Synergistic work of cations in anion exchange membranes for OH- transport in fuel cells
Application in alkaline anion exchange membrane fuel cells
2023-09-30
(Press-News.org)
Anion exchange membrane fuel cells (AEMFCs) have gained attention in the process of fuel cell development because they operate in alkaline environments, the redox reaction rate at the electrodes is faster, and non-precious metal catalysts such as Ni, Co, and Ag can be used, which reduces the cost of fuel cells. However, the mobility of OH- is only 56.97% of that of H+ under the same conditions, and its stability is poor, so improving the ionic conductivity and mechanical properties of anion exchange membranes (AEM) is the key to the commercialization of AEMFC. Recently, a team of scientists has constructed a poly (p-terphenyl isatin) anion exchange membrane with quaternary ammonium and piperidine cations synergistic functionalization that provides excellent mechanical properties and OH-ion conductivity for alkaline anion membrane fuel cells. Their work is published in the journal Industrial Chemistry & Materials on 14 September 2023.
AEM can act on alkaline fuel cells and in the form of transported OH-, greatly reducing production costs. This is a boost to the general application of clean energy, but the biggest challenge is the "trade-off" between the ionic conductivity and stability of anion exchange membranes. “Anion exchange membrane is an important component in fuel cells, and the performance of the membrane profoundly affects the performance and development of fuel cells. How to make a breakthrough in the performance of anion exchange membrane and how to achieve high power density are the issues that our research team has been exploring,” explains Zhe Wang, a professor at the Changchun University of Technology.
Most of the conventional anion exchange membrane polymer backbones contain ether bonds, whose subsequent reactions are not only toxic and harmful, but also highly susceptible to attack and degradation during OH- transport. Not only that, the presence of hydrophilic groups in the polymers containing ether-bonded structures may cause the AEM to dissolve too much, leading to a sharp decrease in its stability.
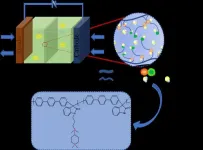
The researchers used a polymer backbone without ether bonds to fundamentally solve the problems associated with conventional backbones. The quaternary ammonium cation and piperidine cation in the anion exchange membrane work in concert to construct a tighter ion-transport channel, which reduces the activation energy required to transport OH- and facilitates the flow of OH- within the membrane. The piperidinium cation also has superior alkaline stability due to its cyclic conformation, while the alkali stability of a series of anion exchange membranes in the paper reached 800 h on the basis of the ether-bond-free backbone.
In addition to these aspects, the researchers also confirmed that the mechanical properties of poly (p-terphenyl isatin) series membranes are in an excellent state. The tensile strength of the pure membranes reaches more than 60 MPa, which provides a stable foundation for further functionalization of subsequent anion exchange membranes.
Looking ahead, the team hopes that their work will provide new ideas for the further development of anion exchange membranes. “Our next step will be to focus on targeting battery power density improvement to achieve the ultimate goal of industrialized application of anion-exchange membranes,” said Wang.
The research team includes Yiman Gu, Yanchao Zhang, Zhe Wang*, Di Liu, Yan Wang, Tianming Dong, Song Wang, Zhanyu Li, Jingyi Wu and Yijia Lei from the Changchun University of Technology.
This research is funded by the Natural Science Foundation of China, Jilin Provincial Science & Technology Department.
Industrial Chemistry & Materials is a peer-reviewed interdisciplinary academic journal published by Royal Society of Chemistry (RSC) with APCs currently waived. Icm publishes significant innovative research and major technological breakthroughs in all aspects of industrial chemistry and materials, especially the important innovation of the low-carbon chemical industry, energy, and functional materials.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-09-30
Tokyo, Japan – Scientists from Tokyo Metropolitan University have realized a new polymer that can effectively transport plasmid DNA into T-cells during chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy, a key treatment for blood cancer. Importantly, it can get genes into floating T-cells, not only ones fixed to surfaces. It is stable, non-toxic, and doesn’t use viruses. It outperforms polyion compounds considered a gold standard in the field, paving the way for new therapies.
T-cells, or lymphocytes, are a type of white blood cell that helps our immune system fight germs and protect us from disease. Recently, technology has become available that helps reprogram T-cells to fight cancer. ...
2023-09-30
(Santa Barbara, Calif.) — Sometimes simple solutions are better. It all depends on the nature of the problem. For humpback whales, the problem is the rope connecting a crab trap on the seafloor to the buoy on the surface. And for fishermen, it’s fishery closures caused by whale entanglements.
Managing this issue is currently a major item on California’s agenda, and it appears less fishing gear may be the optimal solution. So says a team of researchers led by Christopher Free, at UC Santa Barbara, after modeling the benefits and impacts that several management strategies would have on whales and fishermen. ...
2023-09-30
A virtual reality (VR) game crashes. A robot rolls dangerously close to the edge of a cliff. An autonomous vehicle speeds toward a pedestrian. Without intelligent control happening every millisecond, accidents can occur. This control can mean applying the brake of an autonomous vehicle to save a life or creating a more user-friendly augmented reality experience.
Two professors in the Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering at Texas A&M University are working to enhance and advance the future ...
2023-09-30
Wheat is a global staple food and plays a pivotal role in the livelihoods of billions of people. Although long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) have been recognized as crucial regulators of numerous biological processes, our knowledge of lncRNAs associated with wheat (Triticum aestivum) grain development remains minimal.
Seed Biology published an online paper entitled “A comprehensive atlas of long non-coding RNAs provides insight into grain development in wheat” on 04 September 2023.
To ...
2023-09-30
Researchers with the ongoing Arizona CoVHORT research study at the University of Arizona Mel and Enid Zuckerman College of Public Health were awarded $3.2 million by the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases for a five-year study of gastrointestinal symptoms, specifically irritable bowel syndrome, as a condition of long COVID.
Led by epidemiologist Kristen Pogreba-Brown, PhD, MPH, the CoVHORT study is a longitudinal research study of COVID-19 and post-COVID conditions. The ...
2023-09-29
WASHINGTON, D.C. - The U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) today announced up to $500 million in funding for basic research in support of DOE’s clean energy, economic, and national security goals. The funding will advance the priorities of DOE’s Office of Science and its major programs, including Advanced Scientific Computing Research, Basic Energy Sciences, Biological and Environmental Research, Fusion Energy Sciences, High Energy Physics, Nuclear Physics, Isotope R&D and Production, and Accelerator R&D and Production. This funding opportunity will help achieve the Biden Administration’s ...
2023-09-29
Standing at a crosswalk, the signal changes from “don’t walk,” to “walk.” You might step out into the street straight away, or you might look both ways before you cross.
In either scenario, you see the light change, you cross the street. But the context is different; in one case, you didn’t think twice. In the other, you waited; looked to the left and right; saw the coast was clear; then stepped into the street.
Researchers have known that certain brain activity when you see the light change and certain brain activity when you step out into the street are the same no matter the context -- there’s a known “pathway” ...
2023-09-29
Manufacturers throughout Illinois will have the chance to learn about working with the Materials Manufacturing Innovation Center (MMIC) at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Argonne National Laboratory, when the MMIC gets on the bus for the second annual Makers on the Move tour.
The Illinois Manufacturing Association and Illinois Manufacturing Excellence Center (IMEC) sponsor the eight-day, 1,000-mile tour, designed to showcase high-tech, clean, diverse and sustainable modern manufacturing. The branded Makers on the Move bus will stand out on the state’s roadways as it visits facilities, colleges ...
2023-09-29
ARLINGTON, Va., September 29, 2023 — People with intermediate risk, localized prostate cancer can be treated as effectively using fewer and higher doses of radiation therapy delivered over five treatment sessions as they can with lower doses delivered over several weeks, a new phase III randomized trial suggests. The findings, which are the latest from a series of studies investigating the benefits of stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) for people diagnosed with prostate cancer, will be presented Monday at the American Society for Radiation Oncology (ASTRO) Annual Meeting.
The PACE ...
2023-09-29
MIAMI, FLORIDA (STRICTLY EMBARGOED UNTIL SEPT. 29, 2023 AT 5PM ET) – Is it true progression or pseudoprogression in tumor growth?
That’s the critical question for radiation and medical oncologists treating patients with glioblastoma, the most common and aggressive form of brain cancer. Distinguishing between these types of progression is vitally important for treatment management.
“Knowing if it’s true progression, indicative of a poor response to treatment, or pseudoprogression, a favorable response that may look worse due to swelling or tumor necrosis, is essential for clinicians,” said Eric Mellon, MD, PhD, a radiation oncologist and researcher ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Synergistic work of cations in anion exchange membranes for OH- transport in fuel cells
Application in alkaline anion exchange membrane fuel cells