(Press-News.org) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsb.2024.02.015
This new article publication from Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B, discusses how the use of a radiation-based immunogenic vaccine combined with a macrophage “checkpoint inhibitor” can boost innate and adaptive immunity against metastatic colon cancers.
Immunogenic dying tumor cells hold promising prospects as cancer vaccines to activate systemic immunity against both primary and metastatic tumors. Especially, X-ray- induced dying tumor cells are rich in highly immunogenic tumor-associated antigens and self-generated dsDNA as potent adjuvants.
The authors of this article note that the X-ray induction process can result in the excessive exposure of phosphatidylserine in cancer vaccines, which can specifically bind with the MerTK receptor on macrophages, acting as a “checkpoint” to facilitate immune silence in the tumor microenvironment.
Therefore, a novel strategy was developed combining X-ray-induced cancer vaccines with UNC2250, a macrophage MerTK “checkpoint inhibitor,” for treating peritoneal carcinomatosis in colon cancer. By incorporating UNC2250 into the treatment regimen, immunosuppressive efferocytosis of macrophages, which relies on MerTK-directed recognition of phosphatidylserine on vaccines, was effectively blocked. Consequently, the immune analysis revealed that this combination strategy promoted the maturation of dendritic cells and M1-like repolarization of macrophages, thereby simultaneously eliciting robust adaptive and innate immunity.
This innovative approach utilizing X-ray-induced vaccines combined with a checkpoint inhibitor may provide valuable insights for developing effective cancer vaccines and immunotherapies targeting colon cancer.
Keywords: Immunogenic cell death; Cancer vaccine; X-ray; Efferocytosis; Macrophage; STING; Adaptive immunity; Innate immunity
Graphical Abstract: available at https://ars.els-cdn.com/content/image/1-s2.0-S2211383524000534-ga1.jpg
Frozen dying tumor cells (FDT) combined with efferocytosis inhibitors can mobilize dendritc cells and macrophages simultaneously, thereby eliciting robust innate and adaptive immunity against peritoneal carcinomatosis in colon cancer.
# # # # # #
The Journal of the Institute of Materia Medica, the Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and the Chinese Pharmaceutical Association.
For more information please visit https://www.journals.elsevier.com/acta-pharmaceutica-sinica-b/
Editorial Board: https://www.journals.elsevier.com/acta-pharmaceutica-sinica-b/editorial-board
APSB is available on ScienceDirect (https://www.sciencedirect.com/journal/acta-pharmaceutica-sinica-b).
Submissions to APSB may be made using Editorial Manager® (https://www.editorialmanager.com/apsb/default.aspx).
CiteScore: 19.4
Impact Factor: 14.5
JIF without self-citation: 13.7
ISSN 2211-3835
# # # # #
Hongbo Xu, Xianya Qin, Yuanyuan Guo, Siyu Zhao, Xingxing Feng, Runzan Zhang, Tianyi Tian, Li Kong, Conglian Yang, Zhiping Zhang, Radiation-based immunogenic vaccine combined with a macrophage “checkpoint inhibitor” for boosting innate and adaptive immunity against metastatic colon cancers, Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B, Volume 14, Issue 5, 2024, Pages 2247-2262, ISSN 2211-3835, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsb.2024.02.015
END
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsb.2024.02.006
This new article publication from Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B, discusses how branched glycopolymer prodrug-derived nanoassembly combined with a STING agonist activates an immuno-supportive status to boost anti-PD-L1 antibody therapy.
Despite the great potential of anti-PD-L1 antibodies for immunotherapy, their low response rate due to an immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment has hampered their application.
To address this issue, the authors of this article constructed a cell membrane-coated nanosystem (mB4S) to reverse an immunosuppressive microenvironment to an immuno-supportive ...
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsb.2024.02.020
This new article publication from Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B, discusses how 5S-Heudelotinone alleviates experimental colitis by shaping the immune system and enhancing the intestinal barrier in a gut microbiota-dependent manner.
Aberrant changes in the gut microbiota are implicated in many diseases, including inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Gut microbes produce diverse metabolites that can shape the immune system and impact the intestinal barrier integrity, indicating that microbe-mediated modulation may be a promising strategy for preventing and treating IBD.
Although ...
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsb.2024.02.004
This new article publication from Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B, discusses how ALS-linked C9orf72 dipeptide repeats inhibit starvation-induced autophagy through modulating BCL2–BECN1 interaction.
Growing evidence indicate that dysfunction of autophagy contributes to the disease pathogenesis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and frontotemporal dementia (FTD), two neurodegenerative disorders. The GGGGCC·GGCCCC repeat RNA expansion in chromosome 9 open reading frame 72 (C9orf72) ...
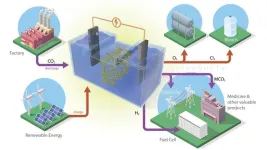
Researchers at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory are developing battery technologies to fight climate change in two ways, by expanding the use of renewable energy and capturing airborne carbon dioxide.
This type of battery stores the renewable energy generated by solar panels or wind turbines. Utilizing this energy when wind and sunlight are unavailable requires an electrochemical reaction that, in ORNL’s new battery formulation, captures carbon dioxide from industrial emissions and converts it to value-added products.
ORNL researchers recently created and tested two different formulations for batteries that ...
Georgia’s saltwater marshes — living where the land meets the ocean — stretch along the state’s entire 100-mile coastline. These rich ecosystems are largely dominated by just one plant: grass.
Known as cordgrass, the plant is an ecosystem engineer, providing habitats for wildlife, naturally cleaning water as it moves from inland to the sea, and holding the shoreline together so it doesn’t collapse. Cordgrass even protects human communities from tidal surges.
Understanding how these ...
The onset of the COVID-19 pandemic changed how nearly everyone mediated their social interactions through technology. Some moved happy hours into video chats. Others delved deeper into social media, or took a step back from it. Millions of people worked or learned through computers.
University of Washington researchers took particular interest in how this tech shift affected older adults’ social relationships. The team interviewed 16 older adults in Washington and Oregon, ages 65 to 80, about how their technology ...
Records from nearly 30,000 nursing home residents indicate that blood pressure medications more than double the risk of life-threatening bone fractures, according to Rutgers Health research.
The authors of the study, which appears in JAMA Internal Medicine, said the increased risk stems from the medications’ tendency to impair balance, particularly when patients first stand up and temporarily experience low blood pressure that deprives the brain of oxygen. Interactions with other drugs and low baseline balance in many nursing home patients compound the problem.
“Bone fractures often start nursing home patients on a downward spiral,” ...
Many organisms are far more complex than just a single species. Humans, for example, are full of a variety of microbes. Some creatures have even more special connections, though. Acoels, unique marine worms that regenerate their bodies after injury, can form symbiotic relationships with photosynthetic algae that live inside them. These collections of symbiotic organisms are called a holobiont, and the ways that they “talk” to each other are something scientists are trying to understand – especially ...
Compared with pre-surgical (neoadjuvant) chemotherapy alone, adding perioperative immunotherapy – given before and after surgery – significantly improved event-free survival (EFS) in patients with resectable early-stage non-small cell lung cancer(NSCLC), according to researchers from The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center.
Results from the Phase III CheckMate 77T study were published today in the New England Journal of Medicine. At a median follow-up of 25.4 months, the median EFS with chemotherapy alone was 18.4 months, while the median had not yet ...
“I consider the drugs available on the marked today as the first generation of weight-loss drugs. Now we have developed a new type of weight-loss drug that affects the plasticity of the brain and appears to be highly effective.”
So says Associate Professor and Group Leader Christoffer Clemmensen, from the Novo Nordisk Foundation Center for Basic Metabolic Research at the University of Copenhagen, who is senior author of the new study, which has been published in the prestigious scientific journal Nature.
In the study, Christoffer Clemmensen and colleagues demonstrate a new use of the weight loss hormone GLP-1. GLP-1 can be used as a ‘Trojan ...