(Press-News.org)
The transition from vegetative to reproductive stages in plants involves both internal and external cues, with grapevines (Vitis vinifera L. cv. Pixie) presenting a unique case. Research shows that a mutation in the grapevine's DELLA proteins enhances the conversion of tendrils to inflorescences, diverging from DELLA's typical role in suppressing flowering in annual plants. While DELLA proteins regulate plant growth by interacting with various genes and environmental signals, the specific mechanisms and genes targeted by VvDELLA1 in grapevine to promote flowering, in contrast to its usual growth-restrictive functions in other species, warrant further exploration.
Fruit Research published online a paper entitled “Transcriptome analysis unveils a potential novel role of VvAP1 in regulating the developmental fate of primordia in grapevine” on 04 March 2024.
To explore the differential gene expression induced by the gain-of-function VvDELLA1 in L1 dwarf grape mutants, RNA sequencing (RNAseq) profiling was conducted on shoot apices from four mutant cultivars and the wild-type Pinot Meunier. These shoot apices included various developmental structures, and the samples were collected from vines grown hydroponically for over two years. Pairwise comparisons between each mutant and the wild-type identified thousands of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) across the cultivars, with a significant number of these DEGs being common across three or four mutants, indicating a robust differential expression pattern linked to the VvDELLA1 mutation. The analysis showed a broad range of expression changes among these DEGs, with some exhibiting up to 550-fold differences compared to the wild type. Gene Ontology (GO) analysis of up-regulated DEGs highlighted their involvement in fundamental cellular processes and biosynthesis pathways, while down-regulated DEGs were associated with processes like defense response and reproduction.
The study also focused on genes within the gibberellin (GA) pathway, noting significant regulatory patterns, particularly with GA2ox genes showing substantial downregulation, suggesting a pivotal role of VvDELLA1 in GA-mediated pathways. Importantly, it was found that the positive regulatory gene VvAP1 and the flowering inhibitory factor VvTFL1a related to flower development were significantly downregulated in mutants, further indicating the complex regulatory complexity of grape vine unique flower development. The investigation into GA pathway genes and flowering regulation underscores VvDELLA1's central role in modulating these pathways, disrupting conventional growth patterns, and promoting the unusual development of inflorescences in L1 dwarf mutants.
In conclusion, this study provides insights into the complex regulatory mechanisms disrupted by the VvDELLA1 mutation. It highlights the mutation's impact on flowering and hormonal response pathways, offering a deeper understanding of grapevine's unique developmental processes and the pivotal role of VvDELLA1 in diverging these processes from typical patterns observed in other plants.
###
References
DOI
10.48130/frures-0024-0004
Original Source URL
https://www.maxapress.com/article/doi/10.48130/frures-0024-0004
Authors
Jie Arro1,2, Yingzhen Yang1, Guo-qing Song3, Peter Cousins4, Zongrang Liu5,*, & Gan-Yuan Zhong1,*
Affiliations
1.Grape Genetics Research Unit, USDA-Agricultural Research Service, Geneva, NY 14456, USA
2.Institutional Research and Engagement Office & Department of Natural Science College of Arts and Science, University of St. La Salle, Bacolod City 6100 Philippines
3.Plant Biotechnology Resource and Outreach Center, Department of Horticulture, Michigan State University, East Lansing, MI 48824, USA
4.E&J Gallo Winery, Modesto, CA95358, USA
5.Appalachian Fruit Research, USDA-Agricultural Research Service, Kearneysville, WV 25430, USA
About Gan-Yuan Zhong
He serves as Research Leader for the USDA-ARS Grape Genetics Research Unit (GGRU) and Plant Genetic Resources Unit (PGRU) at the AgriTech of Cornell University, Geneva, NY. He conducts research for improving grapevine fruit quality, plant architecture, and breeding processes. One recent focus is to develop and use non-transgenic genome editing tools for grapevine fruit trait improvement.
END
Osaka, Japan – Antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs) are next-generation drugs that can treat disease by blocking the transfer of harmful messages from our genes. In people with cancer, ASOs have the potential to block messages that encourage the growth and spread of the tumor. However, ASOs aren’t used for treating cancer yet. They must first get delivered inside cancer cells, but the cancer cells won’t let them in.
Finding an effective ASO delivery system is a major challenge. Cancer cells have gatekeeper molecules that stop unwanted substances from entering. Although investigators have tried many ways of getting ASOs past ...
A research team has unveiled 20 β-galactosidase (BGAL) genes within the longan genome, highlighting their crucial roles in embryogenic development and heat stress adaptation. Particularly, the research team spotlighted DlBGAL9, activated by transcription factors DlAGL61 and DlAGL80, as pivotal in enhancing β-galactosidase activity for cell wall thickening and stress response. These discoveries not only deepen our understanding of BGAL's function in plant development and stress mechanisms but also open pathways for agricultural innovations to improve crop resilience and productivity through genetic ...
The chloroplast (cp) is critical for various biological functions in plants, such as photosynthesis and stress responses, with its genome offering simpler analysis and sequencing due to its size and reduced homologous influence. This genome's stability and unique features have made it essential for species identification and understanding plant phylogeny. In the context of Carya illinoinensis, or pecan, a key nut crop in China, there's an observed pollination deficiency exacerbated by the timing of pollen release in cultivars like 'Pawnee'. Recent research has expanded to include the cp genomes of various C. illinoinensis cultivars, aiding ...
Crowdsourcing efficiently delegates tasks to crowd workers for labeling, though their varying expertise can lead to errors. A key task is estimating worker expertise to infer true labels. However, the noise transition matrix-based methods for modeling worker expertise often overfit annotation noise due to oversimplification or inaccurate estimations.
To solve the problems, a research team led by Shao-Yuan LI published their new research on 12 Mar 2024 in Frontiers of Computer Science co-published by Higher Education Press and Springer Nature.
The team proposed a knowledge distillation-based framework KD-Crowd, which leverages noise-model-free ...
HONG KONG (16 April 2024)—A groundbreaking discovery that appears to confirm the existence of discrete number sense in rats has been announced by a joint research team from City University of Hong Kong (CityUHK) and The Chinese University of Hong Kong (CUHK).
The findings offer a crucial animal model for investigating the neural basis of numerical ability and disability in humans, the Hong Kong-based researchers say.
This innovative study deployed a numerical learning task, brain manipulation techniques and AI modelling to tackle an ongoing debate about whether rats can count, says Professor Yung Wing-ho, Chair Professor of Cognitive Neuroscience at CityUHK, who ...
New research into generative AI images shows only over a third of media organisations surveyed at the time of research have an image-specific AI policy in place.
The study, led by RMIT University in collaboration with Washington State University and the QUT Digital Media Research Centre, interviewed 20 photo editors or related roles from 16 leading public and commercial media organisations across Europe, Australia and the US about their perceptions of generative AI technologies in visual journalism.
Lead researcher and RMIT Senior Lecturer, Dr TJ Thomson, said while most staff interviewed ...
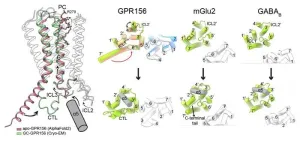
Professor Yunje Cho’s research team from the Department of Life Sciences at Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH, Republic of Korea) has collaborated with Professor Kwang Pyo Kim’s group from the Department of Applied Chemistry at Kyung Hee University (KHU, ROK), Professor Vsevolod Katritch’s team from the University of Southern California (USC, USA), and Professor Carol V. Robinson from the University of Oxford (UK) to uncover the mysteries surrounding a specific receptor protein associated with hearing. Their findings have recently been published in the online edition of Nature Structural & Molecular Biology.
Deep ...
A research team reviews the critical relationship between the accumulation of anthocyanins and organic acids in fruits, highlighting how these factors influence fruit color and consumer appeal through changes in vacuolar pH. The analysis focused on the transcription factors (TFs) responsible for the co-regulation of genes affecting these quality traits, aiming to enhance fruit marketability. By establishing a genetic link and identifying the regulatory mechanisms involved, the team provides a roadmap for breeders to target specific traits for modification. Although progress has been made, the review underlines the ...
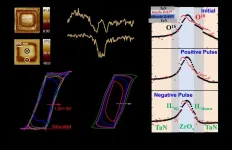
Ferroelectric binary oxides thin films are garnering attention for their superior compatibility over traditional perovskite-based ferroelectric materials. Its compatibility and scalability within the CMOS framework make it an ideal candidate for integrating ferroelectric devices into mainstream semiconductor components, including next-generation memory devices and various logic devices such as Ferroelectric Field-effect Transistor, and Negative Capacitance Field-effect Transistor. It has been reported that challenges ...
Citrus is the world’s most economically significant fruit crop, but it faces various environmental adversities that restrict its distribution. Grafting is a crucial factor in enhancing citrus productivity. Current research focuses on selecting genetically uniform rootstocks, such as trifoliate orange for its disease resistance. However, issues such as sensitivity to alkalinity and incompatibility with certain cultivars persist.
Addressing these challenges, a study (DOI: 10.48130/frures-0023-0042) published in Fruit Research on 01 February 2024, introduces 'Shuzhen No.1', a novel rootstock ...