(Press-News.org) New drugs are often used not only for one disease (first approved indication) but also for other diseases (supplemental indications).
But a study published by The BMJ today finds that less than half of approved first indications for new drugs in the US and Europe between 2011 and 2020 add substantial therapeutic value over existing treatments and only around a third of supplemental approvals add substantial therapeutic value compared with first approvals.
The researchers argue that when first or supplemental indications do not offer added benefit over existing treatments, this information should be clearly communicated to patients and reflected in the price of the drugs.
Previous research on the added value of new drugs is unclear. So researchers set out to examine all new drugs approved for more than one indication in the US and Europe between 2011 and 2020 and assess the therapeutic value of supplemental indications compared with first indications.
They used publicly available data to identify 124 first and 335 supplemental indications approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and 88 first and 215 supplemental indications approved by the European Medicines Agency (EMA) between January 2011 and December 2020.
In the US, 48% of drugs had one supplemental indication, 20% had two, 14% had three, and 18% had four or more. In Europe, 48% of drugs had one supplemental indication, 23% had two, 13% had three, and 17% had four or more. Most (58%) of indications approved by the FDA and EMA were for treatment of cancer.
Therapeutic ratings from French and German health technology assessment (HTA) bodies were available for 107 (86%) first and 179 (53%) supplemental indications in the US and for 87 (99%) first and 184 (86%) supplemental indications in Europe.
Among FDA-approved indications with available ratings, 41% (44 of 107) had high therapeutic value ratings for first, compared with 34% (61 of 179) for supplemental indications. In Europe, 47% (41 of 87) of first and 36% (67 of 184) of supplemental indications had high therapeutic value ratings.
Among FDA approvals, when the sample was restricted to the first three approved indications, second indication approvals were 36% less likely to have a high value rating and third indication approvals were 45% less likely when compared to the first indication approval. Similar findings were observed for Europe.
These are observational findings and the researchers acknowledge that therapeutic value ratings were not available for all indications, particularly indications approved in the US but not in Europe. Furthermore, the methods and value assessment system can be influenced by country specific factors and assumptions.
However, they point out that they focused on the highest rating provided by one of the two HTA bodies and did sensitivity analyses with the value scores of each authority separately, which confirmed the initial results.
As such, they conclude: “Fewer than half of approved first indications in the US and Europe were rated as having high therapeutic value, and the proportion of approved supplemental indications rated as having high therapeutic value was substantially lower than for approved first indications."
"When indications do not offer added therapeutic benefit over other available treatments, that information should be clearly communicated to patients and reflected in the price of the drugs.”
The fact that new does not necessarily mean better needs to be clearly communicated to both patients and clinicians, agrees Beate Wieseler at the German Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care, in a linked editorial.
“The system’s current performance does not meet the expectations of patients and the public, clinicians, or policy makers,” she writes. “Having experienced the potential of a coordinated drug development effort during the covid-19 pandemic, we should seek to align current legislation on drug development more closely with defined public health goals.”
[Ends]
END
Fewer than half of new drugs add substantial therapeutic value over existing treatments
Patients need better treatments, not just more of the same, says expert
2023-07-06
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Lack of sleep lessens cognitive benefits of physical activity
2023-07-06
Lack of sleep lessens cognitive benefits of physical activity
Regular physical activity may protect against cognitive decline as we get older, but this protective effect may be diminished for people who are not getting enough sleep, according to a new study by UCL researchers.
The study, published in The Lancet Healthy Longevity, looked at cognitive function over 10 years in 8,958 people aged 50 and over in England. The research team investigated how different combinations of sleep and physical activity habits might affect people’s cognitive function over time.
They found that people who were more physically ...
Amsterdam UMC led eHealth app ensures 30% faster recovery after major abdominal operations
2023-07-06
Through the use of eHealth application ikHerstel, patients recover from major abdominal operations 30% faster than patients who do not use the app. That is the main conclusion of research led by Amsterdam UMC across eleven Dutch hospitals. The app aims to empower patients to feel more in control of their recovery process. The results were published today in Lancet Digital Health.
Patients are being discharged from the hospital quicker after treatment. Where patients used to receive care, information and support in the hospital for a number of days, they are now often ...
Holograms for life: Improving IVF success
2023-07-06
In a world-first, 3D holographic images of an embryo have been developed as part of a collaborative research project between the University of Adelaide and University of St Andrews. The images are created using miniscule amounts of light in a fraction of a second.
The team, led by Dr Kylie Dunning, Hospital Research Foundation fellow from the University of Adelaide’s Robinson Research Institute, and Professor Kishan Dholakia from the University of Adelaide and the University of St Andrews, developed an approach to create 3D holographic images of the pre-clinical model of an embryo at various stages ...
Helping adolescents to feel competent and purposeful – not just happy – may improve grades
2023-07-06
Encouraging adolescents to feel capable and purposeful – rather than just happy – could improve their academic results as well as their mental health, according to new research which recommends changing how wellbeing is supported in schools.
The University of Cambridge study, involving over 600 teenagers from seven English schools, examined two separate aspects of their wellbeing: life satisfaction and ‘eudaimonia’. While life satisfaction roughly equates to how happy a person is, eudaimonia refers to how well that person feels they are functioning. It incorporates feelings of competence, motivation and self-esteem.
Researchers ...
Unlocking the mystery of long-lasting cancer treatment
2023-07-06
New insights explaining why some children have a longer remission than others after having cutting-edge CAR T-cell therapy for leukaemia have been revealed by researchers at UCL, Great Ormond Street Hospital, and the Wellcome Sanger Institute.
The collaborative research project, published today in Nature Medicine, combines expertise in novel immune therapy design and state-of-the-art computational analysis to identify a genetic signature of CAR T-cells that will be the most effective in the long term.
In recent years, CAR T-cells – genetically engineered ...
Astronomers identify the earliest strands of the cosmic web
2023-07-06
Using NASA's James Webb Space Telescope, a team of scientists led by University of Arizona astronomers has discovered a threadlike arrangement of 10 galaxies that existed just 830 million years after the Big Bang.
Lined up like pearls on an invisible string, the 3-million-light-year-long structure is anchored by a luminous quasar – a galaxy with an active, supermassive black hole at its core. The team believes the filament will eventually evolve into a massive cluster of galaxies, much like the well-known Coma Cluster in the "nearby" universe. The results are published in two papers in The Astrophysical Journal ...
Professor spreads the gospel of ‘good fire’ through eco-cultural lens
2023-07-06
LAWRENCE – A pyromaniac is someone unhealthily obsessed with the destructive power of fire. Melinda Adams instead is pulled toward the term pyromantic – a lover of “good fire” for the benefits it can bring to people, communities and the environment as a whole.
The Langston Hughes Assistant Professor in Indigenous Studies and Geography & Atmospheric Science at the University of Kansas, Adams extols the benefits of cultural or ceremonial fire in a new paper she has co-authored ...
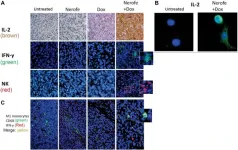
Transformation of immunosuppressive mtKRAS tumors into immunostimulatory tumors by Nerofe and Doxorubicin
2023-07-05
“[...] we demonstrated that the combination of Nerofe and DOX exerts a synergistic effect during mCRC treatment [...]”
BUFFALO, NY- July 5, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Oncotarget's Volume 14 on July 1, 2023, entitled, “Transformation of immunosuppressive mtKRAS tumors into immunostimulatory tumors by Nerofe and Doxorubicin.”
Members of the rat sarcoma viral oncogene (RAS) subfamily KRAS are frequently mutated oncogenes in human cancers and have been identified ...
Bar-Ilan University study reveals disparity in quality of life among COVID-19 survivors from different ethnic groups
2023-07-05
A new study conducted by researchers at Bar-Ilan University in Israel has shed light on the long-term impact of COVID-19 on the quality of life among different ethnic groups in the country. The study, part of a larger cohort project, highlights a significant discrepancy between Arabs and Druze, and Jews, with the two former groups experiencing a more pronounced decline in quality of life one year after infection.
In this cohort study, researchers regularly followed up with individuals who had been infected with the SARS-CoV-2 virus to assess various aspects of their health. The findings, published in the International ...
Fossils reveal how ancient birds molted their feathers— which could help explain why ancestors of modern birds survived when all the other dinosaurs died
2023-07-05
Every bird you’ve ever seen— every robin, every pigeon, every penguin at the zoo— is a living dinosaur. Birds are the only group of dinosaurs that survived the asteroid-induced mass extinction 66 million years ago. But not all the birds alive at the time made it. Why the ancestors of modern birds lived while so many of their relatives died has been a mystery that paleontologists have been trying to solve for decades. Two new studies point to one possible factor: the differences between how modern birds and their ancient cousins molt their feathers.
Feathers are one of the key traits that all birds share. They're made of a protein called keratin, the same material ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Increased risk of bullying in open-plan offices
Frequent scrolling affects perceptions of the work environment
Brain activity reveals how well we mentally size up others
Taiwanese and UK scientists identify FOXJ3 gene linked to drug-resistant focal epilepsy
Pregnancy complications impact women’s stress levels and cardiovascular risk long after delivery
Spring fatigue cannot be empirically proven
Do prostate cancer drugs interact with certain anticoagulants to increase bleeding and clotting risks?
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
[Press-News.org] Fewer than half of new drugs add substantial therapeutic value over existing treatmentsPatients need better treatments, not just more of the same, says expert