(Press-News.org) A team of researchers led by Professor Young S. Park at UNIST’s Department of Chemistry has achieved a significant breakthrough in the field of organic semiconductors. Their successful synthesis and characterization of a novel molecule called “BNBN anthracene” has opened up new possibilities for the development of advanced electronic devices.
Organic semiconductors play a crucial role in improving the movement and light properties of electrons in carbon-centered organic electronic devices. The team’s research focused on enhancing the chemical diversity of these semiconductors by replacing carbon-carbon (C−C) bonds with isoelectronic boron-nitrogen (B−N) bonds. This substitution allows for precise modulation of the electronic properties without significant structural changes.
The researchers successfully synthesized the BNBN anthracene derivative, which contains a continuous BNBN unit formed by converting the BOBN unit at the zigzag edge. Compared to conventional anthracene derivatives composed solely of carbon, the BNBN anthracene exhibited significant variations in the C−C bond length and a larger highest occupied molecular orbital–lowest unoccupied molecular orbital energy gap.
In addition to its unique properties, the BNBN anthracene derivative demonstrated promising potential for application in organic electronics. When used as the blue host in an organic light-emitting diode (OLED), the BOBN anthracene exhibited a remarkably low driving voltage of 3.1V, along with higher efficiency in terms of current utilization, energy efficiency, and light emission.
The research team further confirmed the properties of the BNBN anthracene derivative by studying its crystal structure using an X-ray diffractometer. This analysis revealed structural changes, such as bonding length and angle, resulting from the boron-nitrogen (BN) bonding.
“Our study on anthracene, a type of acene widely recognized as an organic semiconductor, has laid the groundwork for future advancements in the field,” commented Songhua Jeong (Combined MS/Ph.D. Program of Chemistry, UNIST), the first author of this study. “The continuous BN bonding synthesized through this research holds great potential for applications in organic semiconductors.”
Professor Park emphasized the significance of this breakthrough, stating, “The synthesis and characterization of compounds with continuous boron-nitrogen (BN) bonds contribute to fundamental research in chemistry. It provides a valuable tool for synthesizing new compounds and controlling their electronic properties.”
The research findings, which also involve the contributions of Professor Joonghan Kim’s team from the Catholic University of Korea, Professor Wonyoung Choe’s team from the Department of Chemistry at UNIST, and a research team from SFC Co., Ltd., were published online on December 11 in the prestigious journal, Angewande Chemie International Edition. The study received support from the mid-sized research enterprise SFC and was promoted by the National Research Foundation (NRF) of the Ministry of Science and ICT, under the projects of the Ministry of Trade, Industry, and Energy.
Journal Reference
Seonghwa Jeong, Eunji Park, Jiyeon Kim, et al., “Increasing Chemical Diversity of B2N2 Anthracene Derivatives by Introducing Continuous Multiple Boron-Nitrogen Units,” Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., (2023).
END
Breakthrough in organic semiconductor synthesis paves the way for advanced electronic devices
2023-12-29
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Korean Artificial Sun, KSTAR, installation of a tungsten divertor for long pulse operations
2023-12-29
The Korean artificial sun, KSTAR, has completed divertor upgrades, allowing it to operate for extended periods sustaining high-temperature plasma over the 100 million degrees.
The Korea Institute of Fusion Energy announced the successful installation of the newly developed tungsten divertor for KSTAR. KSTAR, now equipped with the new divertor, commenced a plasma experiment on the 21st of December 2023.
The divertor, a crucial plasma-facing component installed at the bottom of the vacuum vessel in a magnetic fusion device known as a Tokamak, manages the exhaust of ...
New perspectives on treating gallbladder inflammation
2023-12-28
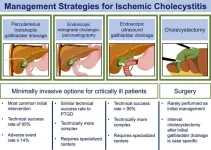
Ischaemic cholecystitis is a form of gallbladder inflammation that occurs without gallstones or another form of external compression. It is caused by poor perfusion to the gallbladder tissue.
This new research is important because it helps to better understand the cause of ischaemic cholecystitis and to develop more effective treatments for this condition.
A team of researchers from the University of California, San Francisco, conducted a study investigating the cause of ischaemic cholecystitis. They found that the gallbladder is particularly susceptible to ischaemia ...
Brain health after COVID-19, pneumonia, heart attack, or critical illness
2023-12-28
About The Study: The findings of this study including 345 participants suggest that post–COVID-19 brain health was impaired but, overall, no more than the brain health of patients from 3 non–COVID-19 cohorts of comparable disease severity. Long-term associations with brain health might not be specific to COVID-19 but associated with overall illness severity and hospitalization. This information is important for putting understandable concerns about brain health after COVID-19 into perspective.
Authors: Daniel Kondziella, M.D., M.Sc., Dr.Philos., ...
Post–COVID-19 condition in children 6 and 12 months after infection
2023-12-28
About The Study: In this study of children tested for SARS-CoV-2 infection in Canadian pediatric emergency departments, although children infected with SARS-CoV-2 reported increased chronic symptoms, few of these children developed post–COVID-19 condition, and overall quality of life did not differ from children with negative SARS-CoV-2 tests.
Authors: Stephen Freedman, M.D.C.M., M.Sc., of the University of Calgary in Calgary, Alberta, Canada, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: ...
Self-reported frequency of adding salt to food and risk of incident chronic kidney disease
2023-12-28
About The Study: In this study of 465,000 individuals, a higher self-reported frequency of adding salt to foods was associated with a higher risk of chronic kidney disease in the general population. These findings suggest that reducing the frequency of adding salt to foods at the table might be a valuable strategy to lower chronic kidney disease risk in the general population.
Authors: Lu Qi, M.D., Ph.D., of Tulane University in New Orleans, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The ...
Breakthrough in hydrate-based desalination technique unveiled
2023-12-28
A research team, led by Professor Yongwon Seo in the Graduate School of Carbon Neutrality at UNIST has unveiled a highly efficient method for desalinating seawater using hydrate-based desalination (HBD) technology. The breakthrough is expected to have far-reaching implications for the application of hydrate-based desalination techniques, with the ability to calculate optimal temperatures for enhanced efficiency.
Hydrate desalination technology, known for its eco-friendly freshwater production capabilities, offers a low-energy solution that can be effectively used in treating high concentrations of brine or contaminated water. By ...
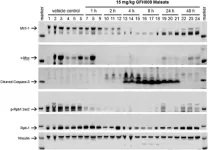
GFH009: A potent and highly selective CDK9 inhibitor for the treatment of hematologic malignancies
2023-12-28
“[...] the results of this preclinical investigation program suggest that induction of apoptosis is a key component of GFH009’s anti-tumor mechanism of action [...]”
BUFFALO, NY- December 28, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Oncotarget's Volume 14 on December 20, 2023, entitled, “The pharmacodynamic and mechanistic foundation for the antineoplastic effects of GFH009, a potent and highly selective CDK9 inhibitor for the treatment of hematologic malignancies.”
To evade cell cycle controls, malignant cells rely upon rapid expression of select proteins to mitigate pro-apoptotic signals ...
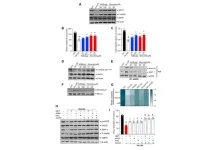
Angelica gigas extract inhibits acetylation of eNOS in vascular dysfunction
2023-12-28
“Angelica gigas Nakai (AG), a traditional medicinal herb, is garnering scientific attention for its potential in addressing a variety of health conditions.”
BUFFALO, NY- December 27, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 23, entitled, “Angelica gigas extract inhibits acetylation of eNOS via IRE1α sulfonation/RIDD-SIRT1-mediated posttranslational modification ...
Johns Hopkins researchers: Regret rarer than believed among patients who undergo gender affirming surgery
2023-12-28
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
In a Viewpoint article published Dec. 27, 2023, in JAMA Surgery, three Johns Hopkins researchers urge the medical community to dismiss a widely held, but scientifically unsupported belief that many people who are transgender and gender diverse (TGD), and undergo gender affirming surgery (GAS), later regret their decision to undergo such procedures.
The researchers are:
Harry Barbee, Ph.D., assistant professor and interdisciplinary social scientist at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health
Bashar ...
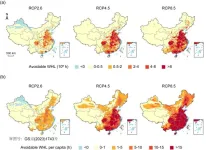
Future labor losses due to heat stress in China under climate change scenarios
2023-12-28
Climate change is the biggest global health threat in the 21st century, and the rising temperatures have undermined the health and safety of the working population, as well as caused labor losses, which are closely tied to social-economic development. Although the future temperatures increase in China has been forecasted by state-of-the-art climate change projections, to what extent the influence on labor has not been well studied. In a paper published in Science Bulletin, a Chinese research team presents evidence of future labor losses due to heat stress in China under climate change scenarios. This study was led by Cunrui Huang, a professor at the Vanke School of Public ...