(Press-News.org) Osaka, Japan – The Haber–Bosch reaction helps feed the world by converting nitrogen into ammonia, a fertilizer precursor. However, its carbon footprint is huge: this one reaction is the source of nearly 2% of global carbon emissions. Now, in a study recently published in ACS Energy Letters, researchers from Osaka University have helped re-imagine this reaction to improve the sustainability of the chemical industry.
Replacing the Haber–Bosch reaction with a more sustainable alternative has been an active area of research for many years. These efforts have led to a globally well-established electrochemical reaction for ammonia synthesis. However, efforts at optimizing this reaction are hindered by insufficient understanding of how it proceeds. A general consensus is the need to minimize the water concentration in the reaction as much as possible. Revisiting this consensus—with the goal of providing chemical reaction details that will be useful for optimizing ammonia production—is the problem that the researchers sought to address.
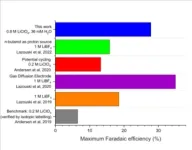
"There are various creative ways to improve the Faradaic efficiency by increasing the nitrogen partial pressure or solubility," explains Yu Katayama. "We have complemented these studies by showing that trace water can facilitate the reaction progress."
The researchers report a trace water concentration (ca. 36 millimolar) and a lithium perchlorate concentration (0.8 molar) that results in a Faradaic efficiency of ca. 28% at atmospheric pressure. This selectivity is the highest reported to date at ambient pressure, without using a gas diffusion electrode.
"X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy experiments indicate that the selectivity is attributable in part to the trace water facilitating lithium oxide incorporation into the solid electrolyte interphase," says Katayama. "Higher water concentrations might facilitate hydrogen evolution, an undesired side reaction.” “This surprising result can only be found with help and discussion with researchers from ICL. I believe the outcome emphasizes the importance of research collaboration.”
This work succeeded in improving the Faradaic efficiency of nitrogen reduction into ammonia at ambient pressure by straightforward means and uncovering the chemistry that leads to this result. Fine-tuning chemical process parameters dramatically improved the output of this reaction. Thus, there are many previously discounted electrochemical systems that might be worthwhile revisiting for future research efforts that investigate their detailed mechanisms. Researchers are now closer to optimizing fertilizer precursor synthesis in industry and minimizing the carbon footprint of its production.
###
The article, “Water Increases the Faradaic Selectivity of Li-Mediated Nitrogen Reduction,” was published in ACS Energy Letters at DOI: 10.1021/acsenergylett.2c02792
END
The devil is in the details: Re-imagining fertilizer precursor synthesis
Researchers from Osaka University have used trace water to improve the Faradaic efficiency of nitrogen into ammonia. This work will help optimize the sustainability of a reaction that contributes substantially to global carbon emissions
2023-03-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Unmasking the secret of broadly neutralising COVID-19 therapeutic antibodies
2023-03-22
The rapid evolution and emergence of new SARS-CoV-2 variants, such as the Omicron variant, renders it highly capable of evading the host immunity.
At the same time, vaccines based on original wild-type strain of SARS CoV-2 shows reduced protection against newer variants, particularly for the Omicron variant. This results in break-through infections among those vaccinated and highly infectious among non-vaccinated individuals.
Thus, it remains uncertain whether new emerging variants of the COVID-19 disease can escape the protective immune response ...
BetaLife and A*STAR Collaborate to develop next generation cell-based therapy for diabetes treatment
2023-03-22
Up-and-coming local biotech startup BetaLife Pte Ltd (“BetaLife”) is collaborating with the Agency for Science, Technology and Research (A*STAR) to accelerate the development of next generation cell-based therapy for diabetes. BetaLife, a stem cell therapy company focused on developing regenerative medicine for diabetes, has acquired the rights to human induced Pluripotent Stem Cell (iPSC) technology from A*STAR. This technology enables the generation of iPSCs, which are cells that have similar properties to embryonic ...
Endangered vulture returns to Bulgaria after being extinct for 36 years
2023-03-22
The Cinereous Vulture (Aegypius monachus) - also known as Black Vulture, Monk Vulture or Eurasian Black Vulture - is the largest bird of prey in Europe.
Globally classified as Near Threatened, its populations in southern Europe, once abundant, have been experiencing a dramatic decline since the late 1800s. So dramatic, in fact, that by the mid-1900s, these birds had already been nowhere to be seen throughout most of their distributional range across the Old Continent. In Bulgaria, the species has been considered locally extinct since 1985.
Thanks to the re-introduction initiative that was started in 2015 by three Bulgarian non-governmental organisations: ...
Nine in 10 women enter pregnancy with at least one indicator that risks baby’s health
2023-03-22
Nine in ten women in England enter pregnancy with at least one indicator that may increase health risks to them and their baby, according to new research.
Common indicators were women not quitting smoking, failing to take folic acid before pregnancy or having a previous pregnancy loss.
Researchers from the NIHR Southampton Biomedical Research Centre, hosted by University Hospital Southampton and University of Southampton, analysed data from over 650,000 mothers.
They created a first national picture of women’s health before ...
CABBI/GLBRC team explores leaf microbiome in perennial bioenergy crops
2023-03-21
"Have you ever wondered about life on a leaf?"
Great Lakes Bioenergy Research Center (GLBRC) researcher Ashley Shade asks a simple question, but it’s one well worth investigation. The aboveground part of plants where microbes reside, or the phyllosphere, represents the largest environmental surface area on the plant. Much of this area is grown as cultivated agriculture, and understanding the interactions between plants and the microorganisms that live on their surfaces may help us develop agricultural management practices that can increase crop productivity and resilience. In their newly published study, Department ...
Turn off porch light to aid caterpillars — and safeguard backyard ecosystems
2023-03-21
ITHACA, N.Y. – Moderate levels of artificial light at night – like the fixture illuminating your backyard – bring more caterpillar predators and reduce the chance that these lepidoptera larvae grow up to become moths and serve as food for larger prey.
This ecological impact was demonstrated in a new Cornell University study published in the Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences.
The scientists placed more than 550 lifelike caterpillar replicas made of soft clay in a forest, setting to ascertain how the mockups were attacked and hunted by predators compared to a control group.
“We measured predation ...
Anne Kornahrens, Hertz Foundation Director of Community, selected as delegate to International Younger Chemists Network Assembly
2023-03-21
The Fannie and John Hertz Foundation is proud to announce that Anne Kornahrens, Director of Community, has been selected as a 2023 U.S. delegate to the International Younger Chemists Network (IYCN) Assembly.
Kornahrens will attend the 52nd International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) General Assembly and World Chemistry Congress, to be held in The Hague, Netherlands, August 18–25, 2023.
The IUPAC Young Observer Program strives to introduce the work of IUPAC to a new generation of distinguished researchers and to provide them with an opportunity to address international science policy issues. IYCN, an affiliated ...
Novel drug makes mice skinny even on sugary, fatty diet
2023-03-21
SAN ANTONIO (March 21, 2023) — Researchers from The University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio (UT Health San Antonio) have developed a small-molecule drug that prevents weight gain and adverse liver changes in mice fed a high-sugar, high-fat Western diet throughout life.
“When we give this drug to the mice for a short time, they start losing weight. They all become slim,” said Madesh Muniswamy, PhD, professor of medicine in the health science center’s Joe R. and Teresa Lozano Long School of Medicine.
Findings by the collaborators, also from the University of Pennsylvania and Cornell University, were published Feb. 27 in the high-impact journal Cell ...
Department of Energy announces $150 million for research on the science foundations for Energy Earthshots
2023-03-21
WASHINGTON, D.C. - Today, the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) announced $150 million for research into the crosscutting foundational science for multiple Energy Earthshots. This funding, provided by the Office of Science, will support fundamental research to accelerate breakthroughs in support of the Energy Earthshots Initiative.
“Our Energy Earthshot solutions start with science,” said Asmeret Asefaw Berhe, DOE’s Director of the Office of Science. “The Office of Science is working to find those solutions by supporting research that will target the remaining and emerging scientific challenges underlaying ...
Turn up your favorite song to improve medication efficacy
2023-03-21
EAST LANSING, Mich. – While listening to a favorite song is a known mood booster, researchers at Michigan State University have discovered that music-listening interventions also can make medicines more effective.
“Music-listening interventions are like over-the-counter medications,” said Jason Kiernan, an assistant professor in the College of Nursing. “You don’t need a doctor to prescribe them.”
While previous research studies have used music-listening interventions as a tool to treat pain and anxiety, Kiernan took a novel approach by studying the effects of music-listening interventions ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal reports faster robot-assisted brain angiography
New study clarifies how temperature shapes sex development in leopard gecko
[Press-News.org] The devil is in the details: Re-imagining fertilizer precursor synthesisResearchers from Osaka University have used trace water to improve the Faradaic efficiency of nitrogen into ammonia. This work will help optimize the sustainability of a reaction that contributes substantially to global carbon emissions