(Press-News.org) A common test used to decide whether breast cancer patients should get chemotherapy may be making bad recommendations for some Black women, leading them to forgo chemotherapy when it might have helped, according to new research from the University of Illinois Chicago.
The test, known as the 21-gene breast recurrence score, is the most commonly ordered biomarker test used to guide doctor’s recommendations for patients with estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer — the most common form of the cancer. The test helps identify which tumors are likely to be most aggressive and thus better candidates for chemotherapy.
The researchers conducted a statistical analysis on a database that included both test results and death records for more than 70,000 women with early-stage, estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer. They found that the test may underestimate the benefit of chemotherapy for Black women by ranking some, especially young patients, as unlikely to benefit from chemotherapy when in fact they may have benefited.
“The test could be misguiding treatment,” explained Dr. Kent Hoskins, a professor of oncology at UIC and senior author of the Journal of the National Comprehensive Cancer Network study.
The researchers did an exploratory analysis to gauge whether the test’s cutoff point for recommending chemotherapy for Black women should be lowered and found that it should. But Hoskins said a fuller study needs to be done before making that recommendation.
Still, “the research shows that it may be inappropriate for doctors to use exact cutoffs and tests regardless of race or ethnicity because there are underlying differences in biology,” said Hoskins, who is also a member of the University of Illinois Cancer Center.
Almost all patients with this sort of cancer receive pills that block estrogen, whether or not they also get chemotherapy. The researchers suspect the cause of this treatment gap is because Black women’s tumors are less likely to respond to the estrogen-blocking pills than tumors in other women. So chemotherapy helps improve outcomes for them more than it would for women who benefit from the pills alone, Hoskins said. The researchers have another paper in the works looking at this question.
The paper is part of a body of work by UIC researchers looking at outcomes for Black women who have estrogen receptor-positive tumors. While much attention has been paid to the negative outcomes for Black women who have the harder-to-treat triple-negative breast cancer, which makes up only about 20% of breast cancer cases for Black women, Hoskins explained. Previous research from this team found that while Black women are more likely than white women to get triple-negative breast cancer, they aren’t more likely to die from it. Yet they are more likely to die from the more common estrogen receptor-positive form.
Hoskins stresses that while this new paper points to biological differences in tumors for Black versus white women, that does not rule out the contribution of a host of social factors caused by structural racism. But those factors, such as access to health care, do not account for the whole picture. Indeed, Hoskins believes that the same social determinants of health that lead to worse outcomes for Black women in the health care system are also causing the biological differences in tumors. The researchers have a paper in the works looking at this question, too.
“We believe that it’s actually the same forces that lead to inequities in care that are driving this more aggressive biology,” he said.
The other UIC authors on the paper are Hsiao-Ching Huang, Dr. V.K. Gadi, Dr. Oana Danciu, and Garth Rauscher, from the cancer center, College of Pharmacy, College of Medicine and School of Public Health.
Written by Emily Stone
END
Breast cancer test may make bad chemotherapy recommendations for Black patients
2024-01-29
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
First-ever sighting of a live newborn great white
2024-01-29
Great whites, the largest predatory sharks in the world with the most fatal attacks on humans, are tough to imagine as newborn babies. That is partially because no one has seen one in the wild, it seems, until now.
Wildlife filmmaker Carlos Gauna and UC Riverside biology doctoral student Phillip Sternes were scanning the waters for sharks on July 9, 2023, near Santa Barbara on California’s central coast. That day, something exciting appeared on the viewfinder of Gauna’s drone camera. It was a shark ...
Back from the dead: Tropical tree fern repurposes its dead leaves
2024-01-29
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — Plant biologists report that a species of tree fern found only in Panama reanimates its own dead leaf fronds, converting them into root structures that feed the mother plant. The fern, Cyathea rojasiana, reconfigures these “zombie leaves,” reversing the flow of water to draw nutrients back into the plant.
Watch a video about the findings.
This weird phenomenon occurs only after the leaves die and droop to the ground, said University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign plant biology professor James Dalling, ...
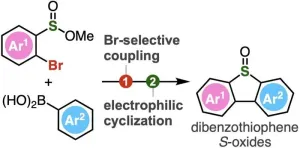
New horizons in chemical biology: A novel approach to synthesize dibenzothiophene s-oxides
2024-01-29
Organic compounds in the field of chemistry range from simple hydrocarbons to complex molecules, with diverse functional groups added to the main carbon backbone. These functional groups impart the compounds distinct chemical properties as well as participate in various chemical transformations, making them important precursors for the synthesis of diverse compounds. Scientists have, therefore, actively engaged in creating molecules that feature novel and highly reactive functional groups.
One such class of compounds are dibenzothiophenes and their derivatives containing ...
Variant in the synaptonemal complex protein SYCE2 associates with pregnancy loss through effects on recombination
2024-01-29
A sequence variant that increases risk of pregnancy loss
Scientists at deCODE genetics, a subsidiary of Amgen and their collaborators from Iceland, Denmark and USA published a study today in Nature Structural and Molecular Biology titled “Variant in the synaptonemal complex protein SYCE2 associates with pregnancy loss through effects on recombination”.
While it is well established that chromosomal abnormalities are a major cause of miscarriages the biology behind pregnancy losses with or without chromosomal errors is not well understood. Over 114 thousand women from Iceland, Denmark, UK, USA and Finland who have ...
How obesity dismantles our mitochondria
2024-01-29
The number of people with obesity has nearly tripled since 1975, resulting in a worldwide epidemic. While lifestyle factors like diet and exercise play a role in the development and progression of obesity, scientists have come to understand that obesity is also associated with intrinsic metabolic abnormalities. Now, researchers from University of California San Diego School of Medicine have shed new light on how obesity affects our mitochondria, the all-important energy-producing structures of our cells.
In a study published January ...
Cancer treatment two and a half times more effective when tumours have defective "energy factories"
2024-01-29
Cancer Research UK-funded scientists have made an unusual discovery that could help to identify patients who are up to two and a half times more likely to respond to currently available cancer drugs.
Scientists at the Cancer Research UK Scotland Institute and Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Centre in the USA have “rewired” the DNA of mitochondria – energy factories found in every living cell. They found that creating mutations in parts of this DNA determines how well cancer will respond to immunotherapy – treatments which harness the body’s natural defences ...
How does a “reverse sprinkler” work? Researchers solve decades-old physics puzzle
2024-01-29
For decades scientists have been trying to solve Feynman’s Sprinkler Problem: How does a sprinkler running in reverse—in which the water flows into the device rather than out of it—work? Through a series of experiments, a team of mathematicians has figured out how flowing fluids exert forces and move structures, thereby revealing the answer to this long-standing mystery.
“Our study solves the problem by combining precision lab experiments with mathematical modeling that explains how a reverse sprinkler operates,” explains Leif Ristroph, an associate professor at New York University’s Courant Institute of Mathematical Sciences and the senior author ...
Neuroblastoma: Liquid biopsies to detect relapse of childhood cancer early
2024-01-29
(Utrecht/Vienna, 29.1.2024) Neuroblastoma mainly affects toddlers and young children - in the EU region there are 1500 new cases per year. Neuroblastoma is a malignant tumor of the peripheral nervous system and around 50% of patients are high-risk cases. Recurrences occur frequently, and conventional therapies are no longer effective for these children. With liquid biopsies it is possible to monitor therapy success and to predict the recurrence of the tumor in time to take medical countermeasures. Scientists from leading European ...
Speaking in a local accent might make social robots seem more trustworthy and competent
2024-01-29
Social robots can help us with many things: teaching, learning, caring. Because they’re designed to interact with humans, they’re designed to make us comfortable — and that includes the way they talk. But how should they talk? Some research suggests that people like robots to use a familiar accent or dialect, while other research suggests the opposite.
“Surprisingly, people have mixed feelings about robots speaking in a dialect — some like it, while others prefer standard language,” said Katharina Kühne of the University of Potsdam, lead author ...
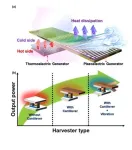
Hybrid energy harvesters that harness heat and vibration simultaneously
2024-01-29
Harvesting energy sources such as heat, vibration, light, and electromagnetic waves from everyday environments such as industrial sites and automobiles and converting them into electrical energy is known as energy harvesting. Energy harvesting makes it easier to power today's popular IoT sensors and wireless devices that are located in environments where battery replacement is difficult.
Dr. Hyun-Cheol Song and Dr. Sunghoon Hur of Electronic Materials Research Center at the Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST) have developed a hybrid energy harvesting ...