(Press-News.org) Digital Science, a technology company serving stakeholders across the research ecosystem, is pleased to share the news that Midwestern University has successfully launched a new faculty profiles portal powered by Symplectic Elements.
Midwestern has been utilizing Symplectic Elements as its Research Information Management System since 2019, and has made the decision to expand its use by adding public profiles. The faculty profiles repurpose the comprehensive data already within Elements to populate enhanced profiles, including biographical information as well as their publications, grants and professional and teaching activities.
Midwestern’s faculty profiles currently include more than 2,700 faculty members, which can be filtered by campus, academic degree program, availability and department. The profiles enhance the discoverability of Midwestern’s research and impact, giving faculty a simple and visible way to share and showcase their work, build new research collaborations, and connect with new students, industry professionals, or the media.
See more here: facultyprofiles.midwestern.edu
Founded in 1900, Midwestern University is a not-for-profit graduate institution of higher education offering degrees in the health sciences across two campuses. The institution and its resources are dedicated to the highest standards of academic excellence to meet the needs of the healthcare community.
“We’re excited to launch Midwestern University’s faculty profiles portal powered by Symplectic Elements,” said Rebecca Caton, Director of Library Services, Midwestern University. “This initiative aligns with our mission to highlight the most important resources of our campuses, which is our faculty. We are dedicated to meeting the highest standards of academic excellence to meet the educational needs of the healthcare community. We believe this tool will greatly benefit our faculty and advance the visibility and impact of Midwestern’s research, academic, scholarship, and service endeavors.”
About Midwestern University
Healthcare education is what we do. We’re an established leader with an exciting vision for the future. Midwestern University offers programs that give you solid footing in the sciences, extensive hands-on experience in outstanding clinical rotations, and a compassionate perspective toward your patients.
About Symplectic
Symplectic works in pursuit of the advancement of knowledge, delivering flexible information management solutions that help universities, institutions and funders achieve their research goals.
Symplectic Elements is a highly configurable platform which ingests data from multiple sources to build a truly comprehensive picture of scholarly data and activities. With over 20 years of experience and 115+ clients, Symplectic Elements is trusted by universities, institutions and research organizations around the world.
About Digital Science
Digital Science is an AI-focused technology company providing innovative solutions to complex challenges faced by researchers, universities, funders, industry and publishers. We work in partnership to advance global research for the benefit of society. Through our brands – Altmetric, Dimensions, Figshare, ReadCube, Symplectic, IFI CLAIMS Patent Services, Overleaf, Writefull, OntoChem, Scismic and metaphacts – we believe when we solve problems together, we drive progress for all. Visit www.digital-science.com and follow @digitalsci on X or on LinkedIn.
Media contacts
Simon Linacre, Head of Content, Brand & Press, Digital Science: Mobile +44 7484 381477, s.linacre@digital-science.com
David Ellis, Press, PR & Social Manager, Digital Science: Mobile +61 447 783 023, d.ellis@digital-science.com
END
Midwestern launches public research profiles through Symplectic Elements
2024-07-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Accelerating motor neurone disease research by harnessing the power of health data
2024-07-25
MND is a devastating disease affecting the motor neurones in the brain and spinal cord, leading to progressive muscle weakness and paralysis. Despite decades of research, several scientific challenges continue to impede the development of effective therapies for the thousands of people living with MND in the UK.
The MND Research Data Catalyst is a new initiative led by HDR UK and DPUK, with the UK Dementia Research Institute (UK DRI) and in partnership with the MND research community, to accelerate the discovery of new diagnostics, treatments and support better care for MND patients. This will be achieved by harnessing the UK’s trustworthy, large-scale health ...
World Hepatitis Day 2024: Madrid study shows decrease in active hepatitis C infection among risk groups, indicating effectiveness of public health measures
2024-07-25
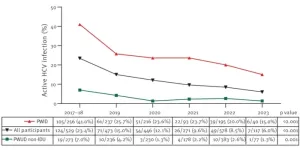
A study conducted through a mobile screening unit in Madrid, Spain from 2017 to 2023 and published in Eurosurveillance found that active hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection decreased from 23% to 6% in that period among people who use drugs (PWUD) that visited the unit. The study found that the use of intravenous drugs was the most significant risk factor for infection among PWUD. It confirmed that HCV screening and treatment programmes targeting this at-risk population are effective and can help achieve the World Health Organization goal of HCV elimination as public health threat by 2030.
Study participants and methods
Participants were recruited in ‘hotspots’ ...
After Trump’s election, women of color had more underweight, premature babies, study finds
2024-07-25
In 2016, President-elect Donald Trump vowed to deport thousands of immigrants. His anti-immigration message vilified foreign-born people living in the U.S. as criminals and rapists. Besides making good on many harsh, immigration-related promises, the years after his election stoked the anxieties of millions of people.
Now, with Trump once again in contention for the White House, a new study from the University of California, Berkeley, reveals the surprising — and potentially lifelong — association between those early Trump years and the health of society's newest citizens.
In ...
Space-trekking muscle tests drugs for microgravity-induced muscle impairment
2024-07-25
A gentle rumble ran under Ngan Huang’s feet as a rocket carrying her research—live, human muscle cells grown on scaffolds fixed on tiny chips—lifted off, climbed, and disappeared into the sky to the International Space Station National Laboratory. These chips would help Huang better understand muscle impairment, often seen in astronauts and older adults, and test drugs to counter the condition.
Now, the results are back. Reporting in a study published July 25 in Stem Cell Reports, Huang’s team showed that space-travelling muscle had metabolic changes that indicate ...
In clinical trial, fecal matter transplant helped half of patients with gastrointestinal cancers overcome resistance to immunotherapy treatment
2024-07-25
Findings from a small, proof-of-concept clinical trial have suggested that fecal microbiota transplants (FMTs) can boost the effectiveness of immunotherapy in a range of gastrointestinal cancers. In the study, published July 25 in the journal Cell Host & Microbe, six of 13 patients who had previously shown resistance to immune checkpoint inhibitors benefited from receiving FMTs from donors who had previously responded to treatment. The investigators also identified specific strains of bacteria associated with better or worse responses to FMT and immune checkpoint drugs.
“This research highlights the complex interplay between beneficial ...
Royal Ontario Museum scientist identifies Great Salt Lake as a significant source of greenhouse gas emissions
2024-07-25
Newly announced research by Royal Ontario Museum (ROM) examining greenhouse gas emissions from the drying lake bed of Great Salt Lake, Utah, calculates that 4.1 million tons of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases were released in 2020. This research suggests that drying lake beds are an overlooked but potentially significant source of greenhouse gases, which may further increase due to climate change. These results were announced in the paper, “A desiccating saline lake bed is a significant source of anthropogenic greenhouse gas emissions,” published in the journal One Earth.
“Human-caused ...
Provision of stroke care services by community disadvantage status
2024-07-25
About The Study: Hospitals in communities with the greatest level of socioeconomic disadvantage had the lowest likelihood of becoming stroke certified while hospitals in the most advantaged communities had the highest likelihood in this cohort study. These findings suggest that there is a need to support hospitals in disadvantaged communities to obtain stroke certification as a way to reduce stroke disparities.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Renee Y. Hsia, M.D., M.Sc., email renee.hsia@ucsf.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link ...
Bilateral mastectomy and breast cancer mortality
2024-07-25
About The Study: This cohort study indicates that the risk of dying of breast cancer increases substantially after experiencing a contralateral breast cancer. Women with breast cancer treated with bilateral mastectomy had a greatly diminished risk of contralateral breast cancer; however, they experienced similar mortality rates as patients treated with lumpectomy or unilateral mastectomy.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Steven A. Narod, M.D., email steven.narod@wchospital.ca.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamaoncol.2024.2212)
Editor’s ...
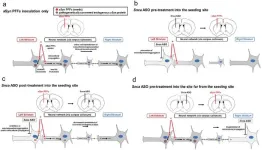
Antisense oligonucleotide treatment shows promise in treating Parkinson's disease progression
2024-07-25
TMDU researchers demonstrate proof of concept of antisense nucleic acid therapy to prevent the spread of α-synuclein pathologies in synucleinopathies.
Tokyo, Japan – Parkinson’s disease (PD), as well as many other neurodegenerative disorders, has shown a link between the abnormal aggregation of a protein called α-synuclein (aSyn) and neuronal death. These aggregates, known as Lewy bodies and Lewy neurites depending on their subcellular localization, can spread by continuously causing normal endogenous aSyn to misfold. The complex nature of this aggregation process poses significant challenges ...
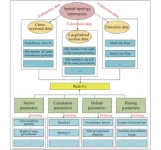
Intelligent engineering: AI transforms spatial arrangement of hydropower underground facilities
2024-07-25
Designing the spatial arrangement of underground powerhouses involves numerous complex parameters and boundaries, requiring frequent reference to various cases and specifications. Traditional methods struggle to efficiently retrieve this information, leading to suboptimal designs and extended project timelines. Due to these challenges, there is a pressing need for a more intelligent and efficient approach to streamline the design process, enhance accuracy, and improve project management in hydropower engineering.
Researchers from Tianjin University, in collaboration with PowerChina Kunming Engineering Corporation Limited and other ...