(Press-News.org) Since the onset of COVID-19, we've become accustomed to seeing antiviral films attached to elevator buttons and public transportation handles. However, conventional antiviral films are made by mixing antiviral metal particles with polymers. Due to the manufacturing process, only a very small fraction of these metal particles is exposed on the surface. As a result, contrary to the belief that these films will protect us from viruses, the actual antiviral effect upon contact with the film surface is not significant.
The Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST) has announced that a collaborative research team led by Dr. So-Hye Cho from the Materials Architecturing Research Center and Dr. Seung Eun Lee of the Research Animal Resources Center has developed a nanocoating technology that not only maximizes the antiviral activity of the surface, but also enables the realization of various colors.
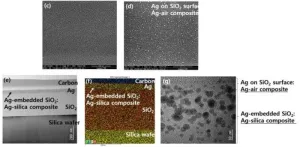
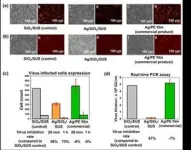
The research team has developed an effective antiviral and antibacterial surface by using the sol-gel method to form a silica coating layer on various surfaces, followed by coating the silica layer with silver (Ag) nanoparticles using an aqueous solution containing silver. In turn, silver nanoparticles limit the infectivity of viruses by binding to the proteins on the virus surface, disrupting the structure and function of the virus, and making it difficult for the virus to penetrate cells.
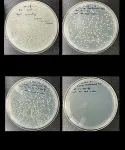
In conventional antiviral films, antiviral functional metal particles are embedded within the thin film, making it difficult for silver to come in contact with viruses. However, the technology developed by the KIST research team showcased remarkable activity with a small amount of silver nanoparticles positioned on the thin film's surface. Experiments involving lentiviruses, developed as analogs to coronaviruses, demonstrated a virus elimination rate more than twice as fast compared to commercial films. In addition, antibacterial tests against E. coli bacteria resulted in complete eradication of the bacteria within 24 hours. The developed antiviral coating technology also has the additional advantage of providing various colors by controlling light interference through different coating layer thickness.
"This metal nanoparticle coating technology demonstrates superior antiviral and antibacterial effects compared to commercial products, even with a small coating of less than 1 g/m2, so its industrialization potential is very high," said Dr. So-Hye Cho of KIST. "It can be used in various industries such as medical materials, home appliances, and building materials to help manage microorganisms and prevent infections by implementing antiviral and antibacterial effects."
###
KIST was established in 1966 as the first government-funded research institute in Korea. KIST now strives to solve national and social challenges and secure growth engines through leading and innovative research. For more information, please visit KIST’s website at https://eng.kist.re.kr/
The research, which was supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT (Minister Lee Jong-ho) through the Korea Research Foundation-Nano and Materials Technology Development Project (2020M3H4A3106354), KIST Future Source Research Project (2E32511), and K-DARPA Innovative Technology Development Project, was published online in the international journal ACS Applied Materials and Interfaces (IF: 9.5, JCR(%): 7.956) on November 9, 2023.
END
Antiviral color nanocoating technology
Virus elimination effect along with a wide range of colors achieved with a low coating amount of 1g/m2. Expected to be utilized in various industries such as medical materials, home appliances, building materials, etc.
2024-01-31
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Key LiDAR sensor elements for autonomous vehicles are now made with our technology
2024-01-31
LiDAR sensors are indispensable for the realization of advanced technologies such as advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS), autonomous driving, and AR/VR. In particular, short- and mid-range LiDAR used in AR/VR devices and smartphones requires better distance (depth) resolution to detect the shape of a person or object more accurately, and so a single-photon detector with better timing jitter performance is required.
LiDAR measures distance and creates a 3D image by calculating the time it takes for a photon emitted by the transmitter to strike an object, reflect, and arrive back at the ...
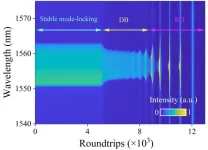
Dissipative soliton vanishes, breathing dynamics occur
2024-01-31
Solitons are quasiparticles that propagate along a non-dissipative wave. Put another way, they are waveforms that hold their shape as they move—like a single wave moving across the surface of a pond. They can also show the particle-like behavior, such as collision, attraction, and repulsion. Ultrafast fiber laser is an ideal platform to explore nonlinear dissipation dynamics, but also deepen the understanding of optical soliton properties. In dissipative system, dissipative soliton can be obtained due to the balance between nonlinearity and ...
American Heart Month 2024 brings renewed focus on CPR, urgent need for Nation of Lifesavers™
2024-01-31
DALLAS, Jan. 30, 2024 — A new survey conducted by the American Heart Association, which is marking one hundred years of service saving lives, suggests that increased visibility of the need for CPR has had a positive impact on someone’s willingness to respond if they are bystanders in a cardiac emergency. However, there remains a significant gap in awareness that emphasizes the urgent need for collaboration between governments, communities, businesses and the media to promote and provide lifesaving training. To help close this gap, the ...
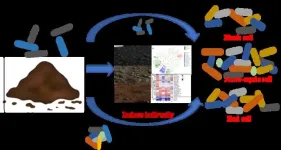
Fluvo-aquic soil treated with pig manure present a higher risk of antibiotic-resistant bacteria than black and red soils
2024-01-31
In agroecosystems where manure is applied as organic fertilizer, these antibiotic residues exert strong selective pressure on soil microbial communities. Antibiotic-resistant bacteria (ARB) from animal manure would increase the concentration of ARB in soils. The influencing mechanisms of soil types on the distribution of ARB were worthy of further exploration. This study demonstrates that CTC-manure induced more resistance of soil indigenous microbes in fluvo-aquic soil, Lactobacillus, Dyella, Ralstonia, and Bacillus ...
Black summer bushfires in Australia wiped $2.8 billion from tourism supply chain
2024-01-31
A first of its kind study of the 2019-2020 ‘Black Summer’ bushfires in Australia has revealed that the tourism industry nationwide took an immediate hit of $2.8 billion in total output to its broader supply chains and almost 7300 jobs disappeared nationwide.
The fires four years ago triggered widespread tourism shutdowns in many parts of the country in the lead up to the peak Christmas and New Year season, resulting in $1.7 billion direct losses to the tourism industry, which triggered the larger drop in supply chain output.
“These results are an illustration of what can be expected in the future not only in Australia, but in other ...
Using computers to design proteins allows researchers to make tunable hydrogels that can form both inside and outside of cells
2024-01-31
When researchers want to study how COVID makes us sick, or what diseases such as Alzheimer's do to the body, one approach is to look at what's happening inside individual cells.
Researchers sometimes grow the cells in a 3D scaffold called a "hydrogel." This network of proteins or molecules mimics the environment the cells would live in inside the body.
New research led by the University of Washington demonstrates a new class of hydrogels that can form not just outside cells, but also inside of them. The team created these hydrogels from protein building blocks designed using a computer to form a specific structure. These hydrogels exhibited similar mechanical properties ...
BIPOC individuals bear greater post-COVID burdens
2024-01-31
A study study published today reports that BIPOC individuals who were infected with COVID-19 experienced greater negative aftereffects in health and work loss than did similarly infected white participants.
Despite similar symptom prevalence, Hispanic participants compared to non-Hispanic participants and BIPOC participants compared to white participants had more negative impacts following a COVID-19 infection in terms of health status, activity level and missed work, the authors wrote.
The findings appeared in the journal Frontiers ...
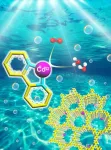
Anchoring single Co sites on bipyridine-based CTF for photocatalytic oxygen evolution
2024-01-31
Photocatalytic water splitting using semiconductors is regarded as a promising technique for producing hydrogen fuel from solar energy. The oxygen evolution half reaction has proven to be the bottleneck for photocatalytic overall water splitting owing to the high energy barrier and the sluggish kinetics. It is a big challenge to develop efficient photocatalysts for the advancement of water oxidation.
Similar to graphene carbon nitride, π-stacked covalent triazine frameworks (CTFs) have gained much attention in photocatalytic water splitting in recent years. The fully conjugated structure with the regular channels in the crystalline network will provide defined pathways for ...
AI-powered app can detect poison ivy
2024-01-31
Poison ivy ranks among the most medically problematic plants. Up to 50 million people worldwide suffer annually from rashes caused by contact with the plant, a climbing, woody vine native to the United States, Canada, Mexico, Bermuda, the Western Bahamas and several areas in Asia.
It’s found on farms, in woods, landscapes, fields, hiking trails and other open spaces. So, if you go to those places, you’re susceptible to irritation caused by poison ivy, which can lead to reactions that require medical attention. Worse, most people don’t know ...
Up to three daily servings of kimchi may lower men’s obesity risk
2024-01-31
Eating up to three daily servings of the Korean classic, kimchi, may lower men’s overall risk of obesity, while radish kimchi is linked to a lower prevalence of midriff bulge in both sexes, finds research published in the open access journal BMJ Open.
Kimchi is made by salting and fermenting vegetables with various flavourings and seasonings, such as onion, garlic, and fish sauce.
Cabbage and radish are usually the main vegetables used in kimchi, which contains few calories and is rich in dietary fibre, microbiome enhancing lactic acid bacteria, vitamins, and polyphenols.
Previously published experimental studies ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
A comprehensive review charts how psychiatry could finally diagnose what it actually treats
Thousands of genetic variants shape epilepsy risk, and most remain hidden
First comprehensive sex-specific atlas of GLP-1 in the mouse brain reveals why blockbuster weight-loss drugs may work differently in females and males
When rats run, their gut bacteria rewrite the chemical conversation with the brain
Movies reconstructed from mouse brain activity
Subglacial weathering may have slowed Earth's escape from snowball Earth
Simple test could transform time to endometriosis diagnosis
Why ‘being squeezed’ helps breast cancer cells to thrive
Mpox immune test validated during Rwandan outbreak
Scientists pinpoint protein shapes that track Alzheimer’s progression
Researchers achieve efficient bicarbonate-mediated integrated capture and electrolysis of carbon dioxide
Study reveals ancient needles and awls served many purposes
Key protein SYFO2 enables 'self-fertilization’ of leguminous plants
AI tool streamlines drug synthesis
Turning orchard waste into climate solutions: A simple method boosts biochar carbon storage
New ACP papers say health care must be more accessible and inclusive for patients and physicians with disabilities
Moisture powered materials could make cleaning CO₂ from air more efficient
Scientists identify the gatekeeper of retinal progenitor cell identity
American Indian and Alaska native peoples experience higher rates of fatal police violence in and around reservations
Research alert: Long-read genome sequencing uncovers new autism gene variants
Genetic mapping of Baltic Sea herring important for sustainable fishing
In the ocean’s marine ‘snow,’ a scientist seeks clues to future climate
Understanding how “marine snow” acts as a carbon sink
In search of the room temperature superconductor: international team formulates research agenda
Index provides flu risk for each state
Altered brain networks in newborns with congenital heart disease
Can people distinguish between AI-generated and human speech?
New robotic microfluidic platform brings ai to lipid nanoparticle design
COSMOS trial results show daily multivitamin use may slow biological aging
Immune cells play key role in regulating eye pressure linked to glaucoma
[Press-News.org] Antiviral color nanocoating technologyVirus elimination effect along with a wide range of colors achieved with a low coating amount of 1g/m2. Expected to be utilized in various industries such as medical materials, home appliances, building materials, etc.