(Press-News.org) Irvine, CA - June 22, 2021 - A new University of California, Irvine-led study reveals albumin (Alb), among the most abundant proteins in the body, activates a proton channel (hHv1), also widespread in the body, giving sperm the ability to penetrate and fertilize an egg, and allowing white blood cells to secrete large amounts of inflammatory mediators to fight infection.
The study titled, "Direct activation of the proton channel by albumin leads to human sperm capacitation and sustained release of inflammatory mediators by neutrophils," was published today in Nature Communications.
Researchers examined the physiological connection between Alb and human voltage-gated proton channels (hHv1), which are both essential to cell biology in health and diseases. They also demonstrated the mechanism by which Alb binds directly to hHv1 to activate the channel. This research explains how sperm are triggered to fertilize, and neutrophils are stimulated to release mediators in the innate immune response, describing a new role for Alb in physiology that will operate in the many tissues expressing hHv1.
"We found that the interaction of Alb and hHv1 activates sperm when they leave semen and enter the female reproductive tract because Alb is low in semen and high in the reproductive tract. We now understand why albumin supplementation improves IVF," said first author Ruiming Zhao, PhD, from the Department of Physiology & Biophysics at UCI School of Medicine. "We also found the same Alb/hHv1 interaction allows the white blood cells called neutrophils to produce and secrete the inflammatory mediators that kill bacteria and fight infection. However, it's important to note that the inflammatory response itself can lead to disease."
The essential stimulatory role of Alb in the physiology of sperm and neutrophils via hHv1 suggests that Alb will have as-yet unrecognized enhancing or deleterious roles in the other tissues, including the central nervous system, heart and lungs, and will influence cancers of the breast and gastrointestinal tract.
"It is exciting to discover that a common protein has the power to activate the proton channel. This finding suggests new strategies to block or enhance fertility, and to augment or suppress the innate immune response and inflammation," said senior author Steve A. N. Goldstein, MD, PhD, vice chancellor of Health Affairs at UCI and distinguished professor in the School of Medicine Departments of Pediatrics and Physiology & Biophysics, and in the new School of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences.
hHv1 is implicated in a wide range of biological processes in addition to the capacitation of sperm and the innate immune responses included in the study. The channels have notable roles in proliferation of cancer cells, tissue damage during ischemic stroke, and hypertensive injury of the kidney. Because Alb is ubiquitous at levels that vary in different human compartments in health and disease, the potentiation of hHv1 by Alb described in the paper will be widespread, tissue-dependent, and play both salutary and unfavorable roles in human physiology.
"We have modeled the structural basis for binding of Alb to the channel that leads to activation and changes in cellular function, and we are now conducting in vivo studies of viral and bacterial infections. Our next steps include studies of the effects of inhibitors of the Alb-hHv1 interaction on infection, inflammation and fertility," said Goldstein.
INFORMATION:
The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health, US-Israel Binational Science Foundation, Universidad Nacional de Cuyo, Argentina, Agencia Nacional de Promocion Cientifica y Tecnologica, Argentina, Universidad Nacional de Cuyo, Argentina, Agencia Nacional de Promocion Cientifica y Tecnologica, Argentina, Universidad Nacional Autonoma de Mexico, Direccion General de Asuntos del Personal Academico, and Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnologia, Fronteras.
About UCI Health Affairs
UCI Health Affairs comprises the schools, institutes, and centers in the Susan and Henry Samueli College of Health Sciences and an academic health system, UCI Health. The college unites the disciplines of medicine, nursing, pharmacy and pharmaceutical sciences, and population and public health to advance a transformative educational and healthcare delivery model that is patient-centered, science-based, transdisciplinary, and team-delivered.
About the UCI School of Medicine
Each year, the UCI School of Medicine educates more than 400 medical students, and nearly 150 doctoral and master's students. More than 700 residents and fellows are trained at UCI Medical Center and affiliated institutions. The School of Medicine offers an MD; a dual MD/PhD medical scientist training program; and PhDs and master's degrees in anatomy and neurobiology, biomedical sciences, genetic counseling, epidemiology, environmental health sciences, pathology, pharmacology, physiology and biophysics, and translational sciences. Medical students also may pursue an MD/MBA, an MD/master's in public health, or an MD/master's degree through one of three mission-based programs: the Health Education to Advance Leaders in Integrative Medicine (HEAL-IM), the Leadership Education to Advance Diversity-African, Black and Caribbean (LEAD-ABC), and the Program in Medical Education for the Latino Community (PRIME-LC). The UCI School of Medicine is accredited by the Liaison Committee on Medical Accreditation and ranks among the top 50 nationwide for research. For more information, visit som.uci.edu.
Machine learning algorithms do a lot for us every day--send unwanted email to our spam folder, warn us if our car is about to back into something, and give us recommendations on what TV show to watch next. Now, we are increasingly using these same algorithms to make environmental predictions for us.
A team of researchers from the University of Minnesota, University of Pittsburgh, and U.S. Geological Survey recently published a END ...
In a cancer that has not seen new targeted therapies for over 20 years, MUSC Hollings Cancer Center researcher and oncologist Nancy Klauber-DeMore, M.D., is pioneering new discoveries.
Using a combination of personal passion and expertise, Klauber-DeMore shifted her knowledge of the pro-angiogenic protein SFRP2 in breast cancer to address the lack of treatment options for patients with aggressive metastatic osteosarcoma. The results of the combination treatment with SFRP2 and PD-1 antibodies in a preclinical model were published in Cancers.
Osteosarcoma expert William Tap, M.D., chief of the Sarcoma Medical Oncology Service at Memorial Sloan Kettering ...
Changes in climate resulting from carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions into the Earth's atmosphere are not equal to the climate changes from deliberate CO2 removals--and assuming such a balance could lead to different climate outcomes that may skew climate targets, according to new Simon Fraser University-led research.
"Because of the complexity of the Earth's system, things are not as simple as "one ton of CO2 in, equals one ton of CO2 out," says Kirsten Zickfeld, a distinguished professor of climate science in SFU's Department of Geography, and lead author of a new paper published ...
The shift to home working brought about by the pandemic could cost the UK economy up to £32bn a year in lost personal income tax.
Highly paid workers who live abroad but work in the UK will pay their income tax in their country of residence, rather than to HMRC - which researchers say could cost billions each year.
This new mobility of the workforce can also affect where corporate income tax is paid and value created, as well as VAT and where goods and services are purchased.
Professor Rita de la Feria, Chair in Tax Law in the University of Leeds' School of Law, co-led the new research with Dr Giorgia Maffini, Tax Policy expert, at PWC, ...
Legend has it that Marie Antoinette's hair turned gray overnight just before her beheading in 1791.
Though the legend is inaccurate--hair that has already grown out of the follicle does not change color--a new study from researchers at Columbia University Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons is the first to offer quantitative evidence linking psychological stress to graying hair in people.
And while it may seem intuitive that stress can accelerate graying, the researchers were surprised to discover that hair color can be restored when stress is eliminated, a finding that contrasts with a recent study in mice that suggested that stressed-induced gray hairs are permanent.
The ...
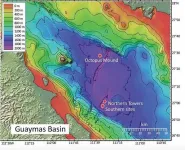
WOODS HOLE, Mass. -- It's cold in the depths of the world's oceans; most of the seafloor is at a chilly 4°C. Not so the seafloor of Guaymas Basin in the Gulf of California. Here, tectonic plates drift apart and heat from Earth's interior can rise up -- so far up that it bakes large areas of the seafloor sediments, turning buried organic matter into methane and other energy-rich compounds.
What kinds of organisms thrive in this oceanic hotspot? In two new studies, MBL Assistant Scientist END ...
Looking for better ways to treat patients with esophageal cancer, University of Colorado Cancer Center member Martin McCarter, MD, is investigating whether a new treatment sequence will result in better outcomes.
As they await the results of a group of clinical trials -- including one at the CU Cancer Center -- McCarter and other University of Colorado researchers (led by surgery resident Bobby Torphy, MD, PhD) looked at data from the National Cancer Database to see if they could identify other patients who have undergone the new sequence, and what the outcomes for those patients were. The group published a paper in the Annals of Surgical Oncology in April ...
Rainfall associated with the Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ), the belt of converging trade winds and rising air that encircles the Earth near the Equator, affects the food and water security of approximately 1 billion people worldwide. They include about 11% of the Brazilian population, concentrated in four states of the Northeast region - Rio Grande do Norte, Ceará, Piauí, and Maranhão. Large swathes of these states have a semi-arid climate, and about half of all their annual rainfall occurs in only two months (March and April), when the tropical rain belt reaches its southernmost position, over the north of the Northeast region. During the rest of the year, the tropical ...
(SACRAMENTO, Calif.) -- The secret to healthier skin and joints may reside in gut microorganisms. A study led by UC Davis Health researchers has found that a diet rich in sugar and fat leads to an imbalance in the gut's microbial culture and may contribute to inflammatory skin diseases such as psoriasis. ...
New research published in the Journal of Medicinal Food suggests eating prunes each day can improve risk factors for cardiovascular disease (CVD) including raising antioxidant capacity and reducing inflammation among healthy, postmenopausal women.
Cardiovascular disease is the number one cause of death worldwide posing a significant public health challenge.
The research led by San Diego State University reveals that prunes can positively affect heart disease risk.
"When you look at our prior research and the research of others combined with this new data, you'll see consistent ...