(Press-News.org) COLUMBUS, Ohio – A neighborhood alcohol control project in Sacramento that reduced cases of child abuse and neglect soon after implementation still had a positive impact seven years later, a new study found.
Results showed that, in one of the neighborhoods where the program was put into place, total entries into foster care were reduced by 11.8% and alcohol-related foster care entries were reduced by 11.2% a full seven years after implementation.
These new results were not as strong as those found right after the project was implemented, and there are other caveats to the success of the program. But the results are still very encouraging, said Bridget Freisthler, lead author of the study and professor of social work at The Ohio State University.
“We knew that this project had short-term success, but it is rare to have the opportunity to see if an intervention like this continues to be effective years afterwards,” Freisthler said.
“Now we have evidence that it actually does have a positive long-term effect.”
The study was published today (Jan. 30, 2024) in the journal Drug and Alcohol Review.
In this study, the researchers examined the effect of the Sacramento Neighborhood Alcohol Prevention Project (SNAPP), an intervention implemented from 1999-2003 aimed at reducing alcohol-related problems in two neighborhoods in the city. The project wasn’t designed specifically to reduce child abuse and neglect, but the researchers believed it would have that positive effect, based on previous studies.
For example, one study led by Freisthler showed that the number of stores selling alcohol in a neighborhood is linked to cases of child abuse and neglect in the same area. Another study found that a 1% increase in the volume of alcohol consumption per capita in Sacramento was related to 3.2% more alcohol-related foster care entries.
The two low-income, racially diverse neighborhoods in the study – dubbed the North area and South area – were selected because they had high rates of crime and alcohol-related problems.
SNAPP was a community-based intervention focused on reducing alcohol supply, namely to underage youth and already intoxicated people. The project included mobilization of local leaders, community awareness activities for neighborhood residents, responsible beverage service training for managers and staff at alcohol outlets, and increased enforcement of alcohol-related laws.
An earlier study showed that, shortly after SNAPP was implemented, alcohol-related foster care entries were reduced by 24% in the North area, but actually increased in the South area.
There may be several reasons for that finding in the South area, Freisthler said. One is that there was a cluster of serious child abuse and neglect cases in the South area during the intervention period, so case workers may have been more likely to place children into foster care when a parent was misusing alcohol during this time period.
In addition, the study implementation for the South area (but not the North) began right before the Sept. 11, 2001, terrorist attacks. Research has shown that alcohol use across the country rose right after the attacks, which may have led to more child abuse cases.
But in this new study, there was no longer any increase in foster care entries in the South area after seven years.
“The increases in child abuse and neglect that we saw in the South area are gone seven years later, but the decreases in the North area are continuing. That’s great news,” Freisthler said.
The researchers don’t know how many parts of SNAPP were still being implemented seven years later. It is possible that some parts were dropped, and others were no longer a priority, Freisthler said.
So the fact that this intervention program was still having a significant positive impact should encourage similar efforts, according to the researchers.
Freisthler noted that most interventions to stop alcohol misuse and its effects on child abuse happen at the individual and family level.
The power of SNAPP is that it is a community-level intervention that is designed to change the neighborhood environment, reducing the easy access to alcohol throughout the entire community.
“Changing the environment surrounding alcohol is more effective and less costly than working just with individuals and families,” Freisthler said.
“This study provides evidence that effects of environmental prevention efforts can be maintained for a significant period of time after they are implemented.”
And an environmental intervention like SNAPP has a lot of positive effects on the neighborhood.
“It reduces traffic crashes, it reduces assaults, it reduces child abuse and neglect,” Freisthler said. “One project like this does a lot to improve public health.”
Freisthler conducted the study with Jennifer Price Wolf, associate professor of social work at San Jose State University.
The research was supported by a grant from the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism.
END
After 7 years, alcohol control program still reduces child abuse
Study examined long-term impact of prevention effort
2024-01-30
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Prenatal substance exposure and childhood mental health
2024-01-30
An observational study found links between prenatal substance exposure and mental health in children 10–12, but also found that controlling for environment and genetics eliminated many associations. Qiang Luo and colleagues analyzed longitudinal data from almost 10,000 participants in the Adolescent Brain Cognitive Development cohort, looking for associations of maternal self-report of prenatal exposure to caffeine, alcohol, tobacco, and marijuana with mental health outcomes from age 10 to 12. Although the authors found many associations between prenatal exposure to the ...
Gene-based therapy may slow development of life-threatening heart condition
2024-01-30
A new study in mice shows that replacement of a dysfunctional gene could prolong survival in some people with arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy (ARVC), a rare inherited disorder in which the muscular walls of the heart progressively weaken and put patients at risk of dangerous irregular heartbeats.
The investigational treatment targets the loss of function of a gene implicated in many cases of ARVC, plakophilin-2 (PKP2). The PKP2 gene provides instructions for making a protein that holds heart tissues together. When the gene — one of several thought to contribute to the disease —is defective ...
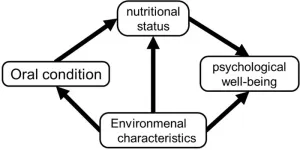
Oral health indirectly influences subjective psychological well-being in older adults
2024-01-30
In humans, oral health influences general health and well-being in many ways. Other than reducing the need for oral rehabilitation later in life, maintaining good oral health reduces the risk of several systemic diseases. Therefore, investing time and effort into improving oral health can be highly beneficial for older adults. However, whether the health benefits of improved oral health extend to psychological domains remains unclear.
Positive psychological well-being is known to positively affect the survival rates of both healthy and unhealthy populations. Thus, to increase life expectancy, it is important to identify the factors associated with ...
Asparagus and orchids are more similar than you think
2024-01-30
What does an asparagus have in common with a vanilla orchid? Not much, if you are just looking at the two plants’ appearances. However, when you look inside - their leaves are more similar than you would think – as revealed by the composition of their cell walls.
By studying plant cell walls – which are to plants what skeletons are to humans – we can reveal the composition of how leaves and stems of plants are actually constructed. This is exactly what a team of University of Copenhagen researchers has done, in a large comprehensive study. In doing so, they have created something truly novel: a large "reference catalogue" ...
DNA particles that mimic viruses hold promise as vaccines
2024-01-30
Using a virus-like delivery particle made from DNA, researchers from MIT and the Ragon Institute of MGH, MIT, and Harvard have created a vaccine that can induce a strong antibody response against SARS-CoV-2.
The vaccine, which has been tested in mice, consists of a DNA scaffold that carries many copies of a viral antigen. This type of vaccine, known as a particulate vaccine, mimics the structure of a virus. Most previous work on particulate vaccines has relied on protein scaffolds, but the proteins used in those vaccines tend to generate an unnecessary immune response that can distract the immune system from the target.
In the mouse study, the researchers found that the ...
Citizen scientists contribute to motor learning research
2024-01-30
A new research study examined the results from data generated by citizen scientists using a simple web-based motor test. The big data approach provides researchers with a unique way to explore how people correct for motor control errors. The resulting insights may one day pave the way for personalized physical therapy or tailor an athlete’s training routine. The results are available in the January 30th issue of the journal Nature Human Behaviour.
“This exploratory approach does not replace lab based studies, but complements ...
New research shows how pollutants from aerosols and river run-off are changing the marine phosphorus cycle in coastal seas
2024-01-30
New research into the marine phosphorus cycle is deepening our understanding of the impact of human activities on ecosystems in coastal seas.
The research, co-led by the University of East Anglia, in partnership with the Sino-UK Joint Research Centre at the Ocean University of China, looked at the impact of aerosols and river run-off on microalgae in the coastal waters of China.
It identified an ‘Anthropogenic Nitrogen Pump’ which changes the phosphorus cycle and therefore likely coastal biodiversity and associated ecosystem services.
In a balanced ecosystem, microalgae, also known as phytoplankton, provide food for a wide ...
How a mouse’s brain bends time
2024-01-30
Life has a challenging tempo. Sometimes, it moves faster or slower than we’d like. Nevertheless, we adapt. We pick up the rhythm of conversations. We keep pace with the crowd walking a city sidewalk.
“There are many instances where we have to do the same action but at different tempos. So the question is, how does the brain do it," says Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Assistant Professor Arkarup Banerjee.
Now, Banerjee and collaborators have uncovered a new clue that suggests the brain bends our processing of time to suit our ...
Religious people coped better with the Covid-19 pandemic, research suggests
2024-01-30
People of religious faith may have experienced lower levels of unhappiness and stress than secular people during the UK’s Covid-19 lockdowns in 2020 and 2021, according to new University of Cambridge research.
The findings follow a recently published Cambridge-led study suggesting that worsening mental health after experiencing Covid infection – either personally or in those close to you – was also somewhat ameliorated by religious belief. This study looked at the US population during early 2021.
University of Cambridge economists argue ...
IHI launches a new interdisciplinary initiative to revolutionize the way Alzheimer’s disease is detected, diagnosed, prevented, and treated
2024-01-30
Stockholm, January 30, 2024 — Members of the AD-RIDDLE consortium announced today that they will begin a new initiative that aims to bridge the gap between Alzheimer’s research, implementation science, and precision medicine. The AD-RIDDLE programme will offer healthcare professionals a suite of validated solutions for timely detection and diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease and dementias, to match individuals with the right interventions at the right time, enabling people to better understand what they can do to reduce risk and prevent cognitive decline.
Alzheimer’s disease represents a major public ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Asteroid samples offer new insights into conditions when the solar system formed
Fecal transplants from older mice significantly improve ovarian function and fertility in younger mice
Delight for diastereomer production: A novel strategy for organic chemistry
Permafrost is key to carbon storage. That makes northern wildfires even more dangerous
Hairdressers could be a secret weapon in tackling climate change, new research finds
Genetic risk for mental illness is far less disorder-specific than clinicians have assumed, massive Swedish study reveals
A therapeutic target that would curb the spread of coronaviruses has been identified
Modern twist on wildfire management methods found also to have a bonus feature that protects water supplies
AI enables defect-aware prediction of metal 3D-printed part quality
Miniscule fossil discovery reveals fresh clues into the evolution of the earliest-known relative of all primates
World Water Day 2026: Applied Microbiology International to hold Gender Equality and Water webinar
The unprecedented transformation in energy: The Third Energy Revolution toward carbon neutrality
Building on the far side: AI analysis suggests sturdier foundation for future lunar bases
Far-field superresolution imaging via k-space superoscillation
10 Years, 70% shift: Wastewater upgrades quietly transform river microbiomes
Why does chronic back pain make everyday sounds feel harsher? Brain imaging study points to a treatable cause
Video messaging effectiveness depends on quality of streaming experience, research shows
Introducing the “bloom” cycle, or why plants are not stupid
The Lancet Oncology: Breast cancer remains the most common cancer among women worldwide, with annual cases expected to reach over 3.5 million by 2050
Improve education and transitional support for autistic people to prevent death by suicide, say experts
GLP-1 drugs like Ozempic could cut risk of major heart complications after heart attack, study finds
Study finds Earth may have twice as many vertebrate species as previously thought
NYU Langone orthopedic surgeons present latest clinical findings and research at AAOS 2026
New journal highlights how artificial intelligence can help solve global environmental crises
Study identifies three diverging global AI pathways shaping the future of technology and governance
Machine learning advances non targeted detection of environmental pollutants
ACP advises all adults 75 or older get a protein subunit RSV vaccine
New study finds earliest evidence of big land predators hunting plant-eaters
Newer groundwater associated with higher risk of Parkinson’s disease
New study identifies growth hormone receptor as possible target to improve lung cancer treatment
[Press-News.org] After 7 years, alcohol control program still reduces child abuseStudy examined long-term impact of prevention effort