(Press-News.org) Hens fluff their head feathers and blush to express different emotions and levels of excitement, according to a study publishing July 24, 2024, in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Cécile Arnould and colleagues from INRAE and CNRS, France.
Facial expressions are an important part of human communication that allow us to convey our emotions. Scientists have found similar signals of emotion in other mammals such as dogs, pigs and mice. Although birds can produce facial expressions by moving their head feathers and flushing their skin, it is unclear whether they express emotions in this way. To investigate, researchers filmed 18 female domestic chickens (Gallus gallus domesticus) from two breeds, as they performed routine behaviors on a French farm. They also filmed the birds while being captured and held by a human, and while being rewarded with an appealing food.
The researchers analyzed the position of their facial feathers and the color of the exposed skin on their faces in seven contexts that differed in their emotional valence and level of excitement. For example, birds preen their feathers when they are relaxed and content, whereas receiving a rewarding food generally causes excitement and happiness, and being captured is an exciting but fearful experience.
The results suggested that the position of the head feathers and the color of the skin varied between contexts. Fluffed head feathers were mainly associated with a state of contentment, whereas blushing indicated that the birds were positively excited or fearful. Hens tended to have redder skin in contexts associated with excitement, and in those that caused negative emotions. In situations that caused both excitement and a positive emotion, the birds displayed an intermediate skin redness, indicating a continuum of blushing that can convey subtle emotional changes.
The study was the first to investigate facial displays of emotion in chickens, and suggests that domestic hens use facial expressions to show their emotions, much like humans and other mammals do. These findings offer a window into the emotional experiences of domestic birds, which could be used to improve the welfare of farmed poultry, the authors say.
The authors add: “The skin blushing on the face of the domestic fowl is a window into their emotions. The intensity of the blushing varies within a few seconds depending on the emotional situations they experience.”
#####
In your coverage please use this URL to provide access to the freely available article in PLOS ONE: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0306601
Citation: Arnould C, Love SA, Piégu B, Lefort G, Blache M-C, Parias C, et al. (2024) Facial blushing and feather fluffing are indicators of emotions in domestic fowl (Gallus gallus domesticus). PLoS ONE 19(7): e0306601. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0306601
Author Countries: France
Funding: This work was supported by INRAE: UMR PRC (CA, SAL, FL, RN, LL, AB) and Métaprogramme SANBA - RED project (CA, SAL, MCB, FL, RN, LL, AB). DS thesis is supported by INRAE and Région Centre Val de Loire. The funders have no role in the data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
END
Hens blush when they are scared or excited
Domestic chickens use flushed skin and feather fluffing to display different emotions, levels of excitement
2024-07-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Weibo posts illuminate public response to China’s three-child policy measures
2024-07-24
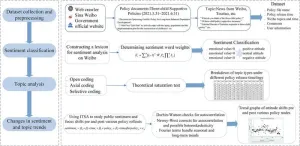
An analysis of comments on Chinese social media platform Sina Weibo reveals trends in the public response to measures implemented to support China’s three-child policy, highlighting concerns about women’s rights and employment. Lijuan Peng of Zhejiang Gongshang University in Hangzhou, China, and colleagues present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on July 24, 2024.
For decades, China’s one-child policy restricted most families to having just one child. In 2021, to combat a falling birthrate, China introduced its three-child policy, allowing couples to have up to three children. To help encourage childbirth, ...
Our ability to recognize music might not diminish with age, with older concert attendees identifying themes in music as well as younger participants
2024-07-24
Our ability to recognize music might not diminish with age, with older concert attendees identifying themes in music as well as younger participants
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0305969
Article Title: Age and familiarity effects on musical memory
Author Countries: Canada, UK
Funding: The author(s) disclosed receipt of the following financial support for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article: this work was supported by BRZ’s Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada grant. The funders had no role ...
The COVID-19 pandemic slowed progress towards health-related Sustainable Development Goals and increased inequalities
2024-07-24
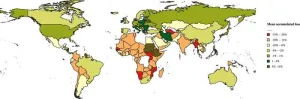
The COVID-19 pandemic significantly widened existing economic and health disparities between wealthy and low-income countries and slowed progress toward health-related Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), according to a new study published July 24, 2024, in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Wanessa Miranda of Federal University of Minas Gerais, Brazil, and colleagues.
The global SDGs were established in 2015 as a wide and integrated agenda with themes ranging from eradicating poverty and promoting well-being to addressing socioeconomic ...
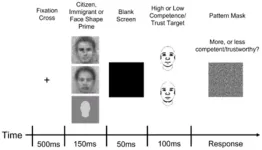
Even people who harbor positive sentiments toward immigrants imagine immigrants' faces as less trustworthy and less competent than US citizens' faces
2024-07-24
Even people who harbor positive sentiments toward immigrants imagine immigrants' faces as less trustworthy and less competent than US citizens' faces
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0306872
Article Title: Intergroup evaluative bias in facial representations of immigrants and citizens in the United States
Author Countries: USA
Funding: This work was facilitated by the National Science Foundation Division of Behavioral and Cognitive Sciences, grant #1764097 awarded to ART and grant #2215236 awarded to ...
Southern Ocean absorbing more CO2 than previously thought, study finds
2024-07-24
New research led by the University of East Anglia (UEA) and Plymouth Marine Laboratory (PML) has found that the Southern Ocean absorbs more carbon dioxide (CO2) than previously thought.
Using direct measurements of CO2 exchange, or fluxes, between the air and sea, the scientists found the ocean around Antarctica absorbs 25% more CO2 than previous indirect estimates based on shipboard data have suggested.
The Southern Ocean plays a major role in absorbing CO2 emitted by human activities, a process vital for controlling the Earth's climate. However, there are big uncertainties ...
Saharan dust regulates hurricane rainfall
2024-07-24
Giant plumes of Sahara Desert dust that gust across the Atlantic can suppress hurricane formation over the ocean and affect weather in North America.
But thick dust plumes can also lead to heavier rainfall – and potentially more destruction – from landfalling storms, according to a July 24 study in Science Advances. The research shows a previously unknown relationship between hurricane rainfall and Saharan dust plumes.
“Surprisingly, the leading factor controlling hurricane precipitation is not, as traditionally thought, sea surface temperature or humidity in the atmosphere. Instead, it’s Sahara dust,” said the corresponding ...
Fighting leukemia by targeting its stem cells
2024-07-24
Acute myeloid leukaemia is one of the deadliest cancers. Leukaemic stem cells responsible for the disease are highly resistant to treatment. A team from the University of Geneva (UNIGE), University Hospital of Geneva (HUG), and Inserm has made a breakthrough by identifying some of the genetic and energetic characteristics of these stem cells, notably a specific iron utilisation process. This process could be blocked, leading to the death or weakening of these stem cells without affecting healthy cells. These results, published in Science Translational Medicine, pave the way for new therapeutic strategies.
Acute ...
NASA’s Webb images cold exoplanet 12 light-years away
2024-07-24
An international team of astronomers using NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope has directly imaged an exoplanet roughly 12 light-years from Earth. The planet, Epsilon Indi Ab, is one of the coldest exoplanets observed to date.
The planet is several times the mass of Jupiter and orbits the K-type star Epsilon Indi A (Eps Ind A), which is around the age of our Sun, but slightly cooler. The team observed Epsilon Indi Ab using the coronagraph on Webb’s MIRI (Mid-Infrared Instrument). Only a few tens of exoplanets have been directly imaged previously by space- and ground-based observatories.
“Our prior observations of this system have been more indirect measurements ...
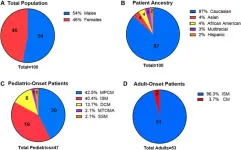
Prevalence and impact of the KIT M541L variant in patients with mastocytosis
2024-07-24
“This study uniquely examines the prevalence and impact of the KIT M541L variant in both adult and pediatric patients with mastocytosis further stratified by disease variant.”
BUFFALO, NY- July 24, 2024 – A new research paper was published in Oncotarget's Volume 15 on July 22, 2024, entitled, “Prevalence and impact of the KIT M541L variant in patients with mastocytosis.”
Activating mutations in KIT, particularly D816V, have been associated with mastocytosis. Additionally, expression of heterozygous KIT M541L has been primarily ...
Experts outline considerations to deploy AI in radiology
2024-07-24
Artificial Intelligence (AI) tools can play a key role in medical imaging if radiologists trust in their design, deploy them with adequate training and establish clear guidelines regarding clinical accountability, according to a recently published Special Report in Radiology: Artificial Intelligence, a journal of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
RSNA and the Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention (MICCAI) Society have led a series of joint panels and seminars focused on the present impact and future directions of AI in radiology. These conversations ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Study finds Earth may have twice as many vertebrate species as previously thought
NYU Langone orthopedic surgeons present latest clinical findings and research at AAOS 2026
New journal highlights how artificial intelligence can help solve global environmental crises
Study identifies three diverging global AI pathways shaping the future of technology and governance
Machine learning advances non targeted detection of environmental pollutants
ACP advises all adults 75 or older get a protein subunit RSV vaccine
New study finds earliest evidence of big land predators hunting plant-eaters
Newer groundwater associated with higher risk of Parkinson’s disease
New study identifies growth hormone receptor as possible target to improve lung cancer treatment
Routine helps children adjust to school, but harsh parenting may undo benefits
IEEE honors Pitt’s Fang Peng with medal in power engineering
SwRI and the NPSS Consortium release new version of NPSS® software with improved functionality
Study identifies molecular cause of taste loss after COVID
Accounting for soil saturation enhances atmospheric river flood warnings
The research that got sick veterans treatment
Study finds that on-demand wage access boosts savings and financial engagement for low-wage workers
Antarctica has lost 10 times the size of Greater Los Angeles in ice over 30 years
Scared of spiders? The real horror story is a world without them
New study moves nanomedicine one step closer to better and safer drug delivery
Illinois team tests the costs, benefits of agrivoltaics across the Midwest
Highly stable self-rectifying memristor arrays: Enabling reliable neuromorphic computing via multi-state regulation
Composite superionic electrolytes for pressure-less solid-state batteries achieved by continuously perpendicularly aligned 2D pathways
Exploring why some people may prefer alcohol over other rewards
How expectations about artificial sweeteners may affect their taste
Ultrasound AI receives FDA De Novo clearance for delivery date AI technology
Amino acid residue-driven nanoparticle targeting of protein cavities beyond size complementarity
New AI algorithm enables scientific monitoring of "blue tears"
Insufficient sleep among US adolescents across behavioral risk groups
Long COVID and recovery among US adults
Trends in poverty and birth outcomes in the US
[Press-News.org] Hens blush when they are scared or excitedDomestic chickens use flushed skin and feather fluffing to display different emotions, levels of excitement