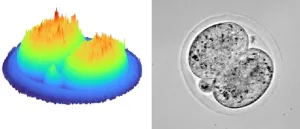
(Press-News.org) In a world-first, 3D holographic images of an embryo have been developed as part of a collaborative research project between the University of Adelaide and University of St Andrews. The images are created using miniscule amounts of light in a fraction of a second.
The team, led by Dr Kylie Dunning, Hospital Research Foundation fellow from the University of Adelaide’s Robinson Research Institute, and Professor Kishan Dholakia from the University of Adelaide and the University of St Andrews, developed an approach to create 3D holographic images of the pre-clinical model of an embryo at various stages of development.
“For couples wishing to conceive, the quality, or developmental potential, of an embryo is critical as it dictates the success of their pregnancy and ultimately, the birth of their child,” said Dr Dunning.
“In vitro fertilisation (IVF) clinics routinely assess embryo quality by visual inspection to check if an embryo is developing in a time-appropriate manner or by an invasive biopsy to determine DNA content of the biopsied sample.
“However, these approaches have failed to improve the success rate of IVF which has remained stagnant for more than a decade.”
A non-invasive approach without biopsy to help pick the most appropriate embryo is a highly beneficial tool for the 21st century embryologist: light can fulfil this need.
3D holographic images are a non-invasive approach which provides insights into the embryo by identifying detailed features. This may augment conventional visual assessment for embryo quality in an IVF clinic, allowing an embryologist to make an informed decision on the selection of best quality embryos.
“Optical technologies hold immense promise to unravel the metabolism and health of the embryo. This gentle, non-invasive approach could lead to improved IVF success,” said Dr Dunning.
Data from 2020 show that the success rates of IVF range from a live birth rate of 38.9 per cent per embryo transfer for patients under 34 years, to a live birth rate of 5.6 per cent per embryo transfer for patients over 43 years. In 2018 it was estimated that eight million babies had been born through IVF since the world’s first in 1978.
“This technology uses miniscule amounts of light - less than that from your smartphone – to allow rapid visualisation of the embryo in a fraction of a second,” said Professor Dholakia.
“It’s a prime example of interdisciplinary success for our new Centre of Light for Life at the University of Adelaide, and of collaborative international work with my group at the University of St Andrews, Scotland.”
The team aims to have the technology, which is being developed through research using a preclinical model, available in five years.
This cutting-edge development would not have been possible without the support of funding from the UK and EU, and the Australian Research Council (ARC), National Health and Medical Research Council and the Hospital Research Foundation in Australia.
Primary authors on the study are George Dwapanyin, postdoctoral researcher at the University of St Andrews and Darren Chow, PhD candidate at the Robinson Research Institute, School of Biomedicine, University of Adelaide.
Postdoctoral researchers Tiffany Tan, Josephine Morizet and Nicolas Dubost were also co-authors on this research, which published its findings in the journal Biomedical Optics Express.
END
Holograms for life: Improving IVF success
2023-07-06
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Helping adolescents to feel competent and purposeful – not just happy – may improve grades
2023-07-06
Encouraging adolescents to feel capable and purposeful – rather than just happy – could improve their academic results as well as their mental health, according to new research which recommends changing how wellbeing is supported in schools.
The University of Cambridge study, involving over 600 teenagers from seven English schools, examined two separate aspects of their wellbeing: life satisfaction and ‘eudaimonia’. While life satisfaction roughly equates to how happy a person is, eudaimonia refers to how well that person feels they are functioning. It incorporates feelings of competence, motivation and self-esteem.
Researchers ...
Unlocking the mystery of long-lasting cancer treatment
2023-07-06
New insights explaining why some children have a longer remission than others after having cutting-edge CAR T-cell therapy for leukaemia have been revealed by researchers at UCL, Great Ormond Street Hospital, and the Wellcome Sanger Institute.
The collaborative research project, published today in Nature Medicine, combines expertise in novel immune therapy design and state-of-the-art computational analysis to identify a genetic signature of CAR T-cells that will be the most effective in the long term.
In recent years, CAR T-cells – genetically engineered ...
Astronomers identify the earliest strands of the cosmic web
2023-07-06
Using NASA's James Webb Space Telescope, a team of scientists led by University of Arizona astronomers has discovered a threadlike arrangement of 10 galaxies that existed just 830 million years after the Big Bang.
Lined up like pearls on an invisible string, the 3-million-light-year-long structure is anchored by a luminous quasar – a galaxy with an active, supermassive black hole at its core. The team believes the filament will eventually evolve into a massive cluster of galaxies, much like the well-known Coma Cluster in the "nearby" universe. The results are published in two papers in The Astrophysical Journal ...
Professor spreads the gospel of ‘good fire’ through eco-cultural lens
2023-07-06
LAWRENCE – A pyromaniac is someone unhealthily obsessed with the destructive power of fire. Melinda Adams instead is pulled toward the term pyromantic – a lover of “good fire” for the benefits it can bring to people, communities and the environment as a whole.
The Langston Hughes Assistant Professor in Indigenous Studies and Geography & Atmospheric Science at the University of Kansas, Adams extols the benefits of cultural or ceremonial fire in a new paper she has co-authored ...
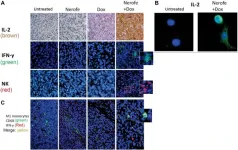
Transformation of immunosuppressive mtKRAS tumors into immunostimulatory tumors by Nerofe and Doxorubicin
2023-07-05
“[...] we demonstrated that the combination of Nerofe and DOX exerts a synergistic effect during mCRC treatment [...]”
BUFFALO, NY- July 5, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Oncotarget's Volume 14 on July 1, 2023, entitled, “Transformation of immunosuppressive mtKRAS tumors into immunostimulatory tumors by Nerofe and Doxorubicin.”
Members of the rat sarcoma viral oncogene (RAS) subfamily KRAS are frequently mutated oncogenes in human cancers and have been identified ...
Bar-Ilan University study reveals disparity in quality of life among COVID-19 survivors from different ethnic groups
2023-07-05
A new study conducted by researchers at Bar-Ilan University in Israel has shed light on the long-term impact of COVID-19 on the quality of life among different ethnic groups in the country. The study, part of a larger cohort project, highlights a significant discrepancy between Arabs and Druze, and Jews, with the two former groups experiencing a more pronounced decline in quality of life one year after infection.
In this cohort study, researchers regularly followed up with individuals who had been infected with the SARS-CoV-2 virus to assess various aspects of their health. The findings, published in the International ...
Fossils reveal how ancient birds molted their feathers— which could help explain why ancestors of modern birds survived when all the other dinosaurs died
2023-07-05
Every bird you’ve ever seen— every robin, every pigeon, every penguin at the zoo— is a living dinosaur. Birds are the only group of dinosaurs that survived the asteroid-induced mass extinction 66 million years ago. But not all the birds alive at the time made it. Why the ancestors of modern birds lived while so many of their relatives died has been a mystery that paleontologists have been trying to solve for decades. Two new studies point to one possible factor: the differences between how modern birds and their ancient cousins molt their feathers.
Feathers are one of the key traits that all birds share. They're made of a protein called keratin, the same material ...
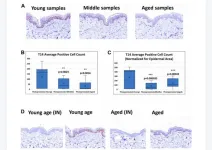
A novel peptide ‘T14’ reflects age and photo-aging in human skin
2023-07-05
“[...] the results suggest a possible novel approach [for] exploring skin disorders [...]”
BUFFALO, NY- July 5, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 12, entitled, “A novel peptide ‘T14’ reflects age and photo-aging in human skin.”
T14 is a 14mer peptide derived from the C-terminus of acetylcholinesterase (AChE). Once cleaved, it is independently bioactive of the parent molecule and enhances calcium influx in different cell types, in a range of scenarios: it binds to an allosteric site selectively ...
Tracking ships’ icy paths amidst climate change
2023-07-05
There has been much buzz about the warming planet’s melting Arctic region opening shipping routes and lengthening travel seasons in ocean passageways that ice once blocked. Expanded fishing, trade and tourism is envisioned.
Operative word: Envisioned.
Scientists at Michigan State University (MSU), University of Waterloo, and University of Alaska Fairbanks report in Climatic Change where vessels are traveling in the ice-covered waters of the Arctic between Alaska and Russia, and what those reports may mean for important wildlife and communities in the region.
“Even with climate change, sea ice is still a substantial barrier to Arctic vessel traffic,” said Kelly Kapsar, ...
Study shines light on why companies use a variety of dark money strategies
2023-07-05
AUSTIN, Texas — As public concerns mount over lack of transparency in political giving, a new study from researchers at The University of Texas at Austin is the first to illuminate how and why corporations choose to legally conceal their lobbying and campaign contributions.
U.S. companies are required to disclose the total amount they spend on political activity, but beyond that, the disclosure is incredibly vague, according to Tim Werner, associate professor of business, government and society at the McCombs ...