(Press-News.org) A new way of imaging the brain with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) does not directly detect neural activity as originally reported, according to scientists at MIT’s McGovern Institute. The method, first described in 2022, generated excitement within the neuroscience community as a potentially transformative approach. But a study from the lab of McGovern associate investigator Alan Jasanoff, reported March 27, 2024, in the journal Science Advances, demonstrates that MRI signals produced by the new method are generated in large part by the imaging process itself, not neuronal activity.
Jasanoff explains that having a noninvasive means of seeing neuronal activity in the brain is a long-sought goal for neuroscientists. The functional MRI methods that researchers currently use to monitor brain activity don’t actually detect neural signaling. Instead, they use blood flow changes triggered by brain activity as a proxy. This reveals which parts of the brain are engaged during imaging, but it cannot pinpoint neural activity to precise locations, and it is too slow to truly track neurons’ rapid-fire communications.
So when a team of scientists reported in Science a new MRI method called DIANA, for “direct imaging of neuronal activity,” neuroscientists paid attention. The authors claimed that DIANA detected MRI signals in the brain that corresponded to the electrical signals of neurons, and that it acquired signals far faster than the methods now used for functional MRI.
“Everyone wants this,” Jasanoff says. “If we could look at the whole brain and follow its activity with millisecond precision and know that all the signals that we're seeing have to do with cellular activity, this would be just wonderful. It could tell us all kinds of things about how the brain works and what goes wrong in disease.”
Jasanoff adds that from the initial report, it was not clear what brain changes DIANA was detecting to produce such a rapid readout of neural activity. Curious, he and his team began to experiment with the method. “We wanted to reproduce it, and we wanted to understand how it worked,” he says.
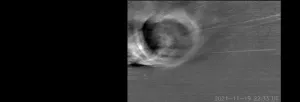
Recreating the MRI procedure reported by DIANA’s developers, postdoctoral researcher Valerie Doan Phi Van imaged the brain of a rat as an electric stimulus was delivered to one paw. Phi Van says she was excited to see an MRI signal appear in the brain’s sensory cortex, exactly when and where neurons were expected to respond to the sensation on the paw. “I was able to reproduce it,” she says. “I could see the signal.”
With further tests of the system, however, her enthusiasm waned. To investigate the source of the signal, she disconnected the device used to stimulate the animal’s paw, then repeated the imaging. Again, signals showed up in the sensory processing part of the brain. But this time, there was no reason for neurons in that area to be activated. In fact, Phi Van found, the MRI produced the same kinds of signals when the animal inside the scanner was replaced with a tube of water. It was clear DIANA’s functional signals were not arising from neural activity.
Phi Van traced the source of the specious signals to the pulse program that directs DIANA’s imaging process, detailing the sequence of steps the MRI scanner uses to collect data. Embedded within DIANA’s pulse program was a trigger for the device that delivers sensory input to the animal inside the scanner. That synchronizes the two processes, so the stimulation occurs at a precise moment during data acquisition. That trigger appeared to be causing signals that DIANA’s developers had concluded indicated neural activity.
Phi Van altered the pulse program, changing the way the stimulator was triggered. Using the updated program, the MRI scanner detected no functional signal in the brain in response to the same paw stimulation that had produced a signal before. “If you take this part of the code out, then the signal will also be gone. So that means the signal we see is an artifact of the trigger,” she says.
Jasanoff and Phi Van went on to find reasons why other researchers have struggled to reproduce the results of the original DIANA report, noting that the trigger-generated signals can disappear with slight variations in the imaging process. With their postdoctoral colleague Sajal Sen, they also found evidence that cellular changes that DIANA’s developers had proposed might give rise to a functional MRI signal were not related to neuronal activity.
Jasanoff and Phi Van say it was important to share their findings with the research community, particularly as efforts continue to develop new neuroimaging methods. “If people want to try to repeat any part of the study or implement any kind of approach like this, they have to avoid falling into these pits,” Jasanoff says. He adds that they admire the authors of the original study for their ambition: “The community needs scientists who are willing to take risks to move the field ahead.”
END
Reevaluating an approach to functional brain imaging
An MRI method purported to detect neurons’ rapid impulses produces its own misleading signals instead.
2024-03-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Food matters: Healthy diets increase the economic and physical feasibility of 1.5°C
2024-03-27
“We find that a more sustainable, flexitarian diet increases the feasibility of the Paris Agreement climate goals in different ways,” says Florian Humpenöder, PIK scientist and co-lead author of the study to be published in Science Advances. “The reduction of greenhouse gas emissions related to dietary shifts, especially methane from ruminant animals raised for their meat and milk, would allow us to extend our current global CO2 budget of 500 gigatons by 125 gigatons and still stay within the limits of 1.5°C with a 50 percent chance,” he adds.
Putting a price on greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions ...
Land under water – what causes extreme flooding
2024-03-27
There are several factors that play an important role in the development of floods: air temperature, soil moisture, snow depth, and the daily precipitation in the days before a flood. In order to better understand how individual factors contribute to flooding, UFZ researchers examined more than 3,500 river basins worldwide and analysed flood events between 1981 and 2020 for each of them. The result: precipitation was the sole determining factor in only around 25% of the almost 125,000 flood events. Soil moisture was the decisive factor in just over 10% of cases, and ...
Understanding why people sell their kidneys
2024-03-27
A systematic review of 35 years of global medical literature finds a spectrum of reasons why people sell kidneys. The study, by Bijaya Shrestha of the Center for Research on Education, Health and Social Science, Kathmandu, Nepal, finds limited efforts toward mitigating the problem as well as a lack of evidence around the impact of policy and biotechnology. It is published in the open access journal PLOS Global Public Health.
Demand for kidney donation is higher than supply, and it has become one of the most saleable human ...
Researchers turn back the clock on cancer cells to offer new treatment paradigm
2024-03-27
St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital scientists reversed an aggressive cancer, reverting malignant cells towards a more normal state. Rhabdoid tumors are an aggressive cancer which is missing a key tumor suppressor protein. Findings showed that with the missing tumor suppressor, deleting or degrading the quality control protein DCAF5 reversed the cancer cell state. These results suggest a new approach to curing cancer — returning cancerous cells to an earlier, more normal state rather than killing cancer cells with toxic therapies — may be possible. The results were published today in Nature.
“Rather than making a toxic event that kills rhabdoid ...
SwRI leads airborne, ground-based 2024 eclipse observation projects
2024-03-27
SAN ANTONIO — March 27, 2024 —Southwest Research Institute is leading two groundbreaking experiments — on the ground and in the air — to collect astronomical data from the total solar eclipse that will shadow a large swath of the United States on April 8, 2024. SwRI’s Dr. Amir Caspi leads the Citizen Continental-America Telescopic Eclipse (CATE) 2024 experiment, a broad scientific outreach initiative funded by the National Science Foundation (NSF) and NASA, that will ...
Lighting up the future
2024-03-27
New multidisciplinary research from the University of St Andrews could lead to more efficient televisions, computer screens and lighting.
Researchers at the Organic Semiconductor Centre in the School of Physics and Astronomy, and the School of Chemistry have proposed a new approach to designing efficient light-emitting materials in a paper published this week in Nature (27 March).
Light-emitting materials are used in organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs) that are now found in the majority of mobile ...
Sweet success: researchers crack sugarcane’s complex genetic code
2024-03-27
Modern hybrid sugarcane is one of the most harvested crops on the planet, used to make products including sugar, molasses, bioethanol, and bio-based materials. It also has one of the most complex genetic blueprints.
Until now, sugarcane’s complicated genetics made it the last major crop without a complete and highly accurate genome. Scientists have developed and combined multiple techniques to successfully map out sugarcane’s genetic code. With that map, they were able to verify the specific location that provides resistance to the impactful brown rust disease ...
WISPR team images turbulence within solar transients for the first time
2024-03-27
WASHINGTON — The Wide-field Imager for Parker Solar Probe (WISPR) Science Team, led by the U.S. Naval Research Laboratory (NRL), captured the development of turbulence as a Coronal Mass Ejection (CME) interacted with the ambient solar wind in the circumsolar space. This discovery is reported in the Astrophysical Journal.
Taking advantage of its unique location inside the Sun’s atmosphere, the NRL-built WISPR telescope on NASA’s Parker Solar Probe (PSP) mission, operated by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (JHUAPL), captured in unparalleled detail the interaction between ...
Undocumented immigrants faced unique mental health challenges during COVID-19 pandemic
2024-03-27
Four years after the U.S. shut down in the face of the COVID-19 pandemic, research from Rice University suggests undocumented immigrants’ mental health challenges were compounded due to stresses stemming from their unauthorized status.
“Implications of Undocumented Status for Latinx Families During the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Call to Action” appears in the Journal of Clinical Child & Adolescent Psychology and examines how undocumented immigrants navigated the COVID-19 pandemic.
During a series of in-depth interviews with undocumented individuals or those from ...
Old immune systems revitalized in Stanford Medicine mouse study, improving vaccine response
2024-03-27
Planes, trains, boats, automobiles and even feet. During the past decades and centuries, global travel and human migration have made all of us more worldly — from our broadening awareness of the world beyond our birthplaces, to our more sophisticated palates, to our immune systems that are increasingly challenged by unfamiliar bacteria and viruses.
In the elderly, these newly imported pathogens can gain the upper hand frighteningly quickly. Unfortunately, however, vaccination in this age group isn’t as effective as it is in younger people.
Now a study conducted in mice by Stanford ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
AI expert and industry leading toxicologist Thomas Hartung hails launch of agentic AI platform a “transformative moment” in chemical safety science
The RESIL-Card tool launches across Europe to strengthen cardiovascular care preparedness against crises
Tools to glimpse how “helicity” impacts matter and light
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
[Press-News.org] Reevaluating an approach to functional brain imagingAn MRI method purported to detect neurons’ rapid impulses produces its own misleading signals instead.