(Press-News.org) While taking snapshots with the high-speed “electron camera” at the Department of Energy’s SLAC National Acceleratory Laboratory, researchers discovered new behavior in an ultrathin material that offers a promising approach to manipulating light that will be useful for devices that detect, control or emit light, collectively known as optoelectronic devices, and investigating how light is polarized within a material. Optoelectronic devices are used in many technologies that touch our daily lives, including light-emitting diodes (LEDs), optical fibers and medical imaging.
As reported in Nano Letters, the team, led by SLAC and Stanford professor Aaron Lindenberg, found that when oriented in a specific direction and subjected to linear terahertz radiation, an ultrathin film of tungsten ditelluride, which has desirable properties for polarizing light used in optical devices, circularly polarizes the incoming light.
Terahertz radiation lies between the microwave and the infrared regions in the electromagnetic spectrum and enables novel ways of both characterizing and controlling the properties of materials. Scientists would like to figure out a way to harness that light for the development of future optoelectronic devices.
Capturing a material’s behavior under terahertz light requires an advanced instrument capable of recording the interactions at ultrafast speeds, and SLAC’s world-leading instrument for ultrafast electron diffraction (MeV-UED) at the Linac Coherent Light Source (LCLS) can do just that. Whereas the MeV-UED is normally used to visualize the motion of atoms by measuring how they scatter electrons after hitting a sample with an electron beam, this new work used the femtosecond electron pulses to visualize the electric and magnetic fields of the incoming terahertz pulses, which caused the electrons to wiggle back and forth. In the study, circular polarization was indicated by images of the electrons that showed a circular pattern rather than a straight line.
The ultrathin material was a mere 50 nanometers thick. “This is 1,000 to 10,000 times thinner than what we typically need to induce this type of response,” said Lindenberg.
Researchers are excited about using these ultrathin materials, known as two-dimensional (2D) materials, to make optoelectronic devices smaller and capable of more functions. They envision creating devices from layers of 2D structures, like stacking Legos, Lindenberg said. Each 2D structure would be composed of a different material, precisely aligned to generate a specific type of optical response. These different structures and functionalities can be combined into compact devices that could find potential applications – for example, in medical imaging or other types of optoelectronic devices.
“This work represents another element in our toolbox for manipulating terahertz light fields, which in turn could allow for new ways to control materials and devices in interesting ways,” said Lindenberg.
The study was supported by the DOE Office of Science and used resources of the National Energy Research Scientific Computing Center (NERSC). LCLS and NERSC are DOE Office of Science user facilities.
END
SLAC’s high-speed electron camera uncovers a new ‘light-twisting’ behavior in an ultrathin material
2024-07-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Jump start your science career: DOE applications for 2025 student internships now open
2024-07-10
WASHINGTON, DC – Applications are currently being accepted for the Spring 2025 term of two programs offered by the Department of Energy (DOE) Office of Science (SC): the Science Undergraduate Laboratory Internships (SULI) program and the Community College Internships (CCI) program. The application deadline for the two programs is 5:00 pm (ET) October 2, 2024.
Through the SULI and CCI programs, undergraduate students and recent graduates discover science and technology careers at the DOE national laboratories and gain the experience ...
New guidance for healthcare professionals to address muscle-building supplement use
2024-07-10
Toronto, ON – In a groundbreaking effort to mitigate the risks associated with muscle-building dietary supplement use among adolescents and young adults, a comprehensive set of guidelines has been introduced to assist healthcare professionals. These guidelines, published in the Journal of Adolescent Health, focus on assessment and harm reduction strategies to better support young individuals engaged in the use of these readily available supplements.
Muscle-building dietary supplements, such as whey protein and creatine monohydrate, are commonly used by adolescents and young adults, particularly boys and young men, and are intended to enhance muscle mass, ...
It is possible to predict cognitive decline in Alzheimer's disease
2024-07-10
Amsterdam UMC's Alzheimer Centre has developed a prediction model that can predict cognitive decline in patients with mild cognitive impairment or mild dementia due to Alzheimer's disease. The next step is developing an app that uses this prediction model, which would represent an important step towards personalised forecasts for patients. The study is published today in the journal Neurology.
After people have been diagnosed with Alzheimer's, their first question is often: "What can I expect now?". This question is difficult ...
Can we predict how fast cognitive decline will occur with early Alzheimer’s?
2024-07-10
MINNEAPOLIS – A new study looks at predicting how quickly people with early Alzheimer’s disease will experience cognitive decline. The study is published in the July 10, 2024, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology. It also looked at how the new drugs recently approved for the disease may reduce decline.
“The rate of cognitive decline varies greatly from person to person, and people are very interested in what to expect from the disease in themselves or their loved ones, so better prediction models are urgently needed,” said study author Pieter J. van der Veere, M.D., of Amsterdam ...
New Consumer Food insights from Purdue explores consumer attitudes toward U.S. farm bill
2024-07-10
The general public has limited knowledge of the U.S. farm bill that politicians are debating on Capitol Hill, according to the June 2024 Consumer Food Insights (CFI) Report.
The survey-based report out of Purdue University’s Center for Food Demand Analysis and Sustainability (CFDAS) assesses food spending, consumer satisfaction and values, support of agricultural and food policies, and trust in information sources. Purdue experts conducted and evaluated the survey, which included 1,200 consumers across the U.S
“Around one-third ...
Lion with nine lives breaks record with longest swim in predator-infested waters
2024-07-10
A record-breaking swim by two lion brothers across a predator-infested African river has been documented in a study co-led by Griffith University and Northern Arizona University.
Dr Alexander Braczkowski, from Griffith’s Centre for Planetary Health and Food Security, led a team that filmed a two-male lion coalition crossing the Kazinga Channel in Uganda at night, using high-definition heat detection cameras on drones. The work was done under the supervision of the Uganda Wildlife Authority.
One half of the lion brother duo was a 10-year-old ...
Pumpkin disease not evolving, could make a difference for management
2024-07-10
URBANA, Ill. -- The pathogen that causes bacterial spot is very good at what it does. Forming small lesions on the rinds of pumpkins, melons, cucumbers, and other cucurbits, it mars the fruits’ appearance and ushers in secondary pathogens that lead to rot and severe yield loss. The bacterium, Xanthomonas cucurbitae, is so successful that it has had no reason to evolve through time or space. That’s according to new University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign research characterizing ...
Aging exacerbates oxidative stress and liver fibrosis in an animal model of Down Syndrome
2024-07-10
“[...] our results put the basis for the use of antioxidants supplementation in Down Syndrome patients to prevent liver-associated pathologies.”
BUFFALO, NY- July 10, 2024 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 16, Issue 12, entitled, “Aging exacerbates oxidative stress and liver fibrosis in an animal model of Down Syndrome.”
Down Syndrome (DS) is a common genetic disorder characterized by an extra copy of chromosome 21, leading to dysregulation of various metabolic pathways. Oxidative stress in DS is associated ...
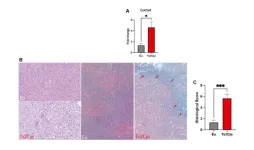
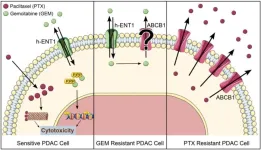
Targeting ABC transporters in PDAC – past, present, or future?
2024-07-10
“[...] it is crucial for the future application of ABC transporter inhibitors [...] to develop a stratification protocol [...] to identify those PDAC patients who are most likely to benefit from chemosensitization induced by these inhibitors.”
BUFFALO, NY- July 10, 2024 – A new editorial paper was published in Oncotarget's Volume 15 on June 20, 2024, entitled, “Targeting ABC transporters in PDAC – past, present, or future?”
In this new editorial, Cecilia Bergonzini, Elisa Giovannetti and Erik ...
Machine learning models could enable earlier identification of at-risk children, aiding social workers and potentially improving outcomes, per Danish study of more than 100,000 children
2024-07-10
Machine learning models could enable earlier identification of at-risk children, aiding social workers and potentially improving outcomes, per Danish study of more than 100,000 children
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0305974
Article Title: Predictive risk modeling for child maltreatment detection and enhanced decision-making: Evidence from Danish administrative data
Author Countries: Denmark, France
Funding: Funding for this project was ...