(Press-News.org) About The Study: This randomized clinical trial of Chinese adults with overweight or obesity and with early type 2 diabetes found that an intermittent fasting plan consisting of two nonconsecutive fasting days and five days of habitual intake per week and meal replacement diet (5:2 MR) could improve glycemic outcomes and weight loss in the short term compared with metformin or empagliflozin, making it a promising initial intervention and early management for type 2 diabetes.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Lixin Guo, M.D., email glx1218@163.com.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.16786)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time http://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.16786?utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_term=062124
About JAMA Network Open: JAMA Network Open is an online-only open access general medical journal from the JAMA Network. On weekdays, the journal publishes peer-reviewed clinical research and commentary in more than 40 medical and health subject areas. Every article is free online from the day of publication.
END
A 5:2 intermittent fasting meal replacement diet and glycemic control for adults with diabetes
JAMA Network Open
2024-06-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Scientists document self-propelling oxygen decline in the oceans
2024-06-21
Scientists from the University of Copenhagen have made significant strides in understanding ancient ocean anoxia, with potential insights for today's marine environments.
500 million years ago the so-called Cambrian ‘SPICE’ event made oxygen levels in the oceans drop dramatically.
Now, researchers from the University of Copenhagen have investigated how large-scale ocean anoxia, or oxygen-depleted conditions, developed during the event, and its potential consequences today.
In the study, titled "Cascading oxygen loss shorewards in the oceans – insights from the Cambrian SPICE event" published in OneEarth ...
Activating molecular target reverses multiple hallmarks of aging
2024-06-21
HOUSTON ― Researchers at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center have demonstrated that therapeutically restoring ‘youthful’ levels of a specific subunit of the telomerase enzyme can significantly reduce the signs and symptoms of aging in preclinical models. If these findings are confirmed in clinical studies, there may be therapeutic implications for age-related diseases such as Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, heart disease and cancer.
The study, published today in Cell, identified a small molecule compound ...
Cannabis use tied to increased risk of severe COVID-19
2024-06-21
As the deadly disease that came to be known as COVID-19 started spreading in late 2019, scientists rushed to answer a critical question: Who is most at risk?
They quickly recognized that a handful of characteristics — including age, smoking history, high body mass index (BMI) and the presence of other diseases such as diabetes — made people infected with the virus much more likely to become seriously ill and even die. But one suggested risk factor remains unconfirmed more than four years later: cannabis use. Evidence has emerged over time indicating both ...
How to make ageing a ‘fairer game’ for all wormkind
2024-06-21
Why do some people live for longer than others? The genes in our DNA sequence are important, helping avoid disease or maintain general health, but differences in our genome sequence alone explain less than 30% of the natural variance of human life expectancy.
Exploring how ageing is influenced at the molecular level could shed light on lifespan variation, but generating data at the speed, scale and quality necessary to study this in humans is unfeasible. Instead, researchers turn to worms (Caenorhabditis elegans). Humans share a lot of biology with these small creatures, who also have a large, natural variation in lifespan.
Researchers ...
Supporting the right small changes can have big impacts
2024-06-21
Small changes in our everyday actions can trigger significant, rapid societal shifts especially when it comes to climate action. A new IIASA-led study highlights the importance of analyzing these dynamics with a comprehensive framework to harness their full potential for reducing carbon emissions.
Making small changes in how we live day-to-day can quickly create significant changes in society, especially in ways that benefit the environment. This idea is captured in the term social tipping points.
According to the authors of a new paper just published in the journal One Earth, social tipping points are crucial for speeding up efforts to reduce carbon emissions. These points occur when ...
Grafted cucumbers get a boost: pumpkin's secret to withstanding salinity
2024-06-21
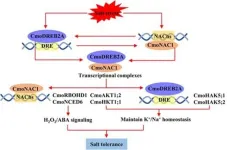
A pivotal study has discovered a genetic synergy between pumpkin and cucumber that fortifies the latter's resilience against salinity. The research illuminates the role of the CmoDREB2A transcription factor from pumpkin, which, when interacted with cucumber's CmoNAC1, forms a regulatory loop that enhances salt tolerance. This breakthrough could be key to developing crops that thrive in saline soils, safeguarding agricultural productivity.
Soil salinity, a silent blight on global agriculture, affects an estimated 10% of the world's arable land, leading to significant crop ...
Unlocking broccoli's genome: key to enhanced health benefits
2024-06-21
A detailed genomic study of broccoli has revealed the genetic foundations for the production of glucosinolates (GSLs), compounds celebrated for their health benefits, including anti-carcinogenic properties. By assembling a high-quality chromosome-level genome, researchers identified key genes involved in GSL biosynthesis. These findings offer critical insights for future genetic studies and the development of Brassica crops with enhanced nutritional value, paving the way for improved health benefits from these widely consumed vegetables.
Broccoli is renowned for its health benefits, primarily due to its rich glucosinolate (GSL) content, which has anti-carcinogenic ...
New insights into methyl jasmonate-induced saponin biosynthesis in balloon flower
2024-06-21
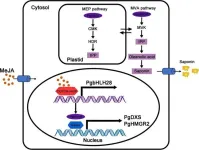
A cutting-edge study has pinpointed the PgbHLH28 gene as a crucial catalyst in the methyl jasmonate-induced (MeJA-induced) saponin biosynthesis in Platycodon grandiflorus. This genetic insight could significantly bolster the production of saponins, which are beneficial in combating cerebrovascular diseases and COVID-19, offering a novel therapeutic avenue in medicinal plant cultivation.
Platycodon grandiflorus, commonly known as balloon flower, is renowned for its medicinal properties, primarily due to its rich saponin content. Saponins are known for ...
Unraveling the role of ADGRF5: Insights into kidney health and function
2024-06-21
Glomerulus, the fundamental filtering unit of the kidney, is an intricate network of capillaries — small blood vessels that regulate the movement of ions, water, and metabolites while maintaining impermeability to essential macromolecules such as proteins. The selectively permeable capillary wall, known as the glomerular filtration barrier (GFB), consists of three main components: glomerular endothelial cells (GEnCs), the glomerular basement membrane, and podocytes. GEnCs line the inner surface of the capillary wall and are covered by a thin layer of glycoproteins and other carbohydrate-based moieties.
Adhesion G-protein-coupled ...
JMIR Dermatology accepted for MEDLINE indexing
2024-06-21
(Toronto, June 21, 2024) JMIR Publications is pleased to announce that JMIR Dermatology (JMIR Derm) has been accepted for inclusion in MEDLINE, which is the U.S. National Library of Medicine's premier bibliographic database.
JMIR Dermatology was previously already indexed in PubMed, but MEDLINE is a more selective subset of PubMed, consisting of the top 5200 biomedical journals, and indexing in MEDLINE also means that articles are now also indexed with NLM Medical Subject Headings (MeSH terms) and other metadata.
Selection for MEDLINE is a result of a thorough review of the ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal reports faster robot-assisted brain angiography
New study clarifies how temperature shapes sex development in leopard gecko
Major discovery sparks chain reactions in medicine, recyclable plastics - and more
Microbial clues uncover how wild songbirds respond to stress
Researchers develop AI tools for early detection of intimate partner violence
Researchers develop AI tool to predict patients at risk of intimate partner violence
New research outlines pathway to achieve high well-being and a safe climate without economic growth
How an alga makes the most of dim light
Race against time to save Alpine ice cores recording medieval mining, fires, and volcanoes
Inside the light: How invisible electric fields drive device luminescence
A folding magnetic soft sheet robot: Enabling precise targeted drug delivery via real-time reconfigurable magnetization
Sylvester Cancer Tip Sheet for March 2026
New tools and techniques accelerate gallium oxide as next-generation power semiconductor
Researchers discover seven different types of tension
Report calls for AI toy safety standards to protect young children
VR could reduce anxiety for people undergoing medical procedures
Scan that makes prostate cancer cells glow could cut need for biopsies
Mechanochemically modified biochar creates sustainable water repellent coating and powerful oil adsorbent
New study reveals hidden role of larger pores in biochar carbon capture
Specialist resource centres linked to stronger sense of belonging and attainment for autistic pupils – but relationships matter most
Marshall University, Intermed Labs announce new neurosurgical innovation to advance deep brain stimulation technology
Preclinical study reveals new cream may prevent or slow growth of some common skin cancers
[Press-News.org] A 5:2 intermittent fasting meal replacement diet and glycemic control for adults with diabetesJAMA Network Open