(Press-News.org) To curb the risk of falls, it may be worth grading skateboard parks like ski runs according to the popularity of the metal and concrete features they contain and the level of expertise required, conclude researchers in the journal Injury Prevention.
Their analysis of the moves performed by more than 500 young skateboarders reveals that flips, jumps, and turns on flat ground and quarterpipe (a curved concave ramp) and ramp tricks seem to pose the greatest risk, and are universally popular.
A grind box, where the T-shaped turn parts under the skateboard deck, known as trucks, slide along the edge or surface of a long relatively narrow box, was also a high risk feature, but more often used by older skateboarders, the analysis shows.
In recent years, the number of skateparks has increased as the popularity of the sport has grown among young people, note the researchers. While falls are a recognised hazard of the activity, not much is known about the design features of skateparks or the types of tricks performed there that might increase injury risk.
To try and plug this knowledge gap, the researchers set out to identify the preferred features and tricks, and to gauge the frequency and severity of falls, among 526 predominantly male (98%) skateboarders at one large skatepark in Canada.
The skateboarders were divided into a younger group of 11–15 year olds (166) and an older group of 16-20 year olds (360) and were unobtrusively video recorded while performing their tricks.
Fall severity was scored whenever a trick was attempted, ranging from 1, indicating successful completion, to 5 and 6, indicating that the skateboarder fell onto part of, or their entire, body.
The proportion of children using each feature was computed for each age group, as was the proportion of falls on each feature. Popular features were defined by at least 10 children in one of the age groups using them.
Among young skateboarders, most (74%) used the flat ground, followed by the quarterpipe (46%) and the ramp (47%). Few attempted the grind box, stairs, or railing.
Older skateboarders spent the most time on the flat ground (71%), the quarterpipe (46%), the ramp (51%), and the grind box (35%). Few used the railing or the stairs.
The highest fall frequency was on the grind box (85% of younger skateboarders; 67% of older ones), followed by the flat ground (65% and 61%, respectively). Lower fall frequency (about 35%) was comparable across both age groups for the quarterpipe and the ramp.
Younger skateboarders experienced the highest risk on the flat ground, followed by the ramp, and the quarter pipe. Older skateboarders also experienced the highest risk on the flat ground, followed by the grind box and the ramp. Fall risk is high on flat ground because it’s used to try out tricks, explain the researchers.
As to the type of preferred tricks, younger skateboarders most often performed turns (61% of them), with jumps, slides, and flips performed less often. They seldom tried other types of tricks.
Older skateboarders mostly did jumps (61% of them) and other types of tricks (53%). Other popular tricks included slides (47%), turns (42%), and stalls (30%).
The highest fall frequency for younger skateboarders was during flips, with 94% of them falling when they tried these, followed by slides (67% fell), and jumps (42%). The highest fall frequency for older skateboarders was also for flips (81% fell) and slides (72%).
There are no universal safety standards for skatepark design, note the researchers, who suggest that features might be grouped together strategically to encourage younger skateboarders in one area and older skateboarders in another.
“Segregating ages by design might reduce imitation of risky tricks performed by older skateboarders that are viewed by younger skateboarders but are beyond their skillset,” they suggest.
“It may prove useful to moderate risk of falling if features are differentially coded across the skatepark to suggest difficulty levels, much like what is done on ski hills,” they add.
Finding ways to encourage skateboarders to use protective gear might also be helpful, given that most of those who featured in the analysis weren’t wearing helmets, for example.
The researchers acknowledge that there were few female skateboarders in their study, and that they graded fall severity on the potential to cause injury.
“It would be useful to talk directly with skateboarders who have experienced a medically attended injury and assess how these affect their decisions with regard to features they will use and/or tricks they plan to attempt on returning to the skatepark,” they conclude.
END
Grade difficulty of skatepark features like ski runs to curb fall risk, say researchers
Flips, jumps, turns on flat ground; quarter pipe and ramp moves pose highest risk at all ages
2023-12-13
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Patients can interrupt treatment of immune-supressing medicines for two weeks in order to boost immunity provided by COVID-19 booster vaccine, finds major study
2023-12-13
A major clinical trial, led by experts at the University of Nottingham, has shown that people with inflammatory conditions are able to improve the antibody response from a COVID-19 booster vaccination by interrupting their treatment for two weeks immediately after having the vaccine.
The antibody response to the jab was doubled at four weeks, and one and a half times greater at 26 weeks, when compared to those who continued with their treatment as usual. The improved antibody response lasted for six months. Patients who interrupted treatment reported experiencing more flare-ups of their inflammatory conditions in the next few weeks, but most flares ...
Mental health care gaps for women veterans - report
2023-12-13
Issues of identity, male-dominated branding and apprehension that their needs will go unmet are among the reasons women are not accessing veterans’ mental health support, according to new research being discussed today (Wednesday, 13 December) at a conference in Cambridge.
The report, I don’t feel like that’s for me: Overcoming barriers to mental healthcare for women veterans, was carried out by the Centre for Military Women’s Research (CMWR) at Anglia Ruskin University (ARU), to investigate the low numbers of ex-servicewomen engaging with veteran-specific mental health services.
The ...
National policy aimed at reducing U.S. greenhouse gases also would improve water quality
2023-12-13
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. — A climate policy that raises the price of carbon-intensive products across the entire U.S. economy would yield a side benefit of reducing nitrate groundwater contamination throughout the Mississippi River Basin.
The Gulf of Mexico, an important U.S. fishery, also would see modest benefits from the nitrate reductions. These were among the conclusions of a recent study published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS).
The study, led by four early career researchers, three of them from ...
Twenty-year study confirms California forests are healthier when burned — or thinned
2023-12-13
Berkeley — A 20-year experiment in the Sierra Nevada confirms that different forest management techniques — prescribed burning, restoration thinning or a combination of both — are effective at reducing the risk of catastrophic wildfire in California.
These treatments also improve forest health, making trees more resilient to stressors like drought and bark beetles, and they do not negatively impact plant or wildlife biodiversity within individual tree stands, the research found. The findings of the experiment, called the Fire Surrogate Study, were published today in the journal Ecological Applications.
“The research ...
Caregiving can be stressful, but it could also lower risk of depression
2023-12-12
Becoming a caregiver to an aging parent or spouse can be stressful, but a new study from a researcher at The University of Texas at Austin is questioning the idea that family caregiving is also a risk factor for depression.
The study, published in the journal Advances in Life Course Research, found that depression in adult caregivers is mostly driven by having a loved one experiencing serious health problems, while becoming a caregiver is associated with fewer symptoms of depression.
“Decades of research on this topic indicate that there are positive and negative aspects to being a caregiver,” said Sae Hwang Han, ...
UCF researcher discovers new technique for photon detection
2023-12-12
University of Central Florida researcher Debashis Chanda, a professor at the NanoScience Technology Center, has developed a new technique to detect photons — elementary particles that span from visible light to radio frequencies and are instrumental in carrying cellular communication.
The advancement could lead to more precise and efficient technologies in various fields, from improving medical imaging and communication systems to enhancing scientific research and even potentially bolstering security measures.
Photon detection has typically relied on change/modulation of voltage or ...
Fat flies live longer on a diet at any age
2023-12-12
Old, obese flies get healthier and live longer if put on a diet, University of Connecticut researchers report on Dec. 8 in PNAS. If the effect holds true for humans, it would mean it’s never too late for obese people to improve their health with diet.
For way too many of us, eating too much goes along with getting old and a tendency to be obese. Different health organizations define obesity differently, but all agree it means having too much body fat, and is associated with a host of diseases related to metabolism including heart disease and diabetes. Many animal studies have shown that eating less—meaning sharply ...
European Policy Lab gathers stakeholders to map forest policy opportunities and barriers
2023-12-12
ForestPaths’ first Policy Lab convened stakeholders in Helsinki, Finland, on 27-29 September 2023. Nineteen carefully selected participants with diverse expertise – including research, policy, governance, civil society, value chain professionals, and forestry practitioners – engaged in discussions on forest-based policymaking and modelling related to climate change and biodiversity.
Tasked with considering policy actions given different timescales, governance paradigms, enablers, and barriers, participants contributed ...
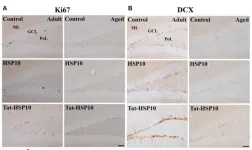
Tat-heat shock protein 10 ameliorates age-related phenotypes in the hippocampus
2023-12-12
“Mitochondrial dysfunction is a major cellular change observed in the hippocampus during aging.”
BUFFALO, NY- December 12, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 22, entitled, “Tat-heat shock protein 10 ameliorates age-related phenotypes by facilitating neuronal plasticity and reducing age-related genes in the hippocampus.”
In this new study, researchers Hyo Young Jung, Hyun Jung Kwon, Kyu ...
MIT researchers observe a hallmark quantum behavior in bouncing droplets
2023-12-12
In our everyday classical world, what you see is what you get. A ball is just a ball, and when lobbed through the air, its trajectory is straightforward and clear. But if that ball were shrunk to the size of an atom or smaller, its behavior would shift into a quantum, fuzzy reality. The ball would exist as not just a physical particle but also a wave of possible particle states. And this wave-particle duality can give rise to some weird and sneaky phenomena.
One of the stranger prospects comes from a thought experiment known as the “quantum bomb tester.” The experiment proposes that a quantum particle, such ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
New compound stops common complications after intestinal surgery
Breaking through water treatment limits with defect-free, high-efficiency next-generation ceramic filters!
Researchers determine structural motifs of water undecamer cluster
Researchers enhance photocatalytic hydrogen evolution performance of covalent organic frameworks by constitutional isomer strategy
Molecular target drives immunogenicity in cancer immunotherapy
Plant cell structure could hold key to cancer therapies and improved crops
Sustainable hydrogen peroxide production: Breakthroughs in electrocatalyst design for on-site synthesis
Cash rewards for behavior change: A review of financial incentives science in one health contexts and implications
One Health antimicrobial resistance modelling: from science to policy
Artificial feeding platform transforms study of ticks and their diseases
Researchers uncover microscopic mechanism of alkali species dissolution in water clusters
Methionine restriction for cancer therapy: A comprehensive review of mechanisms and clinical applications
White House autism briefing linked to swift shifts in prescribing patterns, study finds
Specialist palliative care can save the NHS up to £8,000 per person and improves quality of life
New research warns charities against ‘AI shortcut’ to empathy
Cannabis compounds show promise in fighting fatty liver disease
Study in mice reveals the brain circuits behind why we help others
Online forum to explore how organic carbon amendments can improve soil health while storing carbon
Turning agricultural plastic waste into valuable chemicals with biochar catalysts
Hidden viral networks in soil microplastics may shape the future of sustainable agriculture
Americans don’t just fear driverless cars will crash — they fear mass job losses
Mayo Clinic researchers find combination therapy reduces effects of ‘zombie cells’ in diabetic kidney disease
Preventing breast cancer resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors using genomic findings
Carbon nanotube fiber ‘textile’ heaters could help industry electrify high-temperature gas heating
Improving your biological age gap is associated with better brain health
Learning makes brain cells work together, not apart
Engineers improve infrared devices using century-old materials
Physicists mathematically create the first ‘ideal glass’
Microbe exposure may not protect against developing allergic disease
Forest damage in Europe to rise by around 20% by 2100 even if warming is limited to 2°C
[Press-News.org] Grade difficulty of skatepark features like ski runs to curb fall risk, say researchersFlips, jumps, turns on flat ground; quarter pipe and ramp moves pose highest risk at all ages