(Press-News.org) Amsterdam, Netherlands – 22 Aug 2023: Recognising and acting on heart attack symptoms is linked with faster life-saving treatment, according to research presented at ESC Congress 2023.1
“Patients with a repeat heart attack were more likely to know the symptoms than first-time sufferers, but recognition was low in both groups,” said study author Dr. Kyehwan Kim of Gyeongsang National University Hospital, Jinju, Republic of Korea. “Most patients could identify chest pain but less than one-third knew the other symptoms.”
Heart attack symptoms can include chest pain, radiating pain to the arms, jaw and neck, dizziness, cold sweats, shortness of breath, feeling sick and loss of consciousness. It is crucial to call an ambulance immediately and get fast treatment to survive and make a full recovery. This study investigated the association between symptom recognition, time to treatment and clinical outcomes.
The study used data from KRAMI-RCC, a registry of myocardial infarction patients in the Republic of Korea.2 Trained nurses asked survivors if they recognised the following myocardial infarction symptoms: 1) chest pain, 2) shortness of breath, 3) cold sweats, 4) radiating pain to the jaw, shoulder or arm 5) dizziness/vertigo/lightheadedness/loss of consciousness and 6) stomach ache. Patients were classified as “recognised symptoms” if they could identify at least one symptom; otherwise they were classified as “did not recognise symptoms”. The researchers compared patient characteristics, time to life-saving treatment and survival between the two groups after adjusting for age 70 years and above, sex, education, living with a spouse, previous registration in KRAMI RCC, cancer, dyslipidaemia, cardiogenic shock and presence of acute decompensated heart failure.
The study included 11,894 myocardial infarction patients, of whom 10,623 (90.4%) had a first-time event and 1,136 (9.6%) had a repeat event. Of the 1,136 patients with a repeat event, 118 were excluded due to missing data, failure to answer the survey about symptoms, or presentation with cardiac arrest, leaving 1,018 patients for the analyses. Overall, just over half (52.3%) of patients recognised the symptoms of myocardial infarction. The majority of patients (92.9%) could identify chest pain as a symptom of myocardial infarction, while approximately one-third recognised shortness of breath (32.1%) and cold sweats (31.4%). Just over one in four recognised radiating pain (27.4%), while only 7.5% identified /vertigo/lightheadedness/loss of consciousness and 1.3% recognised stomach ache.
Regarding patient characteristics, men were more likely to recognise symptoms than women (79.3% of men vs. 69.0% of women identified symptoms). Other traits associated with symptom recognition were younger age, higher education level and living with a spouse.
The researchers also compared time to treatment and outcomes between the two groups. Some 57.4% of patients who correctly identified the symptoms of myocardial infarction received treatment to open the arteries and restore blood flow within two hours, compared to just 47.2% of those who did not recognise the symptoms. Patients who recognised symptoms had a lower in-hospital mortality rate (1.5%) compared with those who could not identify the symptoms of a heart attack (6.7%). The group who could not recognise symptoms more often had cardiogenic shock and heart failure.
Among patients with recurrent myocardial infarction, the symptom recognition rate was 57.5% for those previously enrolled in KRAMI-RCC and 43.2% for those not previously enrolled. Just 14.4% of patients with a first-time myocardial infarction could identify the symptoms.
Dr. Kim said: “The findings indicate that education is needed for the general public and heart attack survivors on the symptoms that should trigger calling an ambulance. In our study, patients who knew the symptoms of a heart attack were more likely to receive treatment quickly and subsequently survive. Women, older patients, those with a low level of education, and people living alone may particularly benefit from learning the symptoms to look out for.”
ENDS
Notes to editors
Authors: ESC Press Office
Mobile: +336 61 40 18 84
Email: press@escardio.org
The hashtag for ESC Congress 2023 is #ESCCongress.
Follow us on Twitter @ESCardioNews
Funding: This research was funded by the Ministry of Health and Welfare of Korea, grant number
B0070402000190.
Disclosures: None.
References and notes
1The abstract “Effect of symptoms recognition in patients with recurrent acute myocardial infarction: from KRAMI-RCC” will be presented during the session Risk stratification in acute coronary syndromes (1) which takes place on Friday 25 August from 13:15 to 14:00 CEST at Station 5.
2KRAMI-RCC: Korean Registry of Acute Myocardial Infarction for Regional Cardiocerebrovascular Centres.
About ESC Congress 2023
It is the world’s largest gathering of cardiovascular professionals, disseminating ground-breaking science both onsite in Amsterdam and online – from 25 to 28 August. Explore the scientific programme. More information is available from the ESC Press Office at press@escardio.org.
About the European Society of Cardiology
The European Society of Cardiology brings together health care professionals from more than 150 countries, working to advance cardiovascular medicine and help people lead longer, healthier lives.
END
Heart attack victims who recognise symptoms are less likely to die in hospital
2023-08-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Keep fit to avoid heart rhythm disorder and stroke
2023-08-22
Amsterdam, Netherlands – 22 Aug 2023: A study in more than 15,000 people has found that physical fitness is linked with a lower likelihood of developing atrial fibrillation and stroke. The research is presented at ESC Congress 2023.1
Atrial fibrillation is the most common heart rhythm disorder, affecting more than 40 million people worldwide.2 It is estimated that one in three Europeans will develop atrial fibrillation in their lifetime. Patients with the condition have a five-fold higher risk of stroke ...
City-living may make male song sparrows more doting ‘super’ fathers
2023-08-22
When animals settle in new environments, or when their natural habitats are rapidly changed by human influence, their behaviors change. One such behavioral change that has been observed in several bird species that settled in cities is increased aggression, born out of the need to defend territories.
City-living sparrows have, due to lower species density, fewer encounters with their kin than in the countryside. Yet, urban song sparrows have been shown to be consistently more aggressive in defending their territories. Now, a team of researchers in the US has investigated the effects of urbanization and the associated ...
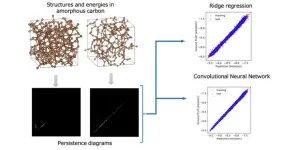
Topology's role in decoding energy of amorphous systems
2023-08-22
Osaka, Japan – How is a donut similar to a coffee cup? This question often serves as an illustrative example to explain the concept of topology. Topology is a field of mathematics that examines the properties of objects that remain consistent even when they are stretched or deformed—provided they are not torn or stitched together. For instance, both a donut and a coffee cup have a single hole. This means, theoretically, if either were pliable enough, it could be reshaped into the other. This ...
Small urban greening projects can dramatically increase number of insect species in cities
2023-08-22
By increasing the diversity of indigenous plants in urban areas, researchers from the University of Melbourne have seen a seven times increase in the number of insect species in just three years, confirming the ecological benefits of urban greening projects. The findings are published in the British Ecological Society journal, Ecological Solutions and Evidence.
The study, conducted in a small greenspace in the City of Melbourne, found that an increase in the diversity and complexity of plant communities leads to a large increase in insect biodiversity, a greater ...
Which is easier to remember, symbols or words?
2023-08-22
Everyday symbols like &?!#@$ are highly memorable, according to new research.
The new study led by the University of Waterloo aimed to investigate how well symbols are remembered compared to words with the same meaning.
“Our work is ground-breaking as it highlights how humans remember graphic symbols and logos,” said Myra Fernandes, co-author and professor of Cognitive Neuroscience at Waterloo. “Symbols are particularly useful as they can be used as logos in advertising, as well as offer a faster ...
Study finds no effect of LEED certification on federal buildings’ energy efficiency
2023-08-22
In 2010, the U.S. government announced a multi-billion-dollar plan to improve the energy efficiency of its buildings, including a focus on LEED certification. Used worldwide, LEED—Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design—is a system that rates buildings on energy efficiency. A new study examined the effects of LEED certification on energy efficiency in federal buildings. The study found no effect on average energy consumption, primarily because many other factors come into play when rating energy.
The study, by researchers ...
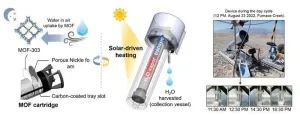
Water harvesting in Death Valley: Conquering the arid wilderness
2023-08-22
Korea is regarded as a “water-stressed nation.” Although the country receives an annual precipitation of approximately 1,300mm, it is characterized by concentrated periods and specific regions, thereby giving rise to challenges stemming from water scarcity. The lack of drinking water extends beyond mere inconvenience, posing life-threatening implications for certain individuals. In March 2023, the United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF) released a report highlighting the plight of roughly 190 million children in Africa who suffer from an absence of safe water, resulting in the tragic daily loss of 1,000 children under the age of five.
Nations across the globe ...
Driverless cars are no place to relax, new study shows
2023-08-22
Early data on activities that will be unsafe to undertake in automated vehicles has been released. From doing work to watching the world, from social media to resting – preliminary results are in.
Research led by RMIT University looked at what happens if a driver is suddenly required to take control of an automated vehicle, such as in an emergency.
The series of papers examines how experience and three types of distractions (work, social media and rest) impacted on the driver’s ability to respond.
Study lead author in the School of Engineering, Dr Neng Zhang, said ...
CORRECTION: MRI scans improve prostate cancer diagnosis in screening trial
2023-08-22
The REIMAGINE study, published today in BMJ Oncology, is the first study to use MRI scans with prostate specific antigen (PSA) density to assess the need for further standard NHS tests. Of the 29 participants found to have serious prostate cancer, 15 had a ‘low’ PSA score that would have meant they were not referred for further investigation under the current system.
Currently, men over 50 in the UK can ask for a PSA test if they are experiencing symptoms or are concerned about prostate cancer. ...
Short-term use of immunosuppressants not linked to cancer risk
2023-08-22
Relatively short-term use of immunosuppressant medications to control an inflammatory disease was not associated with an increased risk of later developing cancer, according to new research led by scientists at the University of Pittsburgh and Mass Eye and Ear, a member of the Mass General Brigham health care system, and published today in the journal BMJ Oncology.
The findings should provide reassurance to patients and clinicians who may hesitate to prescribe the medications because they are known to increase the risk of cancer in people who ...