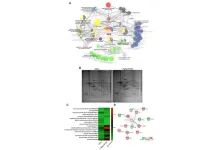
Searching for clues in the history book of the ocean
Increased oxygenation of the tropical ocean during a geological episode of abrupt global warming
2024-02-15
(Press-News.org)
Oxygen is fundamental to sustaining life on Earth. The ocean gets its oxygen from its uppermost layers in contact with the atmosphere. As our planet continues to warm, the ocean is gradually losing its capacity to absorb oxygen, with severe consequences on marine ecosystems and human activities that depend on them. While these trends will likely continue in the future, it remains unclear how ocean oxygen will redistribute across the ocean interior, where ocean currents and biological degradation of biomass dominate over atmospheric diffusion.
“Marine sediments are the history book of the ocean. By studying past intervals of time in which temperatures increased rapidly, we can gain precious insights on how ocean oxygen and biology responded to changes in climate”, said Simone Moretti who is the lead author of a now published in the research journal Science.
Using a combination of chemical and morphological measurements on foraminifera, microscopic fossils preserved in marine sediments over millions of years, a team of researchers led by scientists at the Max Planck Institute for Chemistry in collaboration with Princeton University has reconstructed the response of tropical ocean oxygenation during the PETM.
Nitrogen isotopes and fossil size reveal the oxygen content of seawater
Nitrogen isotopes preserved within fossil foraminifera enabled the scientists to track past changes in column denitrification in the water. This process, in which nitrate is converted to molecular nitrogen (N2) by bacteria, only occurs within the most oxygen-depleted waters of the ocean: the oxygen-deficient zones. “Our measurements showed that, contrary to most expectations, denitrification decreased during the PETM, implying that the oxygen-deficient zones of the ocean contracted during this interval of abrupt global warming”, said Alfredo Martínez-García, head of the laboratory at MPIC where the study was conducted.
In addition, the size of foraminifera fossils proved to be a fundamental piece of the puzzle. Models that describe the metabolism of marine organisms allow to link their body size to the environmental temperature and oxygen content of the water they live in. A reduction in body size is an effective adaptation to a warming climate, as it allows organisms to reduce their metabolism in times of stress. “Remarkably, and unexpectedly, evidence shows that planktonic foraminifera from the central tropical Pacific got bigger during the PETM warming, implying a tropical oxygen rise in the upper layers of the ocean,” commented Curtis Deutsch, Professor of Geosciences at the University of Princeton, who co-authored this study. Planktonic foraminifera live in the upper layers of the ocean, in contrast to those found on the bottom.
Oxygen increase could have mitigated mass extinction in the upper ocean
The finding that oxygen levels in the tropical ocean increased rather than decreased during the PETM warming also provides the researchers with a clue to another puzzle, that of changes in marine biodiversity. The PETM was the largest extinction event among deep ocean organisms within the Cenozoic Era, spanning the past 66 million years. One of many mysteries linked to the PETM is that while this large extinction event unfolded at greater depths, organisms living in the uppermost part of the ocean were less affected. “The transient tropical oxygenation revealed by our study may have contributed to preserving habitability despite a large temperature stress,” said Simone Moretti. “However, during the PETM the fauna in the surface ocean was nonetheless heavily impacted, and it took more than one hundred thousand years for these ecosystems to recover towards their original state, an eternity in human-civilization timescales.”
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-02-15
Springtime brings native wildflowers to bloom in the Santa Monica Mountains, northwest of Los Angeles. These beauties provide food for insects, maintain healthy soil and filter water seeping into the ground — in addition to offering breathtaking displays of color.
They’re also good at surviving after wildfire, having adapted to it through millennia. But new research shows wildflowers that usually would burst back after a blaze and a good rain are losing out to the long-standing, double threat of city smog and nonnative weeds.
A recent study led by Justin Valliere, assistant professor in the UC ...
2024-02-15
In the late 1800s and early 1900s, anti-Chinese sentiment in the United States was high, as working-class laborers in the country viewed Chinese workers as a threat.
Prior research has found that during that period, approximately 400,000 Chinese migrants came to the U.S., many of whom went to California to build the Transcontinental Railroad. Following the project's completion, competition for jobs grew tougher, and passage of the Chinese Exclusion Act in 1882 banned Chinese laborers from immigrating to the U.S.
But ...
2024-02-15
A new study published in Atmospheric Environment by researchers at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill analyzed space and time trends for fine particulate matter (PM2.5) in the continental United States to track the progress of regulatory actions by federal, state and local authorities aimed at curbing air pollution. The team found that while the annual average concentration for PM2.5 had been significantly reduced, its chemical composition had changed during the study period of 2006 to 2020. Their analysis suggests targeted strategies to reduce specific pollutants for different regions ...
2024-02-15
For Immediate Release: Thursday, February 15, 2024, 3:00pm U.S. Eastern Time
Media Contact: Kara Flynn, 202.257.8424, press@ashg.org
ROCKVILLE, MD - The American Society of Human Genetics (ASHG) is excited to announce the selection of Amanda Perl as the organization’s next Chief Executive Officer. Perl has served in numerous association leadership positions with deep experience in strategic planning, membership, publishing, communications, and society operations, as well as meetings and conferences.
“ASHG is delighted to welcome Amanda, a seasoned association executive, to the team,” said ASHG President Bruce D. Gelb, MD. “We are confident ...
2024-02-15
“[...] accelerated aging and Alzheimer’s disease are closely related, and this study confirmed that GV1001 has multiple anti-aging effects.”
BUFFALO, NY- February 15, 2024 – A new research paper was published on the cover of Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 16, Issue 3, entitled, “GV1001 reduces neurodegeneration and prolongs lifespan in 3xTg-AD mouse model through anti-aging effects.”
GV1001, which mimics the activity of human telomerase reverse transcriptase, protects neural cells from amyloid beta (Aβ) toxicity and other stressors through ...
2024-02-15
MIAMI, FL – February 15, 2024 – A study co-led by researchers at Miami Cancer Institute, part of Baptist Health South Florida, found that ablative stereotactic magnetic resonance (MR)-guided adaptive radiation therapy may improve local control (LC) and overall survival (OS) in patients with borderline resectable (BRPC) and locally advanced pancreas cancer (LAPC). Long-term outcomes from the Phase 2 SMART trial demonstrate encouraging OS and limited toxicity as published recently in Radiotherapy & Oncology (“The Green Journal”).
“Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma is a leading cause of cancer death. Surgery is the only known ...
2024-02-15
One of the grand challenges for materials science is the design and discovery of new materials that address global priorities such as Net Zero.
In a paper published in the journal Science, researchers at the University of Liverpool have discovered a solid material that rapidly conducts lithium ions. Such lithium electrolytes are essential components in the rechargeable batteries that power electric vehicles and many electronic devices.
Consisting of non-toxic earth-abundant elements, the new material has high ...
2024-02-15
Why do Serengeti zebra, wildebeest, and gazelle – all sharing limited food resources – follow the same migratory routes, one after another, in a body-size dependent way? This longstanding question has now been evaluated by researchers who used novel data to show how a balance of species interactions and ecological factors regulate this process. They say competition pushes zebra ahead of the wildebeest, and wildebeest then eat plants in a way that facilitates development of newer growth the trailing gazelle like. “Our results highlight a balance between facilitative and competitive forces,” the authors say. Large seasonal migrations are a ...
2024-02-15
Oxygenation in the tropical North Pacific Ocean increased during a warm climatic interval that occurred roughly 56 million years ago, despite high global temperatures, according to a new study. Its findings offer insights into how modern tropical oceans may respond to ongoing anthropogenic climate warming. The availability and distribution of dissolved oxygen in Earth’s oceans play a fundamental role in supporting marine ecosystems and marine life. However, oxygen in the global oceans is declining in response to anthropogenic warming. Although these trends writ large are predicted to continue, the future of oxygen in the highly productive ...
2024-02-15
Cresomycin – a novel synthetic molecule – demonstrates remarkably robust efficacy against multiple, evolutionary divergent forms of antimicrobial resistance (AMR), researchers report. The emergence and widespread distribution of bacteria broadly resistant to approved antibiotics raises serious global public health concerns. Given the growing rate of deaths attributable to antimicrobial resistance (AMR) worldwide, it’s evident the pace of discovery and development of antibiotics effective against AMR has not kept up with the need. Many small ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Searching for clues in the history book of the ocean
Increased oxygenation of the tropical ocean during a geological episode of abrupt global warming