Microbially produced fibers: Stronger than steel, tougher than Kevlar
Artificially designed, amyloid-silk hybrid protein developed in Zhang lab even outperforms some spider silks
2021-07-21
(Press-News.org) Spider silk is said to be one of the strongest, toughest materials on the Earth. Now engineers at Washington University in St. Louis have designed amyloid silk hybrid proteins and produced them in engineered bacteria. The resulting fibers are stronger and tougher than some natural spider silks.
Their research was published in the journal ACS Nano.
To be precise, the artificial silk -- dubbed "polymeric amyloid" fiber -- was not technically produced by researchers, but by bacteria that were genetically engineered in the lab of Fuzhong Zhang, a professor in the Department of Energy, Environmental & Chemical Engineering in the McKelvey School of Engineering.
Zhang has worked with spider silk before. In 2018, his lab engineered bacteria that produced a recombinant spider silk with performance on par with its natural counterparts in all of the important mechanical properties.
"After our previous work, I wondered if we could create something better than spider silk using our synthetic biology platform," Zhang said.
The research team, which includes first author Jingyao Li, a PhD student in Zhang's lab, modified the amino acid sequence of spider silk proteins to introduce new properties, while keeping some of the attractive features of spider silk.
A problem associated with recombinant spider silk fiber -- without significant modification from natural spider silk sequence -- is the need to create β-nanocrystals, a main component of natural spider silk, which contributes to its strength. "Spiders have figured out how to spin fibers with a desirable amount of nanocrystals," Zhang said. "But when humans use artificial spinning processes, the amount of nanocrystals in a synthetic silk fiber is often lower than its natural counterpart."
To solve this problem, the team redesigned the silk sequence by introducing amyloid sequences that have high tendency to form β-nanocrystals. They created different polymeric amyloid proteins using three well-studied amyloid sequences as representatives. The resulting proteins had less repetitive amino acid sequences than spider silk, making them easier to be produced by engineered bacteria. Ultimately, the bacteria produced a hybrid polymeric amyloid protein with 128 repeating units. Recombinant expression of spider silk protein with similar repeating units has proven to be difficult.
The longer the protein, the stronger and tougher the resulting fiber. The 128-repeat proteins resulted in a fiber with gigapascal strength (a measure of how much force is needed to break a fiber of fixed diameter), which is stronger than common steel. The fibers' toughness (a measure of how much energy is needed to break a fiber) is higher than Kevlar and all previous recombinant silk fibers. Its strength and toughness are even higher than some reported natural spider silk fibers.
In collaboration with Young- Shin Jun, professor in the Department of Energy, Environmental & Chemical Engineering, and her PhD student Yaguang Zhu, the team confirmed that the high mechanical properties of the polymeric amyloid fibers indeed come from the enhanced amount of β-nanocrystals.
These new proteins and the resulting fibers are not the end of the story for high-performance synthetic fibers in the Zhang lab. They are just getting started. "This demonstrates that we can engineer biology to produce materials that beat the best material in nature," Zhang said.
INFORMATION:
This work explored just three of thousands of different amyloid sequences that could potentially enhance the properties of natural spider silk. "There seem to be unlimited possibilities in engineering high-performance materials using our platform," Li said. "It's likely that you can use other sequences, put them into our design and also get a performance-enhanced fiber."
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-07-21
ITHACA, N.Y. - Small-scale. Short-lived. All digital. Out of public view. That's how a new form of collective worker resistance is unfolding in China's app-based food delivery economy, new Cornell University research finds.
Though highly fragmented and not always successful, "mini-strikes" by small groups of food couriers - conducted via WeChat - reflect a new form of leverage, suggest Chuxuan "Victoria" Liu and Eli Friedman, associate professor in the ILR School.
Food couriers are able to maintain complete physical invisibility, and each individual worker can 'strike' from anywhere, they write.
The scholars interviewed couriers, in-person and online, who delivered food for Ele.me, an Alibaba-owned company that controlled ...
2021-07-20
Tuesday, July 20, 2021, CLEVELAND: A Cleveland Clinic study demonstrates that adults with obesity lost significantly more weight when they had access to medications for chronic weight management in conjunction with their employer-based weight management program, compared to adults who did not have access to the medications. The study was published in JAMA Network Open.
Obesity is a complex disease that is caused by multiple factors, including genetic, environmental, and biological. A lifestyle intervention with a focus on nutrition and exercise is often not enough to treat obesity, which is a chronic disease that requires long-term therapy. The U.S. Food and Drug ...
2021-07-20
WASHINGTON - A peer-reviewed study by the Environmental Working Group recommends stringent health-based exposure standards for both children and adults for radiofrequency radiation emitted from wireless devices. EWG's children's guideline is the first of its kind and fills a gap left by federal regulators.
The study, published in the journal Environmental Health, relies on the methodology developed by the Environmental Protection Agency to assess human health risks arising from toxic chemical exposures. EWG scientists have applied the same methods to radiofrequency radiation from wireless devices, ...
2021-07-20
ROCHESTER, Minn. -- Mayo Clinic researchers have found that acute kidney injury associated with COVID-19 resembles sepsis-caused kidney injury, and the immune response triggered by the infection plays a pivotal role.
The findings, published in Mayo Clinic Proceedings, also suggest that mitochondrial dysfunction -- a loss of function in cellular energy production -- is commonly found in kidney injury related to COVID-19. More than one-third of hospitalized COVID-19 patients report acute kidney injury, and sudden kidney failure is a risk factor for in-hospital mortality, according to studies published last ...
2021-07-20
The remains of microscopic plankton blooms in near-shore ocean environments slowly sink to the seafloor, setting off processes that forever alter an important record of Earth's history, according to research from geoscientists, including David Fike at Washington University in St. Louis.
Fike is co-author of a new study published July 20 in Nature Communications.
"Our previous work identified the role that changing sedimentation rates had on local versus global controls on geochemical signatures that we use to reconstruct environmental change," said Fike, professor of earth and planetary sciences and director of environmental studies in Arts & Sciences.
"In this study, we investigated organic carbon loading, or how much ...
2021-07-20
Experts say these unexpected healthcare costs may discourage people from seeking recommended preventive care.
Despite a sharp reduction in out-of-pocket (OOP) costs for preventive care since the Affordable Care Act was enacted in 2010, patients are still receiving unexpected bills for preventive services that should be free, according to a new study co-authored by a Boston University School of Public Health (BUSPH) researcher.
Published in the journal Preventive Medicine, study found that total out-of-pocket costs billed for preventive services to Americans with employer-sponsored insurance (ESI) in 2018 ranged from $75.6 million to $219 million, with 1 in 4 patients who used preventive care incurring these charges.
"The ACA enabled great strides in making preventive care free to ...
2021-07-20
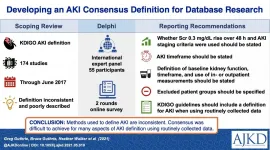
In an article published in the American Journal of Kidney Diseases (AJKD), researchers found that among 176 studies on acute kidney injury, the Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) definitions of kidney injury were inconsistently applied and 80% of studies did not define recovery of kidney function.
The KDIGO definition of AKI is used in both clinical practice and in research. This scoping review demonstrated that there is a wide variation of practice in how this definition is applied and also a lack of transparency about how researchers applied it. An international panel of experts in AKI was formed in an attempt to achieve consensus on how this definition should be applied. They participated in a Delphi process and while they were able to ...
2021-07-20
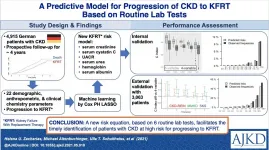
Researchers developed a new risk equation, based on six routinely available patient parameters, that yielded improved performance in estimating the risk of a chronic kidney disease (CKD) patient to progress to end-stage kidney disease (ESKD) requiring kidney replacement therapy (KRT).
A novel risk equation for the timely identification of chronic kidney disease (CKD) patients at risk for progressing to kidney failure requiring kidney replacement therapy was developed in 4,915 patients with CKD stage 1-5 with and without albuminuria, from the German Chronic Kidney Disease (GCKD) Study. It includes six laboratory tests: ...
2021-07-20
TUCSON, Ariz., July 20, 2021 -- The use of digital health technologies across health care and drug development has accelerated. A new paper titled "Digital Progression Biomarkers as Novel Endpoints in Clinical Trials: A Multistakeholder Perspective," co-authored by experts across diverse disciplines, highlights how new remote monitoring technologies present a tremendous opportunity to advance digital medicine in health care even further, specifically in Parkinson's disease. This perspective paper is co-authored by the academic leader of the largest funded project for digital technologies in Europe, Professor Lynn Rochester, University of Newcastle; European Medicines Agency (EMA) ...
2021-07-20
Researchers revealed new insights into how acute myeloid leukemia (AML) develops and progresses, according to a study published in END ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Microbially produced fibers: Stronger than steel, tougher than Kevlar
Artificially designed, amyloid-silk hybrid protein developed in Zhang lab even outperforms some spider silks