(Note: researcher contact information at the end)
Humans drove wolves to extinction in Washington state around the 1930s. Thanks to conservation efforts, by about 80 years later, wolves had returned — crossing first from the Canadian border into Washington around 2008 and later entering the state from Idaho. Since then, wolf numbers in Washington have been steadily growing, raising questions about what the return of this large predator species means for ecosystems and people alike.
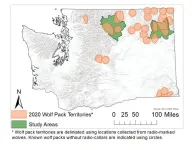
In northeast Washington, where wolves have recovered most successfully, researchers from the University of Washington and the Washington Department of Fish and Wildlife tracked one of their primary prey — white-tailed deer — in part to see what impact wolf packs are having on deer populations. The answer? So far, wolves aren’t having as much of an impact on deer as other factors.
In a paper published June 18 in Ecological Applications, the team reports that the biggest factors shaping white-tailed deer populations in northeast Washington are the quality of habitat available and a different, long-established large predator in the state: the cougar, also known as the mountain lion or puma. Wolves were a distant third in their impact.
“A big take-away from this study is that wolves are not returning to empty landscapes. These are places with humans and other carnivore species, like cougars, which will affect the impact that wolves can have,” said lead author Taylor Ganz, who conducted this research for her UW doctoral degree as part of the Washington Predator-Prey Project. “This area has a relatively high human footprint compared to other areas where wolves have been studied. These are not national parks or dense, old-growth forests. They are areas with active logging, farming, ranching and towns. Our findings show that these factors are likely limiting the impact of wolves on one of their primary food sources.”
It's not that wolves aren’t preying on white-tailed deer. According to the study, they are, just not enough to take a large bite out of the population as a whole.
White-tailed deer are widespread east of the Cascades. The state’s highest-density population of this species lies within the study area, which includes farmland and timber forests in parts of Stevens and Pend Oreille counties in northeast Washington. For the study, researchers radio-collared 280 white-tailed deer, 14 wolves, 50 cougars, 28 coyotes and 33 bobcats from 2016 to 2021. At the time of collaring, the researchers also noted vital statistics, including body condition, age and whether females were pregnant. When collared animals died, the team conducted a mortality investigation, if possible, and attempted to determine the cause of death.
The team, which also includes researchers with Washington State University and the Spokane Tribe of Indians, used the resulting dataset to estimate the growth rate of the white-tailed deer population over the four-year study, and to identify the major factors shaping it. The analysis determined that the white-tail population in the study area was likely stable, or slightly declining, but that wolves were not largely responsible.
The biggest factor impacting the deer population was habitat quality, including the amount of forage available for deer. For white-tailed deer, which are highly adaptable to human activity, foraging sites can range from forests and shrublands to agricultural fields. The study area includes both agricultural land and forests recently harvested for timber, both of which could provide deer with high-caloric density foraging sites, according to Ganz.
After habitat quality, the study found that predation by cougars had a smaller effect on the white-tailed population. Wolf predation had a still smaller impact. Bobcats and coyotes — both medium-sized predators — had a negligible impact on deer numbers.
“Studies like this provide valuable insights about the complexity of these systems and how managing predator and prey populations is challenging and dynamic,” said co-author Melia DeVivo, a research scientist with the WDFW. “It’s important to continue evaluating these systems to understand the impacts of management decisions. Prior to this study, one might have expected that relying solely on wolf management strategies would result in a booming deer population, when it is clearly more complex than that.”
Since their return, the number of wolves in Washington has risen steadily, reaching a minimum of 260 in 2023, according to state researchers. Four wolf packs reside in the northeast Washington Predator-Prey Project study area. The total number of wolves in the study area — about 23 — remained steady overall during the research period.
The team’s findings contrast with studies of long-established wolf populations in protected areas, like Yellowstone National Park, which show a higher impact of wolves on the population dynamics of their prey species. To the authors of this new study, those differences highlight the importance of studying wolves in a variety of habitats.
“This study reminds us that the population dynamics of predator and prey species can vary quite a bit,” said senior author Laura Prugh, a UW associate professor of environmental and forest sciences. “Habitat quality, the species that are present and the degree of human activity all affect the impact that large predators like wolves will have. It’s critical to compare different types of sites.”
The paper is part of the Washington Predator-Prey Project, a partnership between the UW and the WDFW to investigate the impact of the wolves’ return on state ecosystems. Additional co-authors are Sarah Bassing , a UW doctoral alum in environmental and forest sciences; Lauren Satterfield, a UW doctoral student in environmental and forest sciences; biologists Brian Kertson and Benjamin Turnock with the WDFW; Lisa Shipley, a professor at WSU; Savannah Walker and Derek Abrahamson, both biologists with the Spokane Tribe of Indians; Beth Gardner, a UW associate professor of environmental and forest sciences; and Aaron Wirsing, a UW professor of environmental and forest sciences. The research was funded by WDFW, the National Science Foundation, the Rocky Mountain Elk Foundation, and the UW College of the Environment.
###
For more information, contact Ganz at trganz@uw.edu.
Grant numbers:
National Science Foundation: DEB-1652420
Rocky Mountain Elk Foundation: WA190025 END