(Press-News.org) New multidisciplinary research from the University of St Andrews could lead to more efficient televisions, computer screens and lighting.
Researchers at the Organic Semiconductor Centre in the School of Physics and Astronomy, and the School of Chemistry have proposed a new approach to designing efficient light-emitting materials in a paper published this week in Nature (27 March).
Light-emitting materials are used in organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs) that are now found in the majority of mobile phone displays and smartwatches, and some televisions and automotive lighting.
The latest generation of emitter materials under development produce OLEDs that have high efficiency at low brightness, but suffer reduced efficiency as the brightness is increased to the levels required for lighting and outdoor applications. This problem is known as 'efficiency roll-off'.
Researchers have identified the combination of features of materials required to overcome this problem. Guidelines developed by the team of researchers, led by Professor Ifor Samuel and Professor Eli Zysman-Colman, will help OLED researchers develop materials that maintain high efficiency at high brightness, enabling the latest materials to be used for applications in displays, lighting and medicine.
Commenting on the research, Professor Zysman-Colman explained that the findings "provide clearer insight into the link between the properties of the emitter material and the performance of the OLED.”
Professor Samuel said, "Our new approach to this problem will help to develop bright, efficient and colourful OLEDs that use less power.”
Notes for Editors
The paper, 'A Figure of Merit for Efficiency Roll-off in TADF-based Organic LEDs, is published in the journal Nature and is available online: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-024-07149-x
Please include the paper’s DOI 10.1038/s41586-024-07149-x in all online stories and social media posts, and credit Nature as the source.
The full listing of authors and their affiliations for this paper is as follows:
• Ifor Samuel: University of St Andrews
• Stefan Diesing: University of St Andrews
• Le Zhang: University of St Andrews
• Eli Zysman-Colman: University of St Andrews
Professor Samuel is available for interview; please contact the Communications Office in the first instance.
END
Lighting up the future
2024-03-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
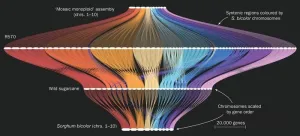
Sweet success: researchers crack sugarcane’s complex genetic code
2024-03-27
Modern hybrid sugarcane is one of the most harvested crops on the planet, used to make products including sugar, molasses, bioethanol, and bio-based materials. It also has one of the most complex genetic blueprints.
Until now, sugarcane’s complicated genetics made it the last major crop without a complete and highly accurate genome. Scientists have developed and combined multiple techniques to successfully map out sugarcane’s genetic code. With that map, they were able to verify the specific location that provides resistance to the impactful brown rust disease ...
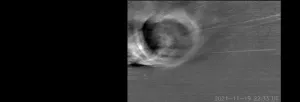
WISPR team images turbulence within solar transients for the first time
2024-03-27
WASHINGTON — The Wide-field Imager for Parker Solar Probe (WISPR) Science Team, led by the U.S. Naval Research Laboratory (NRL), captured the development of turbulence as a Coronal Mass Ejection (CME) interacted with the ambient solar wind in the circumsolar space. This discovery is reported in the Astrophysical Journal.
Taking advantage of its unique location inside the Sun’s atmosphere, the NRL-built WISPR telescope on NASA’s Parker Solar Probe (PSP) mission, operated by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (JHUAPL), captured in unparalleled detail the interaction between ...
Undocumented immigrants faced unique mental health challenges during COVID-19 pandemic
2024-03-27
Four years after the U.S. shut down in the face of the COVID-19 pandemic, research from Rice University suggests undocumented immigrants’ mental health challenges were compounded due to stresses stemming from their unauthorized status.
“Implications of Undocumented Status for Latinx Families During the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Call to Action” appears in the Journal of Clinical Child & Adolescent Psychology and examines how undocumented immigrants navigated the COVID-19 pandemic.
During a series of in-depth interviews with undocumented individuals or those from ...
Old immune systems revitalized in Stanford Medicine mouse study, improving vaccine response
2024-03-27
Planes, trains, boats, automobiles and even feet. During the past decades and centuries, global travel and human migration have made all of us more worldly — from our broadening awareness of the world beyond our birthplaces, to our more sophisticated palates, to our immune systems that are increasingly challenged by unfamiliar bacteria and viruses.
In the elderly, these newly imported pathogens can gain the upper hand frighteningly quickly. Unfortunately, however, vaccination in this age group isn’t as effective as it is in younger people.
Now a study conducted in mice by Stanford ...
Discovery has potential to solve the billion-dollar global cost of poorly managed wound healing
2024-03-27
Scientists have uncovered a key step in the wound healing process that becomes disabled in diseases like diabetes and ageing, contributing to a global healthcare cost of managing poorly healing wounds exceeding $250 billion a year. Importantly, the research published in Nature reveals a molecule involved in the healing of tissues that – when injected into animal models – leads to a drastic acceleration of wound closure, up to 2.5 times faster, and 1.6 times more muscle regeneration.
Lead researcher, Associate Professor Mikaël Martino, from Monash University’s Australian Regenerative Medicine Institute (ARMI) in Melbourne, Australia, said the discovery ...
Newly uncovered history of a key ocean current carries a warning on climate
2024-03-27
It carries more than 100 times as much water as all the world's rivers combined. It reaches from the ocean's surface to its bottom, and measures as much as 2,000 kilometers across. It connects the Indian, Atlantic and Pacific oceans, and plays a key role in regulating global climate. Continuously swirling around the southernmost continent, the Antarctic Circumpolar Current is by far the world's most powerful and consequential mover of water. In recent decades it has been speeding up, but scientists have been unsure whether ...
Evolution of the most powerful ocean current on Earth
2024-03-27
The Antarctic Circumpolar Current plays an important part in global overturning circulation, the exchange of heat and CO2 between the ocean and atmosphere, and the stability of Antarctica’s ice sheets. An international research team led by the Alfred Wegener Institute and the Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory have now used sediments taken from the South Pacific to reconstruct the flow speed in the last 5.3 million years. Their data show that during glacial periods, the current slowed; during interglacials, it accelerated. Consequently, if ...
New topological metamaterial amplifies sound waves exponentially
2024-03-27
Researchers at AMOLF, in collaboration with partners from Germany, Switzerland, and Austria, have realized a new type of metamaterial through which sound waves flow in an unprecedented fashion. It provides a novel form of amplification of mechanical vibrations, which has the potential to improve sensor technology and information processing devices. This metamaterial is the first instance of a so-called ‘bosonic Kitaev chain’, which gets its special properties from its nature as a topological material. It was realized by making nanomechanical resonators interact with laser light through radiation pressure forces. The discovery, which is published on March ...
Making long-term memories requires nerve-cell damage
2024-03-27
March 27, 2024—(BRONX, NY)—Just as you can’t make an omelet without breaking eggs, scientists at Albert Einstein College of Medicine have found that you can’t make long-term memories without DNA damage and brain inflammation. Their surprising findings were published online today in the journal Nature.
“Inflammation of brain neurons is usually considered to be a bad thing, since it can lead to neurological problems such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease,” said study leader Jelena Radulovic, M.D., Ph.D., professor in the Dominick P. Purpura Department of Neuroscience, professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences, and the Sylvia ...
Anastasopoulos studying machine translation for Austronesian languages
2024-03-27
Anastasopoulos Studying Machine Translation For Austronesian Languages
Antonios Anastasopoulos, Assistant Professor, Computer Science, received funding for: "Machine Translation for Austronesian Languages."
He is helping to develop a solution that can automatically translate languages of the southeast Asia and Pacific regions, with a particular focus on languages of lndonesia and the Philippines.
Anastasopoulos received $63,680 from Barron Associates, Inc., on a subaward from the U.S. Department of the Army for this project. Funding began ...