(Press-News.org) Humans are still evolving, and Tatum Simonson, PhD, founder and co-director of the Center for Physiological Genomics of Low Oxygen at University of California School of Medicine, plans to use evolution to improve healthcare for all.
Her latest research, which was published February 9, 2024 in Science Advances, reveals that a gene variant in some Andean people is associated with reduced red blood cell count at high altitude, enabling them to safely live high in the mountains in low-oxygen conditions. Simonson’s UC San Diego lab is applying those findings toward understanding whether there may be a genetic component to why some people with sleep apnea or pulmonary diseases such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) fare better than others.
Explained Simonson, “There are people with COPD who breathe a lot and maintain a higher oxygen saturation. Others with the same disease don't breathe as much, and their oxygen saturation is low. Researchers suspect there may be genetic differences underlying this variation, similar to the variation we find in pathways important for oxygen sensing and responses underlying natural selection at high altitude.”
Our cells need oxygen to survive. When there isn’t enough in the environment, our bodies produce extra red blood cells, which transport oxygen throughout the body. Too many red blood cells, however, create a dangerous condition called excessive erythrocytosis (EE), which makes the blood viscous, which could lead to stroke or heart failure.
Her previous research showed that many mountain-dwelling Tibetans exposed to low-oxygen situations are born with innate mechanisms that protect them from poor outcomes at high altitude, including the overproduction of red blood cells. Part of this is due to changes in the regulation of the EPAS1 gene, which lowers hemoglobin concentrations by regulating the pathway that responds to changing oxygen levels. Advances in genetics have shown that modern Tibetans received this genetic advantage from their ancestors who mixed with archaic humans living in Asia tens of thousands of years ago—a unique evolutionary history confined to this population.
For her latest research, Dr. Simonson, who is also the John B. West Endowed Chair in Respiratory Physiology and associate professor in the Division of Pulmonary, Critical Care, Sleep Medicine & Physiology at UC San Diego School of Medicine, zoomed in on the EPAS1 region of the genome. She and her team focused on a mutation in the gene that is present in some people living in the Andes but is absent in all other human populations. When they scanned whole Andean genomes, they found a pattern surrounding this variant suggesting that the genetic change, which alters only a single amino acid in the protein product, happened by chance, relatively recently (from 9,000 to 13,000 years ago), and spread very quickly through hundreds of generations within the Andean population.
Similar to Tibetans, the EPAS1 gene is associated with lower red blood cell count in Andeans who possess it. However, the researchers were surprised to find that the variant works in a completely different way from the Tibetan version of the gene; rather than regulating its levels, the Andean variant changes the genetic makeup of the protein, altering the DNA in every single cell.
“Tibetans have, in general, an average lower hemoglobin concentration, and their physiology deals with low oxygen in a way that doesn’t increase their red blood cells to excessively high levels. Now we have the first signs of evidence that Andeans are also going down that path, involving the same gene, but with a protein-coding change. Evolution has worked in these two populations, on the same gene, but in different ways,” said Simonson.
This study exemplifies a current approach in research that connects genetic targets of natural selection with complex disease genes—understanding, for example, how natural genetic variation contributes to adaptive and maladaptive responses to low oxygen, as this study reveals.
In Simonson’s lab, that means figuring out what downstream target genes are being turned on in response to low oxygen, among other things. Said Simonson, “This paper shows one gene associated with one particular phenotype, but we think there are many different genes and components of oxygen transport involved. It’s just one piece of that puzzle, and could provide researchers with information relevant to other populations.”
Simonson and her team are working with Latino populations in San Diego and El Centro, California, as well as Tijuana and Ensenada, Mexico, taking them to high altitudes and recording their breathing while awake and asleep. They’re cross-referencing their findings with publicly available databases to determine whether the findings they’ve made in Andeans are also found in local Latinos who may share some genetic variants with the Andeans.
“In precision medicine, it’s important to recognize variation in genetic backgrounds, specifically in historically understudied populations,” Simonson said. “If we can find some shared genetic factors in populations in an extreme environment, that may help us understand aspects of health and disease in that group and groups more locally. In that way, this study aims to push research forward, and towards comprehensive personalized medicine approaches in clinics here in San Diego.”
Co-authors of the study include: Elijah S. Lawrence, Wanjun Gu, James J. Yu, Erica C. Heinrich, Katie A. O’Brien, Carlos A. Vasquez, Quinn T. Cowan , Patrick T. Bruck , Kysha Mercader, Mona Alotaibi, Tao Long, James E. Hall, Esteban A. Moya, Marco A. Bauk, Jennifer J. Reeves, Mitchell C. Kong, Rany M. Salem, Keolu P. Fox, Atul Malhotra, Frank L. Powel, Mohit Jain and Alexis C. Komor at UC San Diego, Ryan J. Bohlender, Hao Hu and Chad D. Huff at University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Cecilia Anza-Ramirez, Gustavo Vizcardo-Galindo , Jose-Luis Macarlupu , Rómulo Figueroa-Mujíca, Daniela Bermudez, Noemi Corante and Francisco C. Villafuerte at Universidad Peruana Cayetano Heredia, Eduardo Gaio at Universidad de Brasília, Veikko Salomaa and Aki S. Havulinna at Finnish Institute for Health and Welfare and Andrew J. Murray at Cambridge University and Gianpiero L. Cavalleri at Royal College of Surgeons in Ireland.
This study was funded, in part, by the National Institutes of Health (Grants R01HL145470 [TSS] and T32HL134632 [JEH]), Geographic Society Explorer Award, and John B West Endowment in Respiratory Physiology (TSS), Wellcome Trust Award 107544/Z/15/Z (FCV), Marie Skłodowska-Curie grant agreement No 890768 (KAO), National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine Ford Foundation Fellowship (CAV), National Science Foundation Grant No DGE-2038238 (PTB), Research Corporation for Science Advancement through Cottrell Scholar Award 27502 (ACK), Science Foundation Ireland 12/IP/1727 (GLC), Finnish Foundation for Cardiovascular Research and Juho Vainio Foundation (VS), and Academy of Finland (ASH).
# # #
END
Harnessing human evolution to advance precision medicine
2024-02-09
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
For Black patients, 'representation matters' in evaluating prostate cancer websites
2024-02-09
Waltham — February 9, 2024 — For Black men with prostate cancer, racial representation is a key factor affecting trust in websites offering information on prostate cancer, reports a study in the March issue of The Journal of Urology®, an Official Journal of the American Urological Association (AUA). The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
"Our study shows that representation matters to Black patients seeking prostate cancer information online," comments lead author Stacy Loeb, MD, MSc, PhD (Hon), of New York University Langone Health. "Not only does it impact trust in the information, but a lack ...
Having COVID-19 and Long COVID can impact women’s sex lives
2024-02-09
From work to school to socializing, COVID-19 has impacted just about every part of our lives—and now Boston University research has shown that also includes what happens in the bedroom. A study of more than 2,000 cisgender women found the coronavirus disease can impair sexual function, with long COVID having an especially detrimental effect.
“If you’re sick with COVID, you’re probably less interested in sex and maybe your body is less prepared to have sex,” says Amelia M. Stanton, a BU College of Arts & Sciences assistant ...
Mechanistically based blood proteomic markers in the TGF-β pathway stratify risk of HCC in patients with cirrhosis
2024-02-09
“A fundamental hypothesis we sought to test was whether biomarkers from the TGF-β signaling pathway might be of novel value in risk stratification of HCC in the clinical cirrhotic setting.”
BUFFALO, NY- February 9, 2024 – A new research paper was published in Genes & Cancer on February 5, 2023, entitled, “Mechanistically based blood proteomic markers in the TGF-β pathway stratify risk of hepatocellular cancer in patients with cirrhosis.”
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the third leading cause of death from cancer worldwide but is often diagnosed at an advanced incurable stage. Yet, despite the urgent need for ...
Speed baiting: new report offers strategy for increasingly crowded Utah fishing
2024-02-09
There may, as they say, be plenty of fish in the sea — but angling opportunities on Utah’s streams, rivers and lakes are getting more crowded.
The number of anglers trying their luck on Utah waters has consistently increased over the years, meanwhile it’s getting more expensive for state managers to raise and stock gamefish and increasingly difficult to access water-based recreation during the ongoing megadrought.
Managers of fisheries in the state are being asked to do more with less these days, and they’re working more strategically to create sustainable opportunities for everyone picking up a rod and ...
Blocking artery supplying the brain covering after subdural hematoma reduced repeat surgery
2024-02-09
Research Highlights:
In the EMBOLISE clinical trial, obstructing (or blocking) an artery that supplies blood to the dura, the protective covering of the brain, along with surgery to remove pooled blood reduced the chances by nearly 3-fold that blood would reaccumulate and require additional surgery. According to researchers, complications related to the embolization procedure were low, and neurological function was comparable to those without embolization.
Chronic subdural hematoma, a pooling of blood between the brain and one of its outer coverings, is one ...
Robotic-assisted surgery and navigation don't affect infection risk after hip arthroplasty
2024-02-09
Waltham — February 8, 2024 — For patients undergoing total hip arthroplasty (THA), the use of robotic-assisted surgery and surgical navigation techniques is not associated with an increased risk of periprosthetic joint infection (PJI), suggests a study in The Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery. The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
Computer navigation (CN) and robotic assistance (RA) do not alter the risk of PJI after total hip replacement surgery, according to the new research by Alberto V. Carli, MD, and colleagues of Hospital for Special Surgery, New York.
Could CN and RA increase risks during hip replacement?
Computer ...
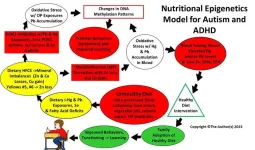
New study shows nutritional epigenetics education improves diet and attitude in parents of children with autism and ADHD
2024-02-09
In a recent publication released by PubMed, American scientists led by Dr. Dufault at the Food Ingredient and Health Research Institute, reported the results of a clinical trial in which parents who received nutritional epigenetics education significantly reduced their consumption of ultra-processed foods while increasing their intake of whole and/or organic foods. The education intervention used curriculum focused on the constructs of the nutritional epigenetics model that explains how autism and attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) may develop from the excess consumption of ultra-processed ...
Immune genes are altered in Alzheimer’s patients’ blood
2024-02-09
· First-of-its-kind study of immune genes in Alzheimer’s patients’ blood
· Immune T cells are altered and entering brain
· Uncertain whether changes precipitate the disease
CHICAGO --- A new Northwestern Medicine study has found the immune system in the blood of Alzheimer’s patients is epigenetically altered. That means the patients’ behavior or environment has caused changes that affect the way their genes work.
Many of these altered immune genes are the same ones that increase an ...
The Biophysical Journal names Erdinc Sezgin the 2023 Paper of the Year-Early Career Investigator Awardee
2024-02-09
ROCKVILLE, MD – Erdinc Sezgin, of Karolinska Institutet, Sweden will be honored as the recipient of the Biophysical Journal Paper of the Year-Early Career Investigator Award at the 68th Annual Meeting of the Biophysical Society, held February 10-14 in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. This award recognizes the work of outstanding early career investigators in biophysics. The winning paper is titled “Influence of the Extracellular Domain Size on the Dynamic Behavior of Membrane Proteins.” The paper was published in Volume 121, Issue ...
Research reveals the key to an irresistible online dating profile
2024-02-09
In writing a good online dating profile, the average love-seeker is likely to fill it up with all the appealing qualities and interests that make them special. They paraglide and do hot yoga on the weekends; enjoy Riesling on the beach or seeing indie bands in basements; are a Libra with Scorpio rising; or have a dog or three kids or an iguana. There’s one thing they routinely leave out, however: what they want to know about their potential partner.
Yet, that detail might the most important thing to include, according ...