(Press-News.org) A new consortium co-led by Weill Cornell Medicine, has been awarded a five-year, $31 million grant from the National Institutes of Health’s National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases to accelerate the development of faster, more effective treatment regimens for tuberculosis (TB). Investigators at the University of California, San Francisco; Johns Hopkins Medicine; and Vanderbilt University Medical Center comprise the other co-leads.
The Preclinical Design and Clinical Translation of TB Regimens (PreDiCTR) consortium brings together more than 30 multidisciplinary investigators from 20 institutions in 6 countries. They aim to identify the most promising new and existing treatment combinations for the disease and help advance them toward clinical trials.
“One of the key goals is to reduce the time patients spend in therapy to be cured of TB,” said Dr. Dirk Schnappinger, professor of microbiology and immunology at Weill Cornell Medicine and one of the study’s four co-principal investigators. “Some progress has been made shortening the even longer regimens needed to treat drug resistant strains, but faster regimens for drug-sensitive strains of the disease are desperately needed.”
Worldwide about 10 million people develop TB and about 1. 5 million die each year from the disease, according to the World Health Organization. Despite the availability of curative antimicrobial therapies, disease control and eradication has proved elusive.
A lack of new drug development and long and arduous existing treatment regimens have contributed to a lack of progress. Dr. Schnappinger explained that current therapies start with an intense phase of four drugs followed by two drugs—a process that can last for six months in total and often requires supervised drug administration. However, patients may stop therapy early, which can lead to relapsing symptoms, disease spread and the emergence of new hard-to-treat drug-resistant strains.
“Symptoms improve relatively quickly, and there is a temptation not to continue therapy as directed,” he said. Limited resources in the lower-income countries where TB is most prevalent may compound these challenges.
The consortium brings together experts with complementary expertise in molecular genetics, computational biology, preclinical studies, and clinical trials to prioritize the most promising combinations of new and existing drugs for clinical trials.
The consortium’s other co-principal investigators are Dr. Rada Savic of the University of California, San Francisco; Dr. Kelly Dooley of Vanderbilt University; and Dr. Eric Nuermberger of Johns Hopkins University. Dr. Schnappinger will work with other Weill Cornell investigators to identify the molecular mechanisms that make some TB drug combinations more effective than others, using data from clinical trials and working backward.
The team plans to collaborate with other ongoing TB consortia and drug companies that make existing TB drugs or are developing new ones.
“We are hoping to close a gap in TB research,” Dr. Schnappinger said. “We are focused on translational studies that advance the results of preclinical research into clinical trials and use insights from clinical trials to further refine TB therapies.”
END
NIH funds consortium to accelerate development of new TB treatments
2024-07-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Older women more likely to receive heart surgery, die at low quality hospitals
2024-07-10
Women over the age of 65 who require complex heart surgery are more likely than men to receive care at low quality hospitals — where they also die in greater numbers following the procedure, a Michigan Medicine study finds.
The research, published in JAMA Network Open, covered nearly 450,000 Medicare beneficiaries who underwent coronary artery bypass grafting, or heart bypass surgery, between late 2015 and early 2020.
Compared to men, women were 1.26 times more likely to be treated at low quality hospitals, meaning facilities with the highest 30-day mortality rates.
At those low quality hospitals, ...
Nanocarbon catalyst design unlocks new avenue for sustainable fuel additive production
2024-07-10
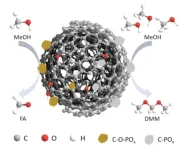
Vehicle exhaust from fossil fuel combustion constitutes a main source of air pollutants like carbon dioxide and carbon monoxide. To mitigate air pollution, researchers are looking into additive to fuels like dimethoxymethane (DMM). But DMM production brings its own environmental hazards.
In their paper published June 21 in Carbon Future, a Chinese research team demonstrated how a series of phosphorous-modified nanocarbon catalysts could advance green DMM production.
Unique fuel properties of this diesel blend fuel include high oxygen content and chemical stability as well as low toxicity. A blend of DMM and ...
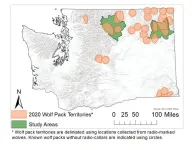
Wolves’ return has had only small impact on deer populations in NE Washington, study shows
2024-07-10
FROM: James Urton
(Note: researcher contact information at the end)
Humans drove wolves to extinction in Washington state around the 1930s. Thanks to conservation efforts, by about 80 years later, wolves had returned — crossing first from the Canadian border into Washington around 2008 and later entering the state from Idaho. Since then, wolf numbers in Washington have been steadily growing, raising questions about what the return of this large predator species means for ecosystems and people alike.
In northeast Washington, where wolves have recovered most successfully, researchers from the University of Washington and the Washington Department ...
Producing ‘space brick’ for moon base using microwave
2024-07-10
The Moon’s recent discovery of energy resources, such as water ice, has refocused interest on its potential as a sustainable hub for space exploration. NASA has also announced the Artemis mission, aiming for long-term human presence on the lunar surface. However, infrastructure expansion, such as lunar base construction plays a vital role.
Yet, transporting construction materials from Earth to the lunar surface via landers incurs a significant cost of 1.2 million USD per kilogram. Weight directly translates to cost, making the transportation of construction materials from Earth to the Moon nearly impossible.
To solve this problem, Korea ...
A simple firmware update completely hides a device’s Bluetooth fingerprint
2024-07-10
A smartphone’s unique Bluetooth fingerprint could be used to track the device’s user–until now. A team of researchers have developed a simple firmware update that can completely hide the Bluetooth fingerprint, eliminating the vulnerability.
The method was developed by a team of researchers at the University of California San Diego. The team discovered the vulnerability caused by Bluetooth fingerprints in a study they presented at the 2022 IEEE Security & Privacy conference. They presented the fix to this vulnerability two years later at the 2024 IEEE Security & Privacy conference. The math behind the update itself is complex but the implementation ...
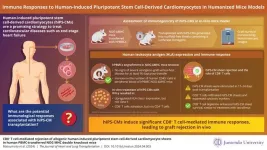
Immunogenicity of human-induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocyte sheets
2024-07-10
Ischemic heart disease stands as a significant global cause of morbidity and mortality. One promising avenue for treatment involves human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes (hiPS-CMs). Derived from adult somatic cells such as blood or skin cells, hiPS cells possess the capacity to differentiate into various tissues, including cardiomyocytes. These cells can potentially repair damaged heart tissue, but their clinical application is limited due to concerns about immune rejection. Understanding the immunogenicity of hiPS-CMs is crucial for advancing their ...
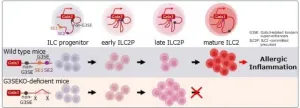
Unravelling a mechanism of Group 2 innate lymphoid immune cell development
2024-07-10
Overproduction of Group 2 innate lymphoid cells or ILC2s—a type of white blood cells—can sometimes exacerbate conditions such as bronchial asthma, chronic rhinosinusitis, atopic dermatitis, and organ fibrosis through an exaggerated immune response. Although there are immunomodulatory drugs that can suppress Type 2 helper T (Th2) cells, drugs capable of suppressing ILC2s are currently lacking.
Now, however, in a breakthrough study that could lead to the development of a new therapeutic strategy targeting ILC2s, researchers led by Associate Professor Arifumi Iwata of the Chiba University Hospital, Japan, have identified molecular ...
Award for Excellence in Natural Product Chemistry to Ricardo Riguera
2024-07-10
The Specialised Group on Chemistry of Natural Products (GQPN) of the Spanish Royal Society of Chemistry (RSEQ) has awarded its Excellence in Research Award 2023 to Professor Ricardo Riguera. The Evaluation Committee thus recognises his valuable contribution to this area of chemistry. Among other advances, his work has made it possible to describe a large number of bioactive metabolites, such as the first heptacyclopeptide and the first cyclodepsipeptide isolated from marine organisms. Riguera also identified one of the first examples of cytotoxic metabolites from marine bacteria, the first description of L-galactose as part of a natural product, and the first description ...
Researchers develop an AI model that predicts Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy survival
2024-07-10
FINDINGS
A UCLA-led team has developed a machine-learning model that can predict with a high degree of accuracy the short-term survival of dialysis patients on Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy (CRRT).
BACKGROUND
CRRT is a therapy used for very sick hospitalized patients whose health status makes them ineligible for regular hemodialysis. It is a gentler therapy that provides continuous treatment over a prolonged period. About half of adults placed on CRRT, however, do not survive, rendering the treatment futile for both patients ...
Living in poverty due to mental health problems or developing mental health problems because of poverty? It's both.
2024-07-10
Poverty and mental illness are not only linked, but there is also a causal relationship. This is the conclusion of researchers from Amsterdam UMC, the University of Edinburgh and the University of Modena. Their study shows that while certain mental health issues can hinder financial stability, poverty is also one of the causal factors leading to mental health problems. This study was published today in Nature Human Behaviour.
"This study indicates that certain mental health problems can make a person's financial situation uncertain. But conversely, we also see that poverty can lead to mental health problems," ...