Longitudinal serological and vaccination responses to SARS-COV-2 in dental professionals
2021-07-22
(Press-News.org) Alexandria, Va., USA - Iain Chapple, University of Birmingham, England, presented the oral session "Longitudinal Serological and Vaccination Responses to SARS-COV-2 in Dental Professionals" at the virtual 99th General Session & Exhibition of the International Association for Dental Research (IADR), held in conjunction with the 50th Annual Meeting of the American Association for Dental Research (AADR) and the 45th Annual Meeting of the Canadian Association for Dental Research (CADR), on July 21-24, 2021.
The COVID-19 pandemic significantly impacted dental professionals, who are thought to be at high occupational risk of infection. The aim of this study was to determine the magnitude, persistence and neutralizing capacity of serum antibody responses to the SARS-COV-2 spike glycoprotein at baseline (3-months following first wave), 3- and 6-months in an observational cohort of United Kingdom dental professionals, and the IgG threshold for protection from re-infection.
Participants provided baseline venous blood samples and the total antibody response (combined IgG, A and M), and individual isotype response against the SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein were measured. The neutralizing ability of antibodies was determined using a plaque reduction micro-neutralization assay.
Baseline seroprevalence was 16.3%. Seropositivity was retained in 73% of participants who returned 3-months post-baseline and 72% of participants who returned at 6-months, prior to their vaccination. Seropositivity arising following natural infection during the first wave, conferred a 74% risk reduction for re-infection during follow-up (9.6% seronegative, vs. 2.8% seropositive). The results show that natural infection with SARS-COV-2 leads to persistent, neutralizing and protective serological responses in over 70% of DPs 9-months post-infection (6-months post-baseline).
INFORMATION:
View this oral session in the IADR General Session Virtual Experience Platform.
View a PDF of this press release.
International Association for Dental Research
The International Association for Dental Research (IADR) is a nonprofit organization with over 10,000 individual members worldwide, with a mission to drive dental, oral and craniofacial research for health and well-being worldwide. To learn more, visit http://www.iadr.org.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-07-22
An international team of scientists has reported strong indications of freshened groundwater offshore the coastline between Valletta and Marsascala, in the south-east of Malta.
This discovery is based on an oceanographic expedition carried out in 2018.
Seismic reflection profiles acquired during this expedition were used to generate a geological model of the seafloor offshore the Maltese Islands, whereas electromagnetic surveying was carried out to identify resistivity anomalies, or high values of electromagnetic resistivity beneath the seafloor.
These observations indicate that freshened groundwater occurs as an isolated body hosted in Globigerina Limestone located 3 ...
2021-07-22
Alexandria, Va., USA - Jiachen Lin, Harvard School of Dental Medicine, Boston, Mass., USA., presented the poster "Burden of Oral Diseases in Emerging Countries: A Prediction Model" at the virtual 99th General Session & Exhibition of the International Association for Dental Research (IADR), held in conjunction with the 50th Annual Meeting of the American Association for Dental Research (AADR) and the 45th Annual Meeting of the Canadian Association for Dental Research (CADR), on July 21-24, 2021.
The goal of this study was to investigate the burden of oral diseases and predict trends by 2025 in the U.S. and emerging countries. Global Burden of Disease data from 1990-2017 was used to analyze the prevalence and disability-adjusted life years of oral diseases ...
2021-07-22
In a new publication from Opto-Electronic Advances; DOI 10.29026/oea.2021.200030 , Researchers led by Professor Liu Yan from Xidian University, China and Professor Gan Xuetao from Northwestern Polytechnical University, China consider generation and application of the high-Q resonance in all-dielectric metasurfaces.
Metamaterials are artificial composite electromagnetic structures consisting of subwavelength units, which can realize efficient and flexible control of the electromagnetic waves. Metamaterials are an emerging research area for optoelectronics, physics, chemistry and materials, due to their novel ...
2021-07-22
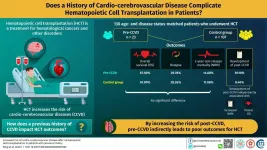
Hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT) is a recognized treatment option for certain blood and bone marrow cancers as well as some autoimmune and hereditary disorders. Performed to replace or modulate the body's malfunctioning hematopoietic system (which produces blood cells) or a compromised immune system following a medical condition or treatment, HCT can be autologous or allogenic. In autologous HCT, a patient's own stem cells are injected into the bloodstream, while in allogenic HCT donor stem cells are used.
Although a difficult procedure, over the years, the safety of HCT has been improved ...
2021-07-22
Irvine, Calif., July 21, 2021 -- It's not exactly X-ray vision, but it's close. In research published in the journal Optica, University of California, Irvine researchers describe a new type of camera technology that, when aimed at an object, can rapidly retrieve 3D images, displaying its chemical content down to the micrometer scale. The new tech promises to help companies inspect things like the insides of computer chips without having to pry them open -- an advancement the researchers say could accelerate the production time of such goods by more than a hundred times.
"This is a paper about a way to visualize things in 3D very fast, even at video rate," said Dmitry Fishman - director of laser spectroscopy labs in the UCI Department of ...
2021-07-22
New University of Otago research has been examining how alpine-based hedgehogs hibernate from a different perspective - their backs.
Dr Nick Foster from the Department of Zoology has been involved with the Te Manahuna Aoraki project and has been attaching small transmitting 'backpacks' onto hedgehogs in the Mackenzie Basin's alpine zones. The mammals are considered pests in New Zealand for the damage they cause to native insects and wildlife throughout the country.
The goal of this study, which has just been published in the New Zealand Journal of Ecology, was to find out whether hedgehogs, which can be found up to 2000 metres in summer, travel ...
2021-07-22
FINDINGS
Scientists from the UCLA Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center have identified a key protein, transcription factor TAF12, that plays a critical role in the formation of a preinitiation complex, which consists of over one hundred proteins that are necessary for the transcription of protein-coding genes. The team found by eliminating TAF12, the entire preinitiation complex is destroyed and the genome-wide transcription is downregulated drastically.
The findings could help pave the way for cancer therapies that target TAF12, potentially stopping transcription in cancer cells and helping decrease the growth of cancerous tumors. TAF12 had previously been shown by ...
2021-07-22
The future of Samoa's electricity system could go green, a University of Otago study has shown.
Pacific Island nations are particularly susceptible to climate change and face high costs and energy security issues from imported fossil fuels.
For these reasons many Pacific Island nations have developed ambitious 100 per cent renewable energy targets. However, they have not been subject to rigorous peer-reviewed studies to help develop these targets and pathways for achieving them in the same way as more developed countries.
To meet this need, Otago Energy Science and Technology Masters student Tupuivao Vaiaso mapped future scenarios for Samoa's electricity system by carefully balancing renewable supply and electricity demand.
The study, published in Renewable ...
2021-07-22
Leesburg, VA, July 22, 2021--According to ARRS' American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR), the standardized non-invasive clear cell likelihood score (ccLS)--derived from MRI--correlates with the growth rate of small renal masses (cT1a, END ...
2021-07-22
Scientists have completed the largest and most diverse genetic study of type 1 diabetes ever undertaken, identifying new drug targets to treat a condition that affects 1.3 million American adults.
Several potential drugs are already in the pipeline. Drugs targeting 12 genes identified in the diabetes study have been tested or are being tested in clinical trials for autoimmune diseases. That could accelerate the drugs' repurposing for treating or preventing type 1 diabetes, the researchers say.
"This work represents the largest, most ancesty-diverse study of type 1 diabetes ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Longitudinal serological and vaccination responses to SARS-COV-2 in dental professionals