at home. Waltham, a satellite city about eight miles west of Cambridge has a population of about 60,000, with about one in six being an elderly citizen. The purpose of the study was to understand how the elderly use the smart speaker technology at home. A smart speaker is a hardware device that is always-on. When a wake-word triggers the software contained in the device, the smart speaker listens to the command to provide a response or carry out the command (accessing resources ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal reports faster robot-assisted brain angiography
New study clarifies how temperature shapes sex development in leopard gecko
Major discovery sparks chain reactions in medicine, recyclable plastics - and more
[Press-News.org] Incidents of serious parasitic disease on the rise in Alberta, CanadaThe province is now the North American hotspot for a rare, potentially fatal disease, say researchers