(Press-News.org) Consider a group of new sociology students who are about to dive into a completely new subject. Half of them are fresh out of upper secondary school.
They need to settle into student life and get to know other students. They are about to embark on studies in a new field and must learn new ways of acquiring knowledge, regardless of their discipline.
They also need to come to grips with concepts such as legitimation, linguistic objectification, internalization and externalization. What on Earth do these terms mean and how are the students going to become familiar with them?
Textbooks and lecturers explain these new ideas, and the students will work on them in study groups. But the question still remains: how can students become familiar with new academic concepts and terms and understand how to use them correctly?
The sociology professor at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU) Aksel Tjora has both tested and studied new ways of teaching and learning.
“In lectures with 200 students or more, not many of them dare to ask questions, provide input or take part in discussions. We have now tested a number of different teaching methods in order to motivate the students,” Tjora says.
Building on American research on podcasts in teaching
Recent American research shows an increasing use of film, art and music in teaching sociology. Podcasts are also used in teaching sociology, but there is still limited knowledge of how subject managers use this tool.
In 2020, one researcher conducted a search in the American journal Teaching Sociology and found exactly zero articles or commentaries published since 2010 on the topic of podcasts.
Since then, other researchers have investigated the potential of using podcasts to teach sociology. Among other things, they found that podcasts seem to increase student engagement.
"We have explored this further, including by seeing what function podcasts can have in interaction-based learning," Tjora said.
Lectures are still the dominant form of teaching
Over the last 30–40 years, universities have paid more and more attention to how students learn best.
"We can see this as part of a specific development of the universities towards education of the masses and the production of study credits, and as a kind of industrial and mercantile approach in much of the sector," Tjora said.
University learning is largely associated with reading, listening, speaking and writing. Speaking and writing require the most active involvement on the part of students, and tend to fare rather poorly in relation to measurements of what students spend their time doing.
The preference for passive strategies contrasts with learning as an active process.
“There are many indications that universities and university colleges have a way to go when it comes to facilitating student learning. Lectures are still the dominant form of teaching,” says Tjora.
Active teaching methods can help integrate students into academic communities, increase motivation and involvement, and facilitate confidence in independent and critical thinking.
“There has been relatively little attention has been paid to how sociological theory should be taught, and there has been little research on the teaching of the subject,” says Tjora.
He and his sociology colleagues have taken a closer look at this by testing new ways of teaching, and evaluating these approaches in conjunction with the students.
Many more students passed the exam
They have investigated how students can be taught a sociological mindset through interaction-based learning, with emphasis on the function of podcasts.
Tjora studied this with Inga Marie Hansen Hoøen and Rebekka Ravn Lysvik, both of whom have been student assistants for the introductory course in sociology. This introductory course was used as a case study.
The introductory course was restructured in autumn 2018, and steps were taken to facilitate the students’ active, creative and collective learning through the use of group work and compulsory attendance in small seminar groups, interactivity in lectures, and academic social gatherings.
The exam was changed to a portfolio consisting of compulsory group-based submissions such as podcasts and blogs. This required significant follow-up from Tjora and his teaching assistants, but increased successful completion (meaning passing the exam) by as much as 36 per cent compared with the previous year.
Before the restructuring took place, the course comprised traditional lectures, voluntary seminars in large groups, individual semester assignments and a 5-hour written exam. A report from 2016 highlighted low levels of interactivity in lectures.
“Dared to raise my hand for the first time”
The empirical basis of the study that Tjora and his two colleagues conducted in 2021 includes the evaluation of the introductory course in sociology (a survey), reference group meetings and a sample of podcast submissions. In all, 166 out of a total of 224 students registered for exams responded to the survey.
The analysis addressed three main topics: (1) a physical student community, (2) group collaboration and (3) podcasts as means of academically thinking aloud.
Physical student community: Despite the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic in the autumn of 2021, NTNU conducted physical lectures and compulsory seminars for introductory courses throughout most of the autumn. The goal was to get students back on campus.
The evaluation shows that the students experienced increased confidence through getting to know their fellow students at compulsory seminars. Each seminar group consisted of 10–20 students, in contrast to the lectures involving up to 220 students, which some found to be socially challenging.
In the evaluation, many students mentioned that they dared to ask questions and participate in academic discussions when they feel comfortable in the social setting. One of the participants writes:
“I have been a student for one year, but the introductory course in sociology was the first time I dared to raise my hand and answer a question out loud.”
Learning by thinking aloud together
Podcasts were tested as a tool for academically thinking aloud.
“Academically thinking aloud is the starting point for introducing podcasts as a compulsory exercise. The intention is to force students to talk about the subject and get them to relax. Everyone in the group has to participate in the conversation because it becomes very obvious if individuals do not speak or participate,” says Tjora.
Groups of 3–4 students were given the task of producing a podcast in which they discussed social institutions using sociological terms. A social institution might be a family, a job, a festival, or a leisure activity, for example.
The students had to use relevant terminology and link it to everyday situations. Some chose Halloween as the topic, others chose residence halls, dating or social media.
Putting on sociology glasses
“We found out how students use sociological terms in their day-to-day lives. They put on ‘sociology glasses’. Listening to the podcasts, it is very clear that they were experimenting with using sociology terms, a little unsophisticatedly and spontaneously, but they did respond to each other’s input and comments,” Tjora said.
The answers were more refined in written group work, he said
The students statesaidthat they “learn a lot of sociology just by having conversations with other fellow students” and that “working together in groups means that you have to practice arguing for your academic point of view.”
“In our observation of the students’ work and in their own feedback, it became clear that learning through more spontaneous thinking aloud is key,” says Tjora.
From scepticism to learning
The fact that the teaching contained a good deal of compulsory group work was not immediately met with great enthusiasm.
“In the beginning, we experienced a general scepticism towards group work. This was a little surprising because it is something they have been used to doing at upper secondary school,” says Tjora.
However, in the evaluations after the students had completed the semester, it appeared that the group work provided good learning outcomes.
The students felt that they gained “insight into how others understand specific tasks”, that there was a “low threshold for asking questions” and “someone to talk to regarding assignments and the syllabus”.
According to the students’ evaluation, experiencing that they can explain something to others using their own words gave them a sense of achievement:
“Having other people explain their perspectives and opinions creates a more nuanced picture where I feel I gain broader insight. It has also helped in explaining difficult theories to others using just a few, understandable words. I also learn from myself when I am forced to understand in order to explain things to others.”
It has been important for the educators that the students become accustomed to talking academically among themselves as a learning process, but also to free themselves from the need to only talk to lecturers when they perceive something in their studies as academically challenging.
Fewer free riders on podcasts
Group work also has problematic aspects, especially when it comes to written group assignments.
This is related to asymmetrical effort, where students find that they “learned the most and remember most of what I myself have written or said,” partly because each group tends to distribute tasks among the individual members rather than working on them together. This meant that the students felt they learned more from working on an entire assignment alone, or that group members who are given the most challenging subtasks learn the most.
Several students reported in the evaluation that they felt that they did most of the work and that they have had to carry the load because of little initiative within the group. This was said to be particularly challenging when it came to producing a piece of written work together.
However, thinking aloud together when producing podcasts and complying with academic requirements was an exercise in which everyone had to contribute. As a result, there were fewer free riders and more involvement, spontaneity – and learning.
“We found that many students developed the ability to academically think aloud, where they were able to understand their own everyday experiences and surroundings sociologically. From an empirical perspective, the podcasts in particular show this most clearly,”
END
Podcasts and compulsory attendance improved student learning
We all know the old one-way lecture to an enormous auditorium of students isn't the best way to teach – so what actually works?
2024-01-17
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Brush biopsy enables early detection of oral cancer without surgery
2024-01-17
A new test invented by University of Illinois Chicago researchers allows dentists to screen for the most common form of oral cancer with a simple and familiar tool: the brush.
The diagnostic kit, created and patented by Guy Adami and Dr. Joel Schwartz of the UIC College of Dentistry, uses a small brush to collect cells from potentially cancerous lesions inside the mouth. The sample is then analyzed for genetic signals of oral squamous cell carcinoma, the ninth most prevalent cancer globally.
This new screening method, which is currently seeking commercialization ...
Diets rich in plant protein may help women stay healthy as they age
2024-01-17
Women who consume higher amounts of protein, especially protein from plant-based sources, develop fewer chronic diseases and are more likely to be healthier overall as they age, according to a study led by researchers at the Jean Mayer USDA Human Nutrition Research Center on Aging (HNRCA) at Tufts University and published Jan. 17 in The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition.
Analyzing self-reported data from more than 48,000 women, the researchers saw notably less heart disease, cancer, and diabetes, and cognitive and mental health decline, in those who included more protein in their diets from sources such as fruits, ...
Study uncovers mechanics of machete-like ‘tail-whipping’ in thresher sharks
2024-01-17
Like Indiana Jones, thresher sharks (Alopias spp.) have mastered the art of the whip using their tails. With incredible speed, their long, machete-like tails can slap and stun their prey, allowing them to swallow multiple fish in one fell swoop. Their exceptionally elongated tail, which can often be as long as their entire body, not only makes this particular shark unique, but also a formidable hunter.
Thresher shark “tail-whipping” consists of four phases: preparation, strike, wind-down recovery, and prey collection. Overhead tail slaps begin in the preparation phase by lunging ...
Glowing COVID-19 diagnostic test prototype produces results in one minute
2024-01-17
Cold, flu and COVID-19 season brings that now-familiar ritual: swab, wait, look at the result. But what if, instead of taking 15 minutes or more, a test could quickly determine whether you have COVID-19 with a glowing chemical? Now, in ACS Central Science, researchers describe a potential COVID-19 test inspired by bioluminescence. Using a molecule found in crustaceans, they have developed a rapid approach that detects SARS-CoV-2 protein comparably to one used in vaccine research.
From fireflies ...
Microplastics from natural fertilizers are blowing in the wind more often than once thought
2024-01-17
Though natural fertilizers made from treated sewage sludge are used to reintroduce nutrients onto agricultural fields, they bring along microplastic pollutants too. And according to a small-scale study published in ACS’ Environmental Science & Technology Letters, more plastic particles get picked up by the wind than once thought. Researchers have discovered that the microplastics are released from fields more easily than similarly sized dust particles, becoming airborne from even a slight breeze.
Microplastics, or small bits of plastic less than 5 millimeters long, have appeared everywhere from clouds to heart tissues. And with these plastics’ increasing prevalence in ...
New AI makes better permafrost maps
2024-01-17
LOS ALAMOS, N.M., Jan. 17, 2024 — New insights from artificial intelligence about permafrost coverage in the Arctic may soon give policy makers and land managers the high-resolution view they need to predict climate-change-driven threats to infrastructure such as oil pipelines, roads and national security facilities.
“The Arctic is warming four times faster than the rest of the globe, and permafrost is a component of the Arctic that’s changing really rapidly,” said Evan Thaler, a Chick Keller Postdoctoral Fellow at Los Alamos National Laboratory. Thaler is corresponding ...
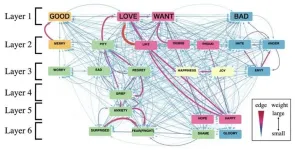
New study unveils emotional hubs that exist across languages
2024-01-17
Emotions exert a profound influence on human behavior, prompting extensive explorations in the realms of psychology and linguistics. Understanding central emotions also has practical utility since it can help organizations create messages that resonate better with people. For instance, businesses can enhance their connection with their customers, and non-profits can prompt quicker action by skillfully leveraging the salient emotions in humans.
Colexification is a phenomenon in which the occurrence of a single word is associated with multiple concepts that share semantic relationships. The analysis of colexification is an innovative linguistic method for ...
Childhood stress linked to higher risk of high blood pressure, obesity, diabetes in adults
2024-01-17
Research Highlights:
Consistently high scores of perceived stress during adolescence through adulthood may contribute to worse cardiometabolic health including obesity in young adults..
Researchers suggest the adoption of healthy coping strategies for stress management early in life may help prevent cardiometabolic diseases, from heart disease to Type 2 diabetes.
Embargoed until 4 a.m. CT/5 a.m. ET Wednesday, January 17, 2024
DALLAS, January 17, 2024 — Young adults who reported higher stress during their teenage years to adulthood were more likely to ...
US air pollution rates on the decline but pockets of inequities remain
2024-01-17
Over the last decades, air pollution emissions have decreased substantially; however, the magnitude of the change varies by demographics, according to a new study by Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health. The results indicate there are racial/ethnic and socioeconomic disparities in air pollution emissions reductions, particularly in the industry and energy generation sectors. The findings are published in the journal Nature Communications.
The research provides a national investigation of air pollution emission ...
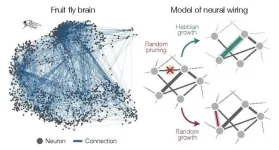
Fly brain, mouse brain, worm brain: They all network the same
2024-01-17
New York, January 17, 2024 — In all species, brain function relies on an intricate network of connections that allows neurons to send information back and forth between one another, commanding thought and physical activity. But within those networks a small number of neurons share much stronger connections to one another than all the others. These abnormally strong connections—known as “heavy tailed” based on the shape of their distribution—are thought to play an outsized role in brain function.
Researchers ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
A folding magnetic soft sheet robot: Enabling precise targeted drug delivery via real-time reconfigurable magnetization
Sylvester Cancer Tip Sheet for March 2026
New tools and techniques accelerate gallium oxide as next-generation power semiconductor
Researchers discover seven different types of tension
Report calls for AI toy safety standards to protect young children
VR could reduce anxiety for people undergoing medical procedures
Scan that makes prostate cancer cells glow could cut need for biopsies
Mechanochemically modified biochar creates sustainable water repellent coating and powerful oil adsorbent
New study reveals hidden role of larger pores in biochar carbon capture
Specialist resource centres linked to stronger sense of belonging and attainment for autistic pupils – but relationships matter most
Marshall University, Intermed Labs announce new neurosurgical innovation to advance deep brain stimulation technology
Preclinical study reveals new cream may prevent or slow growth of some common skin cancers
Stanley Family Foundation renews commitment to accelerate psychiatric research at Broad Institute
What happens when patients stop taking GLP-1 drugs? New Cleveland Clinic study reveals real world insights
American Meteorological Society responds to NSF regarding the future of NCAR
Beneath Great Salt Lake playa: Scientists uncover patchwork of fresh and salty groundwater
Fall prevention clinics for older adults provide a strong return on investment
People's opinions can shape how negative experiences feel
USC study reveals differences in early Alzheimer’s brain markers across diverse populations
300 million years of hidden genetic instructions shaping plant evolution revealed
High-fat diets cause gut bacteria to enter brain, Emory study finds
Teens and young adults with ADHD and substance use disorder face treatment gap
Instead of tracking wolves to prey, ravens remember — and revisit — common kill sites
Ravens don’t follow wolves to dinner – they remember where the food is
Mapping the lifelong behavior of killifish reveals an architecture of vertebrate aging
Designing for hard and brittle lithium needles may lead to safer batteries
Inside the brains of seals and sea lions with complex vocal behavior learning
Watching a lifetime in motion reveals the architecture of aging
Rapid evolution can ‘rescue’ species from climate change
Molecular garbage on tumors makes easy target for antibody drugs
[Press-News.org] Podcasts and compulsory attendance improved student learningWe all know the old one-way lecture to an enormous auditorium of students isn't the best way to teach – so what actually works?