(Press-News.org)
In a groundbreaking study recently published, researchers from Zhejiang University have unveiled significant findings that could enhance brain-computer interface (BCI) technologies, marking a crucial step towards more intuitive neuroprosthetic control and advanced rehabilitation therapies. The study, titled "Neural Correlates of Motor/Tactile Imagery and Tactile Sensation in a BCI paradigm: A High-Density EEG Source Imaging Study," employed high-density electroencephalogram (EEG) recordings to delve into the neural dynamics of motor and tactile imagery.
Brain-computer interfaces, devices that translate brain activity into commands for external software or hardware, have predominantly utilized motor imagery tasks where subjects imagine moving parts of their body without actual motion. This study expands on the BCI concept by integrating sensory imagery tasks, particularly focusing on tactile sensations, thereby providing new avenues for BCI applications.
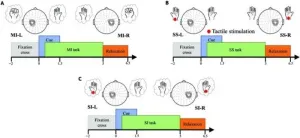
The research team, led by Huan Wen and Lin Yao, conducted experiments involving eleven participants who were instructed to engage in both motor imagery (MI) and sensory imagery (SI) tasks. These tasks were designed to evoke brain responses from imagining motor actions and tactile sensations without physical stimuli. Using sophisticated EEG source imaging techniques, the study systematically examined the cortical activation differences and correlations between these tasks.
Key findings revealed that imagined tactile and motor tasks activate distinct regions within the sensorimotor cortex. While both tasks showed similar patterns in alpha bands, critical differences were noted in other frequency bands, indicating unique underlying neurophysiological processes. For instance, real sensory stimulation (SS) and imagined sensory tasks exhibited comparable activation patterns, suggesting potential strategies for training BCI systems.
This study is the first of its kind to use high-density EEG recordings to explore the intricate relationship between motor and tactile imagery. The researchers' approach has allowed for a detailed examination of the cortical sources of EEG signals, providing insights that were previously unattainable with traditional EEG methods.
The implications of these findings are vast. For one, they could significantly improve the accuracy and efficiency of BCIs, particularly in distinguishing between different types of imagery, which is crucial for the precise control of neuroprosthetics.
Moreover, the study paves the way for the development of new BCI designs that could include more diverse and complex commands, enhancing the interface's functionality.
In rehabilitation, these findings could revolutionize treatment protocols. Patients recovering from strokes or other motor impairments could benefit from tailored BCI therapies that harness both motor and tactile imagery, potentially accelerating the recovery process and improving outcomes.
The research also highlights the importance of sensory imagery in BCIs, an area that has received less attention compared to motor imagery. By demonstrating the feasibility and effectiveness of including sensory tasks in BCI frameworks, the study invites further exploration into multi-modal BCIs that could support more natural interactions with technology.
As we advance towards more integrated and responsive BCIs, the work of Wen, Yao, and their team provides a critical foundation for future innovations. Their study not only expands our understanding of the brain's imaging capabilities but also opens new pathways for enhancing human-computer interaction.
The paper, "Neural Correlates of Motor/Tactile Imagery and Tactile Sensation in a BCI paradigm: A High-Density EEG Source Imaging Study," was published in the journal Cyborg and Bionic Systems on Jun 21, 2024, at DOI: https://spj.science.org/doi/10.34133/cbsystems.0118
END
MIAMI (August 20, 2024) – Inhaler misuse leading to inadequate medication delivery impacts a person’s ability to manage symptoms of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and additional education about proper inhaler use is needed to improve health outcomes, according to two new articles. The articles are published in the July 2024 issue of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases: Journal of the COPD Foundation, a peer-reviewed, open-access journal.
COPD comprises several conditions, including chronic bronchitis and emphysema, and can be caused by irritants like smoke or pollution and genetics. The disease affects more than 30 ...
During a pandemic, attention is usually focused on the immediate challenges, such as managing the disease, ensuring safety and coping with disruptions in daily routines. Adversity, while difficult, can sometimes lead to positive effects.
For older adults living in retirement communities, there has been limited research on how the COVID-19 pandemic and its regulatory measures affected them. Additionally, there is scant research on any potential positive effects for this population.
Now, a new study of 98 older adults (median age 86 years) living in a continuing care retirement community in South Florida during COVID-19 reveals ...
UTSA will partner with Texas A&M University to co-lead SECURE Southwest, one of five new regional centers being launched to strengthen U.S. research security.
Under a five-year, $67 million award from the National Science Foundation (NSF), the Safeguarding the Entire Community of the U.S. Research Ecosystem (SECURE) Center aims to strengthen intellectual property and research security by educating members of the research community about security issues and engaging them in a process of collaborative problem-solving.
The ...
A widely used security protocol that dates back to the days of dial-up Internet has vulnerabilities that could expose large numbers of networked devices to an attack and allow an attacker to gain control of traffic on an organization's network.
A research team led by University of California San Diego computer scientists investigated the Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service (RADIUS) protocol and found a vulnerability they call Blast-RADIUS that has been present for decades. RADIUS, designed in 1991, allows networked devices such as routers, switches or mobile roaming gear to use a remote server to validate login or other credentials.
This is a common set-up in enterprise and ...
A study of children’s conversations with their caretakers sheds light on the timeline of the emergence of moral foundation words in the first six years of life in English-speaking children. Moral Foundations theory posits that morality is largely intuitive and underlaid by modular foundations. The original set of five foundations proposed by researchers includes Care/Harm, Fairness/Cheating, Authority/Subversion, Loyalty/Betrayal, and Purity/Degradation. Aida Ramezani and colleagues systematically ...
Political animus between Republicans and Democrats in the United States is alarmingly high, raising fears of undemocratic or even violent actions. An often-touted intervention to prevent political polarization is to identify and correct misperceptions about people’s partisan opponents. Sean Westwood and colleagues sought to empirically test the effectiveness of this strategy. The authors surveyed 9,810 American partisans online from fall 2022 to fall 2023, finding that their opinions of whether ...
A newly discovered code within DNA – coined “spatial grammar” – holds a key to understanding how gene activity is encoded in the human genome.
This breakthrough finding, identified by researchers at Washington State University and the University of California, San Diego and published in Nature, revealed a long-postulated hidden spatial grammar embedded in DNA. The research could reshape scientists’ understanding of gene regulation and how genetic variations may influence gene expression in development or disease.
Transcription factors, the proteins that control which genes in one’s genome are turned on or off, ...
An ongoing survey captures how the Russian invasion of Ukraine affected attitudes in European countries not directly involved in the conflict. Margaryta Klymak and Tim Vlandas examine how the Russian invasion of Ukraine affected economic and political attitudes in eight European countries. The authors took advantage of the timing of the European Social Survey (ESS), which happened to be administered both just before and just after the Russian invasion of Ukraine in February 2022 in eight countries: Switzerland, Greece, Italy, Montenegro, Macedonia, Netherlands, Norway, and Portugal. Overall, the invasion increased support ...
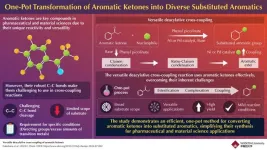
Aromatic ketones have long been valuable intermediates in chemical synthesis, particularly in cross-coupling reactions where different chemical entities are combined to form new compounds. For instance, a process called deacylative cross-coupling removes the acyl group from the aromatic ketone, allowing it to bond with other chemicals and produce a wide variety of useful compounds. These reactions are crucial for producing a wide array of aromatic compounds used in various industries like agrochemicals.
However, the utility of aromatic ketones has been limited due to the difficulty in breaking their strong carbon-carbon bonds. These robust bonds are challenging to cleave, ...
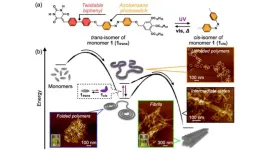
In polymers, the competition between the folding and aggregation of chains, both at an individual level and between chains, can determine the mechanical, thermal, and conductive properties of such materials. Understanding the interplay of folding and aggregation presents a significant opportunity for the development and discovery of polymeric materials with tailored properties and functionalities.
This also holds true for non-covalent counterparts of conventional covalent polymers, i.e., supramolecular polymers (SPs). SPs are expected to have practical applications as novel stimuli-responsive ...