(Press-News.org) Women who consume higher amounts of protein, especially protein from plant-based sources, develop fewer chronic diseases and are more likely to be healthier overall as they age, according to a study led by researchers at the Jean Mayer USDA Human Nutrition Research Center on Aging (HNRCA) at Tufts University and published Jan. 17 in The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition.
Analyzing self-reported data from more than 48,000 women, the researchers saw notably less heart disease, cancer, and diabetes, and cognitive and mental health decline, in those who included more protein in their diets from sources such as fruits, vegetables, bread, beans, legumes, and pasta, compared to those who ate less.
“Consuming protein in midlife was linked to promoting good health in older adulthood,” said Andres Ardisson Korat, a scientist at the HNRCA and lead author of the study. “We also found that the source of protein matters. Getting the majority of your protein from plant sources at midlife, plus a small amount of animal protein seems to be conducive to good health and good survival to older ages.”
Findings were derived from the seminal Harvard-based Nurses’ Health Study, which followed female health care professionals from 1984 to 2016. The women were between the ages of 38 and 59 in 1984 and deemed to be in good physical and mental health at the start of the study.
Ardisson Korat and fellow researchers, including senior author Qi Sun of the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, examined thousands of surveys collected every four years from 1984 to 2016 on how frequently people ate certain foods to pinpoint dietary protein and its effects on healthy aging. They calculated protein intake by multiplying the number of times each food item was consumed by its protein content and then, using the Harvard University Food Composition Database, totaling the amount of protein across all food items.
The researchers then compared the diets of women who didn’t develop 11 chronic diseases or lose a lot of physical function or mental health, with the diets of those who did. Women who ate more plant-based protein, which in 1984 was defined as protein obtained from bread, vegetables, fruits, pizza, cereal, baked items, mashed potatoes, nuts, beans, peanut butter, and pasta, were 46 percent more likely to be healthy into their later years. Those who consumed more animal protein such as beef, chicken, milk, fish/seafood, and cheese, however, were 6 percent less likely to stay healthy as they aged.
“Those who consumed greater amounts of animal protein tended to have more chronic disease and didn’t manage to obtain the improved physical function that we normally associate with eating protein,” said Ardisson Korat.
Animal protein was modestly tied with fewer physical limitations in older age, but plant protein had a stronger, more consistent correlation across all observed models, and was more closely linked with sound mental health later in life. For heart disease in particular, higher plant protein consumption came with lower levels of LDL cholesterol (“bad” cholesterol), blood pressure, and insulin sensitivity, while higher animal protein intake was tied to higher levels, along with increased insulin-like growth factor, which has been detected in multiple cancers.
Dairy protein alone (mainly milk, cheese, pizza, yogurt, and ice cream) was not significantly associated with better health status in older adulthood.
The team acknowledged that the benefits of plant protein might derive from components in plant-based food, rather than the protein—compared to animal foods, plants contain a higher proportion of dietary fiber, micronutrients, and beneficial compounds called polyphenols that are present in plants, rather than exclusively protein.
Ardisson Korat also said data from other groups is needed, as the Nurses’ Health Study surveyed primarily white females working in health care. “The data from the study tended to be very homogeneous in terms of demographic and socioeconomic composition, so it will be valuable to follow up with a study in cohorts that are more diverse. It’s a field that is still evolving,” said Ardisson Korat.
But the team’s findings so far support the recommendation that women eat most of their protein in the form of fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds, although they should also consume some fish and animal protein for their iron and vitamin B12 content.
“Dietary protein intake, especially plant protein, in midlife plays an important role in the promotion of healthy aging and in maintaining positive health status at older ages,” Ardisson Korat said.
Research reported in this article was supported by the U.S. Department of Agriculture’s Agricultural Research Service, and by the National Institutes of Health under award numbers UM1CA186107 (National Cancer Institute), P01CA87969 (National Cancer Institute), R01DK120870 (National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases), U2CDK129670 (National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases), R01DK127601 (National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases), R01HL060712 (National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute), R01HL034594 (National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute), R01HL035464 (National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute), and R01HL088521 (National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute). Andres Ardisson Korat was supported by training grant KL2TR002545 from the National Institutes of Health’s National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences. Complete information on authors, funders, limitations and conflicts of interest is available in the published paper. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the U.S. Department of Agriculture or the National Institutes of Health.
END
Diets rich in plant protein may help women stay healthy as they age
A new Tufts University-led study found women who ate more plant-based protein developed fewer chronic diseases and were generally healthier later in life
2024-01-17
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Study uncovers mechanics of machete-like ‘tail-whipping’ in thresher sharks
2024-01-17
Like Indiana Jones, thresher sharks (Alopias spp.) have mastered the art of the whip using their tails. With incredible speed, their long, machete-like tails can slap and stun their prey, allowing them to swallow multiple fish in one fell swoop. Their exceptionally elongated tail, which can often be as long as their entire body, not only makes this particular shark unique, but also a formidable hunter.
Thresher shark “tail-whipping” consists of four phases: preparation, strike, wind-down recovery, and prey collection. Overhead tail slaps begin in the preparation phase by lunging ...
Glowing COVID-19 diagnostic test prototype produces results in one minute
2024-01-17
Cold, flu and COVID-19 season brings that now-familiar ritual: swab, wait, look at the result. But what if, instead of taking 15 minutes or more, a test could quickly determine whether you have COVID-19 with a glowing chemical? Now, in ACS Central Science, researchers describe a potential COVID-19 test inspired by bioluminescence. Using a molecule found in crustaceans, they have developed a rapid approach that detects SARS-CoV-2 protein comparably to one used in vaccine research.
From fireflies ...
Microplastics from natural fertilizers are blowing in the wind more often than once thought
2024-01-17
Though natural fertilizers made from treated sewage sludge are used to reintroduce nutrients onto agricultural fields, they bring along microplastic pollutants too. And according to a small-scale study published in ACS’ Environmental Science & Technology Letters, more plastic particles get picked up by the wind than once thought. Researchers have discovered that the microplastics are released from fields more easily than similarly sized dust particles, becoming airborne from even a slight breeze.
Microplastics, or small bits of plastic less than 5 millimeters long, have appeared everywhere from clouds to heart tissues. And with these plastics’ increasing prevalence in ...
New AI makes better permafrost maps
2024-01-17
LOS ALAMOS, N.M., Jan. 17, 2024 — New insights from artificial intelligence about permafrost coverage in the Arctic may soon give policy makers and land managers the high-resolution view they need to predict climate-change-driven threats to infrastructure such as oil pipelines, roads and national security facilities.
“The Arctic is warming four times faster than the rest of the globe, and permafrost is a component of the Arctic that’s changing really rapidly,” said Evan Thaler, a Chick Keller Postdoctoral Fellow at Los Alamos National Laboratory. Thaler is corresponding ...
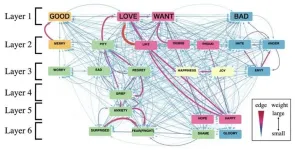
New study unveils emotional hubs that exist across languages
2024-01-17
Emotions exert a profound influence on human behavior, prompting extensive explorations in the realms of psychology and linguistics. Understanding central emotions also has practical utility since it can help organizations create messages that resonate better with people. For instance, businesses can enhance their connection with their customers, and non-profits can prompt quicker action by skillfully leveraging the salient emotions in humans.
Colexification is a phenomenon in which the occurrence of a single word is associated with multiple concepts that share semantic relationships. The analysis of colexification is an innovative linguistic method for ...
Childhood stress linked to higher risk of high blood pressure, obesity, diabetes in adults
2024-01-17
Research Highlights:
Consistently high scores of perceived stress during adolescence through adulthood may contribute to worse cardiometabolic health including obesity in young adults..
Researchers suggest the adoption of healthy coping strategies for stress management early in life may help prevent cardiometabolic diseases, from heart disease to Type 2 diabetes.
Embargoed until 4 a.m. CT/5 a.m. ET Wednesday, January 17, 2024
DALLAS, January 17, 2024 — Young adults who reported higher stress during their teenage years to adulthood were more likely to ...
US air pollution rates on the decline but pockets of inequities remain
2024-01-17
Over the last decades, air pollution emissions have decreased substantially; however, the magnitude of the change varies by demographics, according to a new study by Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health. The results indicate there are racial/ethnic and socioeconomic disparities in air pollution emissions reductions, particularly in the industry and energy generation sectors. The findings are published in the journal Nature Communications.
The research provides a national investigation of air pollution emission ...
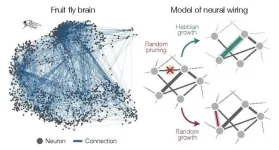
Fly brain, mouse brain, worm brain: They all network the same
2024-01-17
New York, January 17, 2024 — In all species, brain function relies on an intricate network of connections that allows neurons to send information back and forth between one another, commanding thought and physical activity. But within those networks a small number of neurons share much stronger connections to one another than all the others. These abnormally strong connections—known as “heavy tailed” based on the shape of their distribution—are thought to play an outsized role in brain function.
Researchers ...
Surprisingly simple model explains how brain cells organize and connect
2024-01-17
A new study by physicists and neuroscientists from the University of Chicago, Harvard and Yale describes how connectivity among neurons comes about through general principles of networking and self-organization, rather than the biological features of an individual organism.
The research, published on January 17, 2024 in Nature Physics, accurately describes neuronal connectivity in a variety of model organisms and could apply to non-biological networks like social interactions as well.
“When you’re building simple models to ...
Transforming clinical recording of deep brain activity with a new take on sensor manufacturing
2024-01-17
Sensors built with a new manufacturing approach are capable of recording activity deep within the brain from large populations of individual neurons–with a resolution of as few as one or two neurons–in humans as well as a range of animal models, according to a study published in the Jan. 17, 2024 issue of the journal Nature Communications. The research team is led by the Integrated Electronics and Biointerfaces Laboratory (IEBL) at the University of California San Diego.
The approach is unique in several ways. It relies on ultra-thin, flexible and customizable probes, made of clinical-grade materials, and equipped with sensors that can record extremely localized ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
SKKU research team unravels the origin of stochasticity, a key to next-generation data security and computing
Flexible polymer‑based electronics for human health monitoring: A safety‑level‑oriented review of materials and applications
Could ultrasound help save hedgehogs?
attexis RCT shows clinically relevant reduction in adult ADHD symptoms and is published in Psychological Medicine
Cellular changes linked to depression related fatigue
First degree female relatives’ suicidal intentions may influence women’s suicide risk
Specific gut bacteria species (R inulinivorans) linked to muscle strength
Wegovy may have highest ‘eye stroke’ and sight loss risk of semaglutide GLP-1 agonists
New African species confirms evolutionary origin of magic mushrooms
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
IU researchers identify clotting protein as potential target in pancreatic cancer
Human moral agency irreplaceable in the era of artificial intelligence
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
GLP-1RA switching and treatment persistence in adults without diabetes
[Press-News.org] Diets rich in plant protein may help women stay healthy as they ageA new Tufts University-led study found women who ate more plant-based protein developed fewer chronic diseases and were generally healthier later in life