(Press-News.org) When voters cast their ballots in the 2016 and 2020 presidential elections, many were driven by their concern for climate change, according to new research out of CU Boulder’s Center for Environmental Futures (C-SEF). The new report determined that views on climate change played a significant role in whom people voted for, concluding that the climate issue very likely cost Republicans the 2020 election, all else equal.
“This is obviously information that politicians and advocates across the political spectrum will want to know, heading into the 2024 election cycle,” said Matthew Burgess, CIRES Fellow and C-SEF director. “How to reduce political polarization of climate change is one of the questions our research group is most interested in currently, and this provides some insight.”
In their new assessment, published today, Burgess and his co-authors, two C-SEF graduate students and researchers from Vanderbilt University and the University of California Santa Barbara, sought to understand the importance of climate change as a voter issue in the two most recent presidential elections. The team used data from the nonpartisan Voter Study Group, to analyze how issue opinions and demographics affected the 2016 and 2020 elections.
The research team used several techniques to assess how climate change opinion shaped voters' choices: logistic regression, a machine learning model, and a simulation of the Electoral College in which they could turn the role of climate change on or off. Their conclusion: Republicans could have gained at least a 3-percent swing in the popular vote, which almost certainly would have been enough to have taken the White House in 2020.
The team found personal views on climate change were one of the strongest predictors of voting behavior in 2020, especially among independents. Not surprisingly, they found the majority of Democrats and independents are worried about climate change. And, many younger and moderate Republicans also see climate change as an important issue—one-quarter of Republicans who think climate change is “very important” voted for President Biden in 2020.
Such widespread concern about climate change is currently a clear upper hand for the Democratic party. The party holds a 26-point advantage over Republicans on the issue, a lead larger than any other opposing topic between the two parties, in a recent poll. Voters from a broad range of political persuasions seem to see Democrats as more capable of finding solutions and instating policies to address problems created by climate change, even if not every Democratic climate change policy is necessarily popular.
While the issue of climate change strongly predicts whom people voted for in 2020, overall, it is not the number-one concern among voters. Less than 5 percent of adults rank climate change as the single most important issue. More pressing issues include those that affect people’s daily lives, like the economy, healthcare, education, and crime.
If climate change isn’t voters’ top issue, why is it such a strong predictor?
“One reason might be that most people see the evidence for climate change as so strong that, if a candidate were to deny or minimize that issue, they might trust that candidate less on other issues,” Burgess said. “Another reason might be that voters are beginning to see a connection between climate change and the kitchen table issues they care about more, like the economy, security, and health. But we can’t say for sure, and this is a key question for future research.”
As the country prepares for the next election, the odds are good that climate change will influence whom they vote for.
END
U.S. voters’ climate change opinions swing elections
2024-01-17
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Artificial intelligence helps coronary CT angiography and accelerates the development of precision medicine
2024-01-17
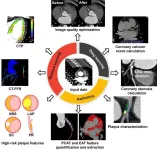
This review was jointly published by Prof. Long-Jiang Zhang (Department of Radiology, Jinling Hospital, Affiliated Hospital of Medical School, Nanjing University) and Prof. Christian Tesche (Division of Cardiovascular Imaging, Department of Radiology and Radiological Science, Medical University of South Carolina and Department of Cardiology, Munich University Clinic, Ludwig-Maximilian-University).
With the continuous progress of science and technology, artificial intelligence (AI) has become an important driving force for a new round of scientific and technological revolution and industrial change. It aims to mimic human consciousness and thought processes, continuously ...
New research finds half-cardio, half-strength training reduces cardiovascular disease risks
2024-01-17
AMES, Iowa — Approximately one in three deaths in the U.S. is caused by cardiovascular disease, according to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. A robust body of evidence shows aerobic exercise can reduce risks, especially for people who are overweight or obese. But few studies have compared results with resistance exercise — also known as strength or weight training — or with workout regimens that are half aerobic and half resistance. Researchers at Iowa State University led one of the longest and largest supervised exercise trials to ...
ECOG-ACRIN Cancer Research Group melanoma research team led by Michael Atkins, MD, receives the 2023 Paper of the Year distinction from the Journal of Clinical Oncology
2024-01-17
A team of melanoma researchers with the ECOG-ACRIN Cancer Research Group (ECOG-ACRIN) is honored with the 2023 Paper of the Year distinction by the Journal of Clinical Oncology. The recognition is for the results of the DREAMseq randomized phase 3 clinical trial. DREAMseq (EA6134) showed an optimal treatment sequence for combination therapy in patients with advanced melanoma with a BRAFV600 tumor gene mutation. The treatment sequence beginning with immunotherapy (nivolumab and ipilimumab), followed by targeted therapy (dabrafenib and trametinib) if there was disease progression, resulted ...
The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition launches new article series to educate physicians and other health care professionals on nutrition
2024-01-17
Rockville, MD (January 16, 2024) – To educate physicians and other health care professionals on the fundamentals of nutrition, The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition has launched a new article series titled Nutrition for the Clinician. The effort supports the White House National Strategy on Hunger, Nutrition, and Health and its directives to expand nutrition knowledge of health care providers, an effort long supported by the American Society for Nutrition. Nancy Krebs, MD, MS, Professor of Pediatrics, University of Colorado ...
New research shows that most early galaxies looked like breadsticks rather than pizza pies or dough balls
2024-01-17
Columbia researchers analyzing images from NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope have found that galaxies in the early universe are often flat and elongated, like breadsticks—and are rarely round, like balls of pizza dough. “Roughly 50 to 80% of the galaxies we studied appear to be flattened in two dimensions,” explained Viraj Pandya, a NASA Hubble Fellow at Columbia University, and the lead author of a new paper slated to appear in The Astrophysical Journal that outlines the findings. “Galaxies that look like long, thin breadsticks seem to be very common in the early universe, which is surprising, since they are uncommon among galaxies ...
Podcasts and compulsory attendance improved student learning
2024-01-17
Consider a group of new sociology students who are about to dive into a completely new subject. Half of them are fresh out of upper secondary school.
They need to settle into student life and get to know other students. They are about to embark on studies in a new field and must learn new ways of acquiring knowledge, regardless of their discipline.
They also need to come to grips with concepts such as legitimation, linguistic objectification, internalization and externalization. What on Earth do ...
Brush biopsy enables early detection of oral cancer without surgery
2024-01-17
A new test invented by University of Illinois Chicago researchers allows dentists to screen for the most common form of oral cancer with a simple and familiar tool: the brush.
The diagnostic kit, created and patented by Guy Adami and Dr. Joel Schwartz of the UIC College of Dentistry, uses a small brush to collect cells from potentially cancerous lesions inside the mouth. The sample is then analyzed for genetic signals of oral squamous cell carcinoma, the ninth most prevalent cancer globally.
This new screening method, which is currently seeking commercialization ...
Diets rich in plant protein may help women stay healthy as they age
2024-01-17
Women who consume higher amounts of protein, especially protein from plant-based sources, develop fewer chronic diseases and are more likely to be healthier overall as they age, according to a study led by researchers at the Jean Mayer USDA Human Nutrition Research Center on Aging (HNRCA) at Tufts University and published Jan. 17 in The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition.
Analyzing self-reported data from more than 48,000 women, the researchers saw notably less heart disease, cancer, and diabetes, and cognitive and mental health decline, in those who included more protein in their diets from sources such as fruits, ...
Study uncovers mechanics of machete-like ‘tail-whipping’ in thresher sharks
2024-01-17
Like Indiana Jones, thresher sharks (Alopias spp.) have mastered the art of the whip using their tails. With incredible speed, their long, machete-like tails can slap and stun their prey, allowing them to swallow multiple fish in one fell swoop. Their exceptionally elongated tail, which can often be as long as their entire body, not only makes this particular shark unique, but also a formidable hunter.
Thresher shark “tail-whipping” consists of four phases: preparation, strike, wind-down recovery, and prey collection. Overhead tail slaps begin in the preparation phase by lunging ...
Glowing COVID-19 diagnostic test prototype produces results in one minute
2024-01-17
Cold, flu and COVID-19 season brings that now-familiar ritual: swab, wait, look at the result. But what if, instead of taking 15 minutes or more, a test could quickly determine whether you have COVID-19 with a glowing chemical? Now, in ACS Central Science, researchers describe a potential COVID-19 test inspired by bioluminescence. Using a molecule found in crustaceans, they have developed a rapid approach that detects SARS-CoV-2 protein comparably to one used in vaccine research.
From fireflies ...