Emerging treatment for children with long COVID and recurrent fever
2023-04-25
(Press-News.org) Researchers at National Jewish Health found that a subset of children suffering recurring fevers as a result of long COVID-19, benefited from a daily medication treatment commonly used for gout and periodic fever syndrome. Using the drug Colchicine, researchers saw rapid improvement not only in their fevers but also with other long COVID symptoms such as brain fog, fatigue, and achiness. The case study was just published in Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, (JACI: In Practice).
Long COVID is defined as persistent symptoms lasting greater than twelve weeks after the initial illness. A previous analysis of pediatric patients observed 25% of patients experiencing long COVID symptoms. Symptoms include fatigue, headache, dizziness, dyspnea, chest pain, reduced appetite, concentration difficulties, memory issues, mental exhaustion, physical exhaustion and sleep issues. In addition to these common symptoms, recurrent fevers are reported in approximately 2% of pediatric patients with long COVID.
For this case study, researchers evaluated two adolescent patients suffering long COVID symptoms, including recurring fever. They found through genetic testing that both individuals had a pathogenic heterozygous mutation in the innate immunity regulator pyrin: MEFV gene. Mutations in MEFV have been identified with periodic fever syndromes, and Colchicine therapy has shown previously effective in those suffering from the condition.
“So much about the cause and treatment for symptoms from long COVID remains unknown. This case report is helpful in identifying a subset of pediatric long COVID patients who respond well to a safe and well-described treatment,” said Nathan Rabinovitch, MD, MPH, director of the pediatric care unit at National Jewish Health and senior author of the study. “Children with persistent recurrent fevers after COVID-19 infection should be tested for this genetic variant.”
Recurrent fevers are seen in pediatric diseases such as familial Mediterranean fever and periodic fever with aphthous stomatitis, pharyngitis and adenitis. Both diseases are associated with changes in a gene that controls a fever-regulating protein called pyrin.
“Once we saw the gene mutation in both children, Colchicine therapy was initiated for both patients and resulted in near immediate resolution of fevers and improvement in other symptoms,” said Dr. Rabinovitch.
National Jewish Health is the leading respiratory hospital in the nation. Founded 124 years ago as a nonprofit hospital, National Jewish Health today is the only facility in the world dedicated exclusively to groundbreaking medical research and treatment of patients with respiratory, cardiac, immune and related disorders. Patients and families come to National Jewish Health from around the world to receive cutting-edge, comprehensive, coordinated care. To learn more, visit njhealth.org or the media resources page.
###
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-04-25
East Hanover, NJ – April 25, 2023 – New data shows that Hispanics with disabilities in the United States rebounded to historic levels in the labor force following the first 12-month period of the COVID-19 pandemic. While the disparity between their non-Hispanic white counterparts remains, their recovery has narrowed this gap and surpassed that of their black/African American counterparts, according to experts speaking during last Friday’s nTIDE Deeper Dive Lunch & Learn Webinar. To further improve employment opportunities ...
2023-04-25
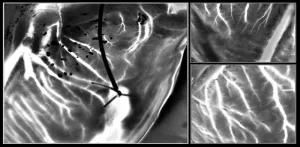
In the majority of cases, graft failure after heart transplantation is attributable to abnormalities like severe coronary artery disease. As donors with extended criteria like advanced age and pre-existing heart conditions become eligible for heart transplantation, careful screening for congenital abnormalities has become crucial. Invasive coronary angiography is an essential screening tool that can detect coronary artery disease (CAD), a condition characterized by cholesterol deposits in the heart's arteries. However, logistical challenges limit utility so it’s used for fewer than a third of donors who are at risk of developing CAD.
To overcome this limitation, a new heart ...
2023-04-25
-- JOINT PRESS RELEASE OF FORSCHUNGSZENTRUM JÜLICH AND JOHANNES GUTENBERG UNIVERSITY MAINZ --
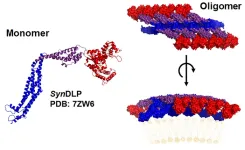
SynDLP could be a bacterial ancestor of eukaryotic membrane proteins
The cells of living organisms are equipped with proteins that are involved in the shaping and remodeling of cellular membranes, thereby performing important tasks. The cell membrane encloses the cell interior, but is constantly remodeled, for example, due to membrane budding, invagination, or fusion processes. This also involves various proteins that were long assumed to be present exclusively or predominantly in higher organisms. ...
2023-04-25
If they exist, intermediate-mass black holes likely devour wayward stars like a messy toddler — taking a few bites and then flinging the remains across the galaxy — a new Northwestern University-led study has found.
In new 3D computer simulations, astrophysicists modeled black holes of varying masses and then hurled stars (about the size of our sun) past them to see what might happen.
When a star approaches an intermediate-mass black hole, it initially gets caught in the black hole’s orbit, the researchers discovered. After that, the black hole begins its lengthy and violent meal. Every time the star makes a lap, the black hole takes a bite — ...
2023-04-25
Dungeness crab fishermen are at high risk for on-the-job injury, but having a metal bar to bang crab pots against as they harvest can help them prevent injury, an Oregon State University study found.
The study sought to determine whether the fishermen-designed “banger bar” actually improves worker safety aboard crab vessels. The metal bar is installed atop the crab-sorting table and makes it easier for fishermen to empty the crab pots they haul up from the ocean floor, but there is no industry standard on whether crabbers install one or how they ...
2023-04-25
1. Introduction
While the pathophysiology of Parkinson’s disease (PD) is not fully understood, it has been traditionally linked to a reduction in the dopamine available to brain regions involved in motor control (Alexander, 2004, Brooks, 2010, Fahn, 2008, Meder et al., 2019, Obeso et al., 2017, Poewe et al., 2017). It is important to note that much of what is known about the neural bases of motor deficits in PD is based on task-based functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) studies showing abnormal motor-related blood oxygen ...
2023-04-25
Lutz Grossmann is on a scientific mission to create tasty, animal-free protein that has a low carbon footprint and is produced without relying on agricultural land – a usual and progressively stressed source of the global food supply.
“The increasing global population and a changing climate increase the pressure on our food and protein supply coming from these natural habitats,” says Grossmann, an assistant professor of food science at the University of Massachusetts Amherst.
“By 2050, we need ...
2023-04-25
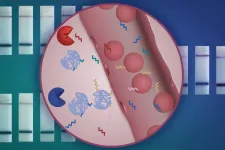
CAMBRIDGE, MA — MIT engineers have designed a new nanoparticle sensor that could enable early diagnosis of cancer with a simple urine test. The sensors, which can detect many different cancerous proteins, could also be used to distinguish the type of a tumor or how it is responding to treatment.
The nanoparticles are designed so that when they encounter a tumor, they shed short sequences of DNA that are excreted in the urine. Analyzing these DNA “barcodes” can reveal distinguishing features of a particular patient’s tumor. The researchers designed their test so that it can be performed using a strip of paper, ...
2023-04-25
99% of the world's population breathes air that exceeds the limits recommended by the World Health Organization (WHO). This scenario is exacerbated in urban areas where more than 50% of the world's population is concentrated. To mitigate the problem of air pollution, considered by the WHO to be the main environmental risk factor for health worldwide, it is crucial to have more reliable and accurate data on the concentration of air pollutants in our cities, especially nitrogen dioxide (NO2) because of its harmful effects on ...
2023-04-25
Humans and horses have enjoyed a strong working relationship for nearly 10,000 years — a partnership that transformed how food was produced, people were transported and even how wars were fought and won. Today, we look to horses for companionship, recreation and as teammates in competitive activities like racing, dressage and showing.
Can these age-old interactions between people and their horses teach us something about building robots designed to improve our lives? Researchers with the University of Florida say yes.
“There are no fundamental guiding principles ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Emerging treatment for children with long COVID and recurrent fever