A substance from Saussurea controversa will help bone tissue regeneration
2021-07-21
(Press-News.org) Metabolic bone diseases, including osteoporosis, when bones lose their mass and become so fragile that they could be damaged while sneezing or under little stress, are called the silent epidemic of the 21st century. A person does not even know about his illness before the first symptom - it can be a fracture of the spine or the neck of the hip. According to statistics, every third woman and every fifth man after 50 have osteoporosis. Thus, it is promising to search for and obtain substances and materials for implants that have osteoinductive properties and are capable of initiating the processes of transformation of stem cells into bone.
Certain trace elements, such as calcium and magnesium, influence the processes of bone regeneration and the maintenance of their normal structure. Organic molecules that can bind to them provide an improvement in the selectivity of their therapeutic action - the resulting complexes play a significant role in bone formation and development. From this point of view, salts of chelidonic acid have great potential, for example, from the Saussurea controversa known since ancient times for its healing properties.
The group of scientists from the Immanuel Kant Baltic Federal University, Siberian State Medical University, and Tomsk Polytechnic University has previously discovered that calcium chelidonate is promising for engineering as a drug for restoring lost bone volume. In their latest work, they obtained this substance in a semisynthetic way: extracts from Saussurea controversa were the source of the chelidonic acid, to which an alkali solution and calcium chloride were added.
"The content of this substance differs in the samples of raw material and, most likely, its biosynthesis depends on the amount of calcium in the soil. For pharmaceutical purposes, it is advisable to use calcium chelidonate obtained by a semisynthetic method," explains Elena Avdeeva, candidate of pharmaceutical sciences, a researcher at the Siberian State Medical University.
Scientists from the Institute of Organic Chemistry carried out an X-ray analysis and confirmed that the substance has a structure identical to a natural compound.
Researchers from the Center for Immunology and Cellular Biotechnologies of the IKBFU, together with scientists from the Siberian State Medical University, tested the effect of the substance in vitro and in vivo: it promoted the conversion of human stem cells derived from adipose tissue (hAMMSC) and mouse mesenchymal stromal cells into osteoblasts respectively. Calcium chelidonate is non-toxic and promotes bone regeneration: the results of in vitro studies have shown that a dose of only 10 mg / L statistically increases the number of viable stem cells compared to the control without this substance. The calcium phosphate-coated titanium implants bearing autologous bone marrow were introduced into mice. Calcium chelidonate stimulated the growth of new bone on the surface of the implant with daily administration of the drug for 35 days.
"The use of substances with osteoprotective properties, in particular, calcium chelidonate, is promising for the treatment of several diseases associated with bone defects or bone metabolism disorders. We are considering the development of a pharmaceutical form of the substance and its introduction into practical medicine," concludes Larisa Litvinova, Doctor of Medicine, professor, head of the laboratory of immunology and cellular biotechnology at the IKBFU.
INFORMATION:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-07-21
In the early days of the pandemic, scientists at Virginia Tech created a COVID-19 testing laboratory and novel test for the virus from scratch.
They not only developed a test in-house that avoided the reagent supply shortages that hampered testing efforts nationwide, but also used 3D-engineered supplies and stable storage media, enabling samples to be transported to rural sites in Virginia without the need for constant refrigeration.
This novel protocol for transforming a research laboratory into a testing operation capable of processing more than 130,000 ...
2021-07-21
Spider silk is said to be one of the strongest, toughest materials on the Earth. Now engineers at Washington University in St. Louis have designed amyloid silk hybrid proteins and produced them in engineered bacteria. The resulting fibers are stronger and tougher than some natural spider silks.
Their research was published in the journal ACS Nano.
To be precise, the artificial silk -- dubbed "polymeric amyloid" fiber -- was not technically produced by researchers, but by bacteria that were genetically engineered in the lab of Fuzhong Zhang, a professor ...
2021-07-21
ITHACA, N.Y. - Small-scale. Short-lived. All digital. Out of public view. That's how a new form of collective worker resistance is unfolding in China's app-based food delivery economy, new Cornell University research finds.
Though highly fragmented and not always successful, "mini-strikes" by small groups of food couriers - conducted via WeChat - reflect a new form of leverage, suggest Chuxuan "Victoria" Liu and Eli Friedman, associate professor in the ILR School.
Food couriers are able to maintain complete physical invisibility, and each individual worker can 'strike' from anywhere, they write.
The scholars interviewed couriers, in-person and online, who delivered food for Ele.me, an Alibaba-owned company that controlled ...
2021-07-20
Tuesday, July 20, 2021, CLEVELAND: A Cleveland Clinic study demonstrates that adults with obesity lost significantly more weight when they had access to medications for chronic weight management in conjunction with their employer-based weight management program, compared to adults who did not have access to the medications. The study was published in JAMA Network Open.
Obesity is a complex disease that is caused by multiple factors, including genetic, environmental, and biological. A lifestyle intervention with a focus on nutrition and exercise is often not enough to treat obesity, which is a chronic disease that requires long-term therapy. The U.S. Food and Drug ...
2021-07-20
WASHINGTON - A peer-reviewed study by the Environmental Working Group recommends stringent health-based exposure standards for both children and adults for radiofrequency radiation emitted from wireless devices. EWG's children's guideline is the first of its kind and fills a gap left by federal regulators.
The study, published in the journal Environmental Health, relies on the methodology developed by the Environmental Protection Agency to assess human health risks arising from toxic chemical exposures. EWG scientists have applied the same methods to radiofrequency radiation from wireless devices, ...
2021-07-20
ROCHESTER, Minn. -- Mayo Clinic researchers have found that acute kidney injury associated with COVID-19 resembles sepsis-caused kidney injury, and the immune response triggered by the infection plays a pivotal role.
The findings, published in Mayo Clinic Proceedings, also suggest that mitochondrial dysfunction -- a loss of function in cellular energy production -- is commonly found in kidney injury related to COVID-19. More than one-third of hospitalized COVID-19 patients report acute kidney injury, and sudden kidney failure is a risk factor for in-hospital mortality, according to studies published last ...
2021-07-20
The remains of microscopic plankton blooms in near-shore ocean environments slowly sink to the seafloor, setting off processes that forever alter an important record of Earth's history, according to research from geoscientists, including David Fike at Washington University in St. Louis.
Fike is co-author of a new study published July 20 in Nature Communications.
"Our previous work identified the role that changing sedimentation rates had on local versus global controls on geochemical signatures that we use to reconstruct environmental change," said Fike, professor of earth and planetary sciences and director of environmental studies in Arts & Sciences.
"In this study, we investigated organic carbon loading, or how much ...
2021-07-20
Experts say these unexpected healthcare costs may discourage people from seeking recommended preventive care.
Despite a sharp reduction in out-of-pocket (OOP) costs for preventive care since the Affordable Care Act was enacted in 2010, patients are still receiving unexpected bills for preventive services that should be free, according to a new study co-authored by a Boston University School of Public Health (BUSPH) researcher.
Published in the journal Preventive Medicine, study found that total out-of-pocket costs billed for preventive services to Americans with employer-sponsored insurance (ESI) in 2018 ranged from $75.6 million to $219 million, with 1 in 4 patients who used preventive care incurring these charges.
"The ACA enabled great strides in making preventive care free to ...
2021-07-20
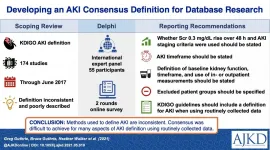
In an article published in the American Journal of Kidney Diseases (AJKD), researchers found that among 176 studies on acute kidney injury, the Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) definitions of kidney injury were inconsistently applied and 80% of studies did not define recovery of kidney function.
The KDIGO definition of AKI is used in both clinical practice and in research. This scoping review demonstrated that there is a wide variation of practice in how this definition is applied and also a lack of transparency about how researchers applied it. An international panel of experts in AKI was formed in an attempt to achieve consensus on how this definition should be applied. They participated in a Delphi process and while they were able to ...
2021-07-20
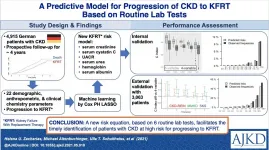
Researchers developed a new risk equation, based on six routinely available patient parameters, that yielded improved performance in estimating the risk of a chronic kidney disease (CKD) patient to progress to end-stage kidney disease (ESKD) requiring kidney replacement therapy (KRT).
A novel risk equation for the timely identification of chronic kidney disease (CKD) patients at risk for progressing to kidney failure requiring kidney replacement therapy was developed in 4,915 patients with CKD stage 1-5 with and without albuminuria, from the German Chronic Kidney Disease (GCKD) Study. It includes six laboratory tests: ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] A substance from Saussurea controversa will help bone tissue regeneration