(Press-News.org) The American Society of Plant Biologists (ASPB) is pleased to announce the recipients of its 2023 awards, which honor distinction in service, outreach, education, and research.
ASPB Innovation Prize for Agricultural Technology
Renata Bolognesi, Stanislaw Flasinski, Sergey Ivashuta, Daniel Kendrick, Curtis Scherder, Gerrit Segers
Bayer, Chesterfield, Missouri
Charles Albert Shull Award
José Dinneny
Stanford University, Stanford, California
Charles Reid Barnes Life Membership Award
John Browse
Washington State University, Pullman
Natasha Raikhel
University of California, Riverside
Early Career Award
Moisés Expósito-Alonso
Carnegie Institute of Science, Stanford University
Enid MacRobbie Corresponding Membership Nominees
Corresponding Member status is conferred by election on the Society’s annual ballot. This honor, initially given in 1932, provides life membership to distinguished plant biologists outside the United States. The following individuals have been nominated this year:
Avraham Levy
Weizmann Institute of Science, Israel
Wataru Sakamoto
Okayama University, Japan
Eric E. Conn Young Investigator Award
Kadeem Gilbert
Michigan State University
Excellence in Education Award
Bonnie Bartel
Rice University, Houston, Texas
Fellow of ASPB Award
Magdalena Bezanilla
Dartmouth College, Hanover, New Hampshire
Siobhan Brady
University of California, Davis
Z. Jeffrey Chen
University of Texas, Austin
Natalia Dudareva
Purdue University, West Lafayette, Indiana
Jonathan Monroe
James Madison University, Harrisonburg, Virginia
Wayne Parrott
University of Georgia, Athens
Martin Gibbs Medal
Xuemei Chen
University of California, Riverside
Stephen Hales Prize
Keiko Torii
The University of Texas at Austin
# # #
ASPB is a professional scientific society, headquartered in Rockville, MD, that is devoted to the advancement of the plant sciences worldwide. With a membership of some 3,000 plant scientists from throughout the United States and around the world, the Society publishes two of the most widely cited plant science journals, The Plant Cell and Plant Physiology, and co-publishes the Open Access journal Plant Direct. ASPB also hosts the annual Plant Biology conference; supports plant science outreach, engagement, and advocacy; and powers the Plantae digital ecosystem for plant scientists. For more information about ASPB, please visit https://aspb.org/. Also follow ASPB on Facebook at facebook.com/myASPB, on Twitter @ASPB, and on LinkedIn at https://www.linkedin.com/company/98656.
END
The rate of eating disorder diagnoses among girls aged 13–16-years-old in the UK during the first two years of the COVID-19 pandemic (from March 2020–March 2022) was 42% higher than the expected rate based on previous trends, suggests a study published in The Lancet Child & Adolescent Health journal. The rate of self-harm diagnoses in the same cohort was 38% higher than the expected rate for the two-year period.
As the largest and most targeted nationwide study in the adolescent population, and the first to cover two years of the pandemic, these findings are the best available evidence on eating disorder and self-harm diagnoses among young ...
Introducing widespread screening of newborns for a deadly disease called severe combined immunodeficiency, or SCID, followed by early treatment boosted the five-year survival rate of children with the disorder from 73% before the advent of screening to 87% since, researchers report. Among children whose disease was suspected because of newborn screening rather than illness or family history, 92.5% survived five years or more after treatment. These findings demonstrate for the first time that newborn screening facilitated the early identification of infants with SCID, leading to prompt ...
The sustainability and scalability of limited duration interventions in low- and middle-income countries remain unclear. A study published in The Lancet Global Health aimed to investigate the sustainability in reduction of blood pressure (BP) through a 12-month lifestyle intervention by community health workers (CHWs) to reduce BP in Nepal four years after the intervention ceased.
During the 12-month intervention, female community health volunteers (FCHVs) visited participants in the intervention groups and provided lifestyle counselling and BP measurement every 4 months.
At the end of the 12-month intervention, ...
Exposure to air pollution meant an average of around four extra days in hospital for Covid-19 patients, further increasing the burden on health care systems, according to a study published today (Wednesday) in the European Respiratory Journal [1].
The researchers say the effect of pollution on patients’ time in hospital was equivalent to being a decade older. Conversely, the effect of reducing exposure to pollution was 40 to 80% as effective in reducing patients’ time in hospital as some of the best available treatments.
In ...
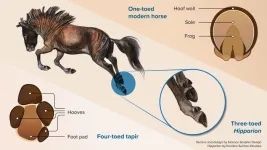
The distant ancestors of modern horses had hooved toes instead of a single hoof, which vanished over time, according to researchers.
The animals, such as the Eocene Hyracotherium, had feet like those of a modern tapir: four toes in front and three behind, each individually hooved with an underlying foot pad.
In contrast, modern equids such as horses, asses, and zebras, have only a single toe, the left over original third toe on each foot, encased in a thick-walled keratinous hoof, with an underlying triangular frog on the sole that acts as a shock absorber.
An international ...
Critical insights into why airborne viruses lose their infectivity have been uncovered by scientists at the University of Bristol. The findings, published in the Journal of the Royal Society Interface today [21 June], reveal how cleaner air kills the virus significantly quicker and why opening a window may be more important than originally thought. The research could shape future mitigation strategies for new viruses.
In the first study to measure differences in airborne stability of different variants of SARS-CoV-2 in inhalable particles, ...
Pupils in the UK are not learning about potentially life-changing issues such as endometriosis, infertility, and miscarriage, according to a new study of curricula in science and in relationships and sex education.
Researchers from University College London (UCL) looked at what schools are expected to teach 14–18-year-olds across the UK, using curriculum requirements and specifications set by exam boards. Findings, published today in the peer-reviewed journal Human Fertility, demonstrate significant gaps and variations in what pupils are taught ...
Hidden beneath the waves of coastal waters lies an important member of the marine food chain – seagrasses. These marine meadows are in many ways the unsung heroes of the ocean, benefiting humans and the planet by producing oxygen, removing carbon dioxide from the air, and providing food and habitat for marine life. But these submerged savannahs may be in danger of disappearing, according to a new Stanford study that modeled the distribution of seagrass species around the world at two different timepoints in the future.
Climate change is expected to hit marine species hard, in part because oceans absorb an estimated ...
Growing up, Brian Kisida always enjoyed going to school. He especially enjoyed the broad spectrum of subjects he was able to explore, including the arts. Now, as an assistant professor in the Truman School of Government and Public Affairs at the University of Missouri, he is researching the relationship between arts education and student success.
Over the years, Kisida, an expert on education policy, has seen the culture of education shift dramatically.
“I saw the impact that the test obsessed culture had on schooling, students’ mental health and enjoyment of learning,” Kisida said. “I wanted to know why we were seeing these changes that seem to not be in line ...
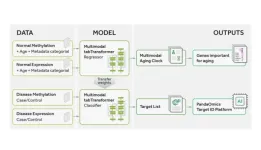
“The development of Precious1GPT [...] has demonstrated the potential of our approach in deciphering the molecular mechanisms of aging.”
BUFFALO, NY- June 20, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 11, entitled, “Precious1GPT: multimodal transformer-based transfer learning for aging clock development and feature importance analysis for aging and age-related disease target discovery.”
Aging is a complex ...