(Press-News.org) https://www.scienceopen.com/hosted-document?doi=10.15212/ZOONOSES-2024-0004
Announcing a new article publication for Zoonoses journal. Songling virus (SGLV) is a spherical, enveloped, fragmented, negative-stranded RNA virus belonging to the genus Orthonairovirus in the Nairoviridae family. SGLV is transmitted by ticks and can cause disease in humans. This study identified and characterized SGLV in Haemaphysalis concinna ticks collected in 2023 in the Yanbian Korean Autonomous Prefecture (China) near the China-North Korea border.
A real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) was used to screen for SGLV nucleic acid in ticks. Baby hamster kidney (BHK-21) and African green monkey kidney (Vero) cells were used to isolate strains of SGLV from nucleic acid-positive samples through three successive passages. Next-generation sequencing and phylogenetics methods were used to characterize the SGLVs.
Of the 1659 ticks collected from 6 towns in the Yanbian Korean Autonomous Prefecture near the China-North Korea border, positive SGLV nucleic acid results were identified in 19 H. concinna tick pools from Helong and Longjing towns. This discovery led to the extraction of 17 SGLV genome sequences. Homology analysis that compared the newly discovered L, M, and S segments of SGLV strain HLJ1202 revealed nucleotide similarities ranging from 95.5%–97.1%, 91.9%–98.9%, and 98.3%–99.2%, respectively, and amino acid similarities ranging from 95.7%–97.4%, 97.1%–98.8%, and 98.2%–98.9%, respectively. Six distinct clades, characterized by specific geographic locations and host organisms, were identified on the Maximum Likelihood tree of the L segment. The YB129 and YB150 isolates demonstrated SGLV nucleic acid replication across three successive passages in Vero cells, as evidenced by the decrease in RT-qPCR Ct values.
This study marks the initial identification of SGLV in H. concinna within the Yanbian Korean Autonomous Prefecture.
# # # # # #
Zoonoses is fully open access journal for research scientists, physicians, veterinarians, and public health professionals working on diverse disciplinaries of zoonotic diseases. Please visit https://zoonoses-journal.org/ to learn more about the journal.
Zoonoses is now open for submissions; articles can be submitted online at https://mc04.manuscriptcentral.com/zoonoses
There are no author submission or article processing fees.
Editorial Board: https://zoonoses-journal.org/index.php/editorial-board/
Zoonoses is available on ScienceOpen (https://www.scienceopen.com/search#collection/839df240-327f-47dd-b636-9b728dff9700).
Follow Zoonoses on Twitter @ZoonosesJ; Facebook (https://www.facebook.com/Zoonoses-Journal-100462755574114 ) and LinkedIn (https://www.linkedin.com/company/zoonoses/)
eISSN 2737-7474
ISSN 2737-7466
# # # # # #
De Li, Jixu Li and Ruichen Wang et al. Detection and Genetic Analysis of Songling Virus in Haemaphysalis concinna near the China-North Korea Border. Zoonoses. 2024. Vol. 4(1). DOI: 10.15212/ZOONOSES-2024-0004
END
A researcher at the University of Missouri has developed a program that improves the quality of care and reduces avoidable hospitalizations in nursing homes — saving Missouri nursing homes and Medicare millions of dollars and allowing Missouri nursing homes to invest more in retaining their most skilled staff members. The program is so successful that it’s being recommended for use in all 50 states.
The Quality Improvement Program for Missouri (QIPMO) was created by Marilyn Rantz in 1999 as a partnership between Mizzou’s Sinclair School of Nursing and the Missouri Department of Health and Senior Services.
For the past 25 years, the program has allowed Rantz and ...
Research in nonhuman primates is opening the possibility of testing treatments for the early stages of Alzheimer’s and similar diseases, before extensive brain cell death and dementia set in. A study published June 21 in Alzheimer’s & Dementia: The Journal of the Alzheimer’s Association shows up to a six-month window in which disease progress could be tracked and treatments tested in rhesus macaques.
“This is a very powerful translational model to test interventions that target the tau protein,” said John H. ...
A new study led by University of Cincinnati researchers sheds new light on the role of a signaling pathway in the brain to maintain health and prevent inflammation and cognitive deficits.
UC’s Agnes (Yu) Luo, PhD, is corresponding author on the research, published June 21 in the journal Nature Communications, and focused on a signaling pathway called TGF-β that plays a number of roles depending on where it is located in the body.
Luo explained that signaling pathways in the body control different cell functions and require two components: a type of molecule called a ligand and a receptor that the ligand binds to and ...
DETROIT -- Early memory loss has been linked to wealth loss, but research has mostly focused on investments. Four years ago, clinical geropsychologist Peter Lichtenberg, Ph.D., wondered what clues might be found in an older person’s financial decisions to indicate their vulnerability to financial victimization. Lichtenberg is director of the Institute of Gerontology at Wayne State University and a national expert in the financial exploitation of older adults. The results of his curiosity have now been published as “The WALLET Study: Financial ...
Though exposure to “trace” (an extremely small amount) elements has been shown to affect ovarian functions in experimental studies, there has been little research on the impact of trace levels of non-essential elements, such as lead (Pb) and mercury (Hg), on female reproduction. Studies have shown that high levels of these non-essential elements may lead to decreased female fertility and reduce the likelihood of getting pregnant. Taken together, this evidence raises concern about the potential negative impact of exposure ...
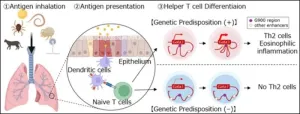
Asthma patients experience respiratory distress due to allergens like house dust mites or pollen. However, the various triggers for asthma share a common pathway involving the release of proteins called type-2 cytokines by Type-2 helper T (Th2) cells and group-2 innate lymphoid cells (ILC2s). Both Th2 and ILC2 require high amounts of GATA-binding protein 3 (GATA3) for their maturation.
Specific gene sequences called enhancers are responsible for elevating the expression of GATA3 genes in humans. Studies have found that by controlling the production of GATA3, enhancers influence the development of Th2 and ILC2. The gene region G900, located close to ...
TALLAHASSEE, Fla. — Imagine zooming in on a dried drop of salt solution — each pattern a unique masterpiece, reminiscent of abstract art, yet no larger than the size of a penny.
New research by scientists in the Florida State University Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry uses the patterns formed by a dried salt solution to train a machine learning algorithm that can identify the chemical composition of different salts. The work will be published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
“We are taking chemical fingerprints ...
Nearly all the neural networks that power modern artificial intelligence tools such as ChatGPT are based on a 1960s-era computational model of a living neuron. A new model developed at the Flatiron Institute’s Center for Computational Neuroscience (CCN) suggests that this decades-old approximation doesn’t capture all the computational abilities that real neurons possess and that this older model is potentially holding back AI development.
The new model developed at CCN posits that individual neurons exert more control over their surroundings than previously thought. The updated neuron model could ultimately lead to more powerful artificial neural ...
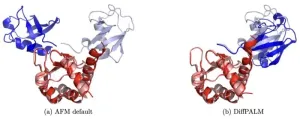
Proteins are the building blocks of life, involved in virtually every biological process. Understanding how proteins interact with each other is crucial for deciphering the complexities of cellular functions, and has significant implications for drug development and the treatment of diseases.
However, predicting which proteins bind together has been a challenging aspect of computational biology, primarily due to the vast diversity and complexity of protein structures. But a new study from the group of Anne-Florence Bitbol at EPFL might now change all that.
The team of scientists, ...
The world of artificial intelligence (AI) has recently seen significant advancements in generative models, a type of machine-learning algorithms that “learn” patterns from set of data in order to generate new, similar sets of data. Generative models are often used for things like drawing images and natural language generation – a famous example are the models used to develop chatGPT.
Generative models have had remarkable success in various applications, from image and video generation to composing music and to language modeling. The problem ...