Aging | AAV1.NT-3 gene therapy prevents age-related sarcopenia
2023-03-15
(Press-News.org)
“Considering the cost and quality of life to the individual, we believe our study has important implications for management of age-related sarcopenia.”
BUFFALO, NY- March 15, 2023 – A new research paper was published on the cover of Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 5, entitled, “AAV1.NT-3 gene therapy prevents age-related sarcopenia.”
Sarcopenia is progressive loss of muscle mass and strength occurring during normal aging with significant consequences on the quality of life for elderly. Neurotrophin 3 (NT-3) is an important autocrine factor supporting Schwann cell survival and differentiation and stimulating axon regeneration and myelination. NT-3 is involved in the maintenance of neuromuscular junction (NMJ) integrity, restoration of impaired radial growth of muscle fibers through activation of the Akt/mTOR pathway.
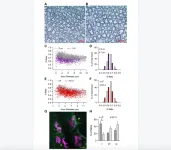
In this new study, researchers Burcak Ozes, Lingying Tong, Morgan Myers, Kyle Moss, Alicia Ridgley, and Zarife Sahenk from Nationwide Children’s Hospital and The Ohio State University used a triple muscle-specific creatine kinase (tMCK) promoter to restrict NT-3 expression to the skeletal muscle and self-complimentary adeno-associated virus serotype 1 (scAAV1) as vector to assess the therapeutic efficacy of AAV1.NT-3 in wild type-aged C57BL/6J mice, a model for natural aging and sarcopenia.
“Quantitative histopathologic parameters served to address age-related changes in muscle, peripheral nerve and NMJ.”
The treatment efficacy was assessed at 6 months post-injection using run to exhaustion and rotarod tests, in vivo muscle contractility assay, and histopathological studies of the peripheral nervous system, including NMJ connectivity and muscle. AAV1.NT-3 gene therapy in WT-aged C57BL/6 mice resulted in functional and in vivo muscle physiology improvements, supported by quantitative histology from muscle, peripheral nerves and NMJ.
Hindlimb and forelimb muscles in the untreated cohort showed the presence of a muscle- and sex-dependent remodeling and fiber size decrease with aging, which was normalized toward values obtained from 10 months old WT mice with treatment. The molecular studies assessing the NT-3 effect on the oxidative state of distal hindlimb muscles, accompanied by western blot analyses for mTORC1 activation were in accordance with the histological findings.
“When considering the burden of sarcopenia on the lifestyle of elderly, and on the healthcare system, we believe this preclinical study is providing strong support for AAV.NT-3 gene therapy in the successful management of sarcopenia, as a serious and plausible option in the future.”
DOI: https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.204577
Corresponding Author: Zarife Sahenk - zarife.sahenk@nationwidechildrens.org
Keywords: sarcopenia, gene therapy, aging, NT-3, muscle remodeling
Sign up for free Altmetric alerts about this article: https://aging.altmetric.com/details/email_updates?id=10.18632%2Faging.204577
About Aging-US:
Launched in 2009, Aging (Aging-US) publishes papers of general interest and biological significance in all fields of aging research and age-related diseases, including cancer—and now, with a special focus on COVID-19 vulnerability as an age-dependent syndrome. Topics in Aging go beyond traditional gerontology, including, but not limited to, cellular and molecular biology, human age-related diseases, pathology in model organisms, signal transduction pathways (e.g., p53, sirtuins, and PI-3K/AKT/mTOR, among others), and approaches to modulating these signaling pathways.
Please visit our website at www.Aging-US.com and connect with us:
SoundCloud
Facebook
Twitter
Instagram
YouTube
LabTube
LinkedIn
Reddit
Pinterest
For media inquiries, please contact media@impactjournals.com.
Aging (Aging-US) Journal Office
6666 E. Quaker Str., Suite 1B
Orchard Park, NY 14127
Phone: 1-800-922-0957, option 1
###
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-03-15
It’s easier than ever to view maps of any place you’d like to go — by car, that is. By foot is another matter. Most cities and towns in the U.S. do not have sidewalk maps, and pedestrians are usually left to fend for themselves: Can you walk from your hotel to the restaurants on the other side of the highway? Is there a shortcut from downtown to the sports arena? And how do you get to that bus stop, anyway?
Now MIT researchers, along with colleagues from multiple other universities, have developed an open-source tool that uses aerial imagery and image-recognition to create complete maps of sidewalks and crosswalks. The tool can help planners, policymakers, ...
2023-03-15
Researchers of the HSE Graduate School of Business trained a machine-learning (ML) model to infer users' subjective wellbeing from social media posts. Having processed 10 million tweets, the researchers compiled a rating of holidays celebrated in Russia based on their popularity. The New Year tops the list, but Russian-speaking users of Twitter are also happy to celebrate Defender of the Fatherland Day, International Women's Day, Victory Day and Halloween. The study findings have been published in PeerJ Computer Science.
As one of the most popular methods for ...
2023-03-15
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 4 P.M. ET, WEDNESDAY, MARCH 15, 2023
MINNEAPOLIS – There’s good news for those with multiple sclerosis (MS). A new study has found that female participants were no more likely to have a flare-up of the disease after receiving fertility treatments than they were before their treatments. The study is published in the March 15, 2023, online issue of Neurology® Neuroimmunology & Neuroinflammation, an official journal of the American Academy of Neurology. Earlier studies had shown conflicting results. The study also found a link between the use of MS medications and a lack of increase in relapses during fertility ...
2023-03-15
A University of Texas at Arlington civil engineering researcher received a one-year, $300,000 competitive grant from the Water Research Foundation to evaluate a trenchless process to renew sanitary sewer pipes in Soapstone Valley Park, a popular Washington, D.C., attraction.
Mohammad Najafi, associate professor in the Department of Civil Engineering, is leading the project.
Najafi said the project will use a trenchless cured-in-place-pipe (CIPP) method that relines the old sewer pipe with new plastic material. That material then is cured in place with hot water.
“We will ...
2023-03-15
PHILADELPHIA – The Pezcoller Foundation–American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) International Award for Extraordinary Achievement in Cancer Research will be presented to Tak W. Mak, PhD, Fellow of the AACR Academy, during the AACR Annual Meeting 2023, April 14-19 at the Orange County Convention Center in Orlando, Florida.
Mak is a senior scientist at the Princess Margaret Cancer Centre, University Health Network, as well as a university professor in the departments of medical biophysics and immunology at the Temerty Faculty of Medicine ...
2023-03-15
Sharareh “Sherri” Kermanshachi, a University of Texas at Arlington associate professor of civil engineering, has received the 40 Under 40 Award from Mass Transit magazine, which recognizes individuals who have shown a capacity for innovation and demonstrated leadership and a commitment to making an impact in transit.
“I am honored and humbled to receive this award and be named to the 40 Under 40 Mass Transit award list,” said Kermanshachi, who is also director of the Resilient Infrastructures and Sustainable Environment ...
2023-03-15
PHILADELPHIA – The American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) will honor Nobel Laureate Carolyn R. Bertozzi, PhD, with the 2023 AACR Award for Outstanding Achievement in Chemistry in Cancer Research during the AACR Annual Meeting 2023, April 14-19 in Orlando, Florida.
Bertozzi is the Anne T. and Robert M. Bass Professor of Chemistry in the School of Humanities and Sciences and a professor (by courtesy) of chemical and systems biology and of radiology at Stanford University, an investigator with the Howard Hughes Medical Institute, and the Baker Family Director of Sarafan ChEM-H. Bertozzi is being recognized for advancing basic ...
2023-03-15
PHILADELPHIA – A new approach that delivers a “one-two punch” to help T cells attack solid tumors is the focus of a preclinical study by researchers from the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. The findings, published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), showed that targeting two regulators that control gene functions related to inflammation led to at least 10 times greater T cell expansion in models, resulting in increased antitumor immune activity and durability.
CAR T cell therapy was pioneered at Penn Medicine by ...
2023-03-15
A comprehensive analysis of an archaeological site in Saudi Arabia sheds new light on mustatils—stone monuments from the Late Neolithic period thought to have been used for ritual purposes. Melissa Kennedy of the University of Western Australia, Perth, and colleagues, in conjunction with The Royal Commission for AlUla present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on March 15, 2023.
Built around 7,000 years ago, mustatils are rectangular, low-walled, stone structures that range from 20 to 600 meters in length. Researchers first discovered them in the 1970s, and more than 1,600 mustatils have now been discovered, primarily concentrated in northern ...
2023-03-15
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0282239
Article Title: Eight years of community structure monitoring through recreational citizen science at the “SS Thistlegorm” wreck (Red Sea)
Author Countries: Italy
Funding: STE project was funded by Project AWARE Foundation, ASTOI Association, Ministry of Tourism of the Arab Republic of Egypt, Settemari S.p.A Tour Operator, Scuba Nitrox Safety International, Viaggio nel Blu Diving Center. The funders had no role in study design, data collection ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Aging | AAV1.NT-3 gene therapy prevents age-related sarcopenia




