Computer training program for seniors can reduce hazardous driving
2021-06-29
(Press-News.org) A recent proof-of-concept study finds that a low-cost training program can reduce hazardous driving in older adults. Researchers hope the finding will lead to the training becoming more widely available.
"On-road training and simulator training programs have been successful at reducing car accidents involving older drivers - with benefits lasting for years after the training," says Jing Yuan, first author of the study and a Ph.D. student at North Carolina State University. "However, many older adults are unlikely to have access to these training programs or technologies."
"We developed a training program, called Drive Aware, that would be accessible to anyone who has a computer," says Jing Feng, corresponding author of the study and a professor of psychology at NC State. "Specifically, Drive Aware is a cognitive training program for older adults to help them accurately detect road hazards. The goal of our recent study was to determine the extent to which Drive Aware influences driving behaviors when trainees actually get behind the wheel."
To test Drive Aware, the researchers enlisted 27 adults, ages 65 and older. All of the study participants took a baseline driving test in a driving simulator. Nine of the study participants were then placed in the "active training" group. The active training group received two interactive Drive Aware training sessions, about a week apart. Nine other study participants were placed in a "passive training" group. This group watched video of other people receiving the Drive Aware training sessions. This took place twice, with sessions about a week apart. The remaining nine study participants served as the control group and received no training. All 27 study participants then took a second driving test in the driving simulator.
The researchers found that study participants who were part of the active training group had 25% fewer "unsafe incidents" after the training. Unsafe incidents included accidents with other vehicles, pedestrians, running off the road, etc. There was no statistically significant change in the number of unsafe incidents for study participants in the passive training group or the control group.
"In short, we found that older adults were less likely to have an accident in the driving simulator after receiving the Drive Aware training," Yuan says.
"This testing was done with a fairly modest number of study participants," Feng says. "If we can secure the funding, we'd like to scale up our testing to more clearly establish how effective this training is at reducing accidents among older drivers. If the results are as good as they look right now, we'd want to find ways to share the training program as broadly as possible. Not many people can afford one-on-one on-the-road training, or training that involves high-end driving simulators. But we think a lot of people would be able to access Drive Aware, and it has the potential to save a lot of lives."
INFORMATION:
The paper, "Drive Aware Training: A Computerized Training Program for Older Drivers' Detection of Road Hazards," is published in the journal Traffic Injury Prevention. The paper was co-authored by Aaron Crowson, a Ph.D. student at NC State; and Geoffrey Richardson, an undergraduate at NC State. The work was done with support from the Governor's Highway Safety Program at the North Carolina Department of Transportation.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-29
Populations of Drosophila suzukii fruit flies - so-called "spotted-wing Drosophila" that devastate soft-skinned fruit in North America, Europe and parts of South America - could be greatly suppressed with the introduction of genetically modified D. suzukii flies that produce only males after mating, according to new research from North Carolina State University.
D. suzukii are modified with a female-lethal gene that uses a common antibiotic as an off switch. Withholding the antibiotic tetracycline in the diet of larvae essentially eliminates birth of female D. suzukii flies as the modified male flies successfully mate with females, says Max Scott, an NC State entomologist who is the corresponding author of a paper describing the research.
"We use a genetic female-lethal system - a ...
2021-06-29
Researchers from the Laboratory of Oncolytic-Virus-Immuno-Therapeutics (LOVIT) at the LIH Department of Oncology (DONC) are working on the development of novel anticancer strategies based on oncolytic viruses, "good" viruses that can specifically infect, replicate in and kill cancer cells. In particular, the LOVIT team elucidated the mechanism through which the H-1PV cancer-destroying virus can attach to and enter cancer cells, thereby causing their lysis and death. At the heart of this process lie laminins, and specifically laminin γ1, a family of proteins on the surface of a cancer cell to which this virus binds, and which therefore act as the 'door' through which the virus enters the cells. The findings, which were published in the prestigious ...
2021-06-29
Beetles are creatures with built-in body armor. They are tiny tanks covered with hard shells, also known as exoskeletons, protecting their soft, skeleton-less bodies inside. In addition to providing armored protection, the beetle's exoskeleton offers functions like sensory feedback and hydration control. Notably, the exoskeletons of many beetles are also brilliantly colored and patterned, which enhances visual communication with other beetles and organisms.
Ling Li, lead investigator and assistant professor in mechanical engineering, has joined colleagues from six other universities to investigate the interplay between mechanical and optical performance ...
2021-06-29
Globally, more than 400 million people have diabetes, most of them suffering from type 2 diabetes.
Before the onset of actual type 2 diabetes, people are often diagnosed with abnormalities in glucose metabolism that are milder than those associated with diabetes. The term used to indicate such cases is prediabetes. Roughly 5-10% of people with prediabetes develop type 2 diabetes within a year-long follow-up.
Insulin resistance in muscle tissue is one of the earliest metabolic abnormalities detected in individuals who are developing type 2 diabetes, and the phenomenon is already seen in prediabetes.
In a collaborative study, researchers from the University of Helsinki, the ...
2021-06-29
URBANA, Ill. - Despite soybean's high protein and oil content and its potential to boost food security on the continent, Africa produces less than 1% of the world's soybean crop. Production lags, in part, because most soybean cultivars are bred for North and South American conditions that don't match African environments.
Researchers from the Soybean Innovation Lab (SIL), a U.S. Agency for International Development-funded project led by the University of Illinois, are working to change that. In a new study, published in Agronomy, they have developed methods to help breeders improve soybean cultivars specifically for African environments, with the intention of creating fast-maturing ...
2021-06-29
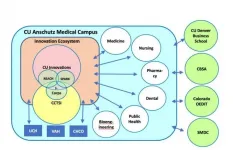
A new study highlights the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus as an example of how an academic medical center can turn groundbreaking research into commercial products that improve patient care and public health.
The paper, published recently in the Journal of Clinical and Translational Science, focuses on the unique ecosystem at CU Anschutz responsible for these innovations. And it specifically details the campus's collaborative culture and how biomedical research is commercialized.
The campus has successfully turned academic research into a variety of products. CU Anschutz, for example, developed two vaccines for shingles, Zostavax and Shingrix, and ...
2021-06-29
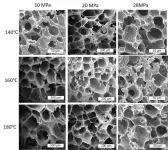
WASHINGTON, June 29, 2021 -- Biodegradable plastics are supposed to be good for the environment. But because they are specifically made to degrade quickly, they cannot be recycled.
In Physics of Fluids, by AIP Publishing, researchers from the University of Canterbury in New Zealand have developed a method to turn biodegradable plastic knives, spoons, and forks into a foam that can be used as insulation in walls or in flotation devices.
The investigators placed the cutlery, which was previously thought to be "nonfoamable" plastic, into a chamber filled with carbon dioxide. ...
2021-06-29
The death of the dinosaurs 66 million years ago was caused by the impact of a huge asteroid on the Earth. However, palaeontologists have continued to debate whether they were already in decline or not before the impact.
In a new study, published today in the journal Nature Communications, an international team of scientists, which includes the University of Bristol, show that they were already in decline for as much as ten million years before the final death blow.
Lead author, Fabien Condamine, a CNRS researcher from the Institut des Sciences de l'Evolution de Montpellier (France), said: "We looked at the six most abundant dinosaur families through the whole of the Cretaceous, spanning from 150 to 66 million ...
2021-06-29
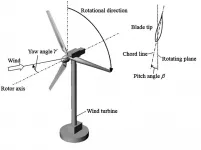
WASHINGTON, June 29, 2021 -- As wind passes through a turbine, it creates a wake that decreases the downstream average wind velocity. The faster the spin of the turbine blades relative to the wind speed, the greater the impact on the downstream wake profile.
For wind farms, it is important to control upstream turbines in an efficient manner so downstream turbines are not adversely affected by upstream wake effects. In the Journal of Renewable and Sustainable Energy, by AIP Publishing, researchers from the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign show by designing controllers based on viewing ...
2021-06-29
WASHINGTON, June 29, 2021 -- Many meteorites, which are small pieces from asteroids, do not experience high temperatures at any point in their existence. Because of this, these meteorites provide a good record of complex chemistry present when or before our solar system was formed 4.57 billion years ago.
For this reason, researchers have examined individual amino acids in meteorites, which come in a rich variety and many of which are not in present-day organisms.
In Physics of Fluids, by AIP Publishing, researchers from Harvard University show the existence of a systematic group of amino acid polymers across several members ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Computer training program for seniors can reduce hazardous driving