(Press-News.org) Per a new study, as of April 2021, US Congress members whose ancestors enslaved 16 or more people had a net worth that was five times higher than that of legislators whose ancestors did not have slaves. Neil Sehgal of the University of Pennsylvania, US, and Ashwini Sehgal of Case Western Reserve University, US present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on August 21, 2024.
Prior research has linked slavery’s intergenerational effects to contemporary inequality, poverty, education, voting behavior, and life expectancy in the US However, the extent to which past slavery in the US contributes to today’s social and economic conditions remains unclear.
In 2023, Reuters released an investigative series that captured information on slaveholder ancestry for all 535 individuals who were US Congress members as of April 15, 2021. To boost understanding of US slavery’s potential contemporary effects, Sehgal and Sehgal cross-referenced information from that report with legislators’ self-disclosed finances.
Statistical analysis of the data revealed that the net worth of US Congress members whose ancestors had 16 or more slaves was about five times higher than that of legislators whose ancestors did not have slaves—even after accounting for demographic factors that could also be linked to net worth, including age, sex, race, ethnicity, and education.
The researchers note that legislators are not personally responsible for their ancestors’ actions. Nonetheless, the findings provide new evidence suggesting the possibility that past slaveholding practices in the US may continue to affect people today.
The authors outline a number of limitations of their study. For instance, the findings do not point to any specific mechanism by which slave ownership by ancestors might affect contemporary legislators’ wealth. In addition, the dataset is small, does not account for ancestors’ history of slavery prior to the founding of the U.S. in 1776, and may lack certain financial assets and information that legislators are not required to disclose. And because US Congress members tend to be wealthier, the findings cannot be extrapolated to other US politicians or the general public.
Additional research in these areas could help clarify links between slaveholder ancestry and current wealth, which may aid efforts to address contemporary social and economic disparities.
The authors add: “Members of Congress hold significant power to shape policies and set national agendas. Understanding the wealth disparities within this influential group can drive conversations about economic equity and motivate legislators to support policies addressing historical injustices.”
#####
In your coverage please use this URL to provide access to the freely available article in PLOS ONE: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0308351
Citation: Sehgal NKR, Sehgal AR (2024) Slaveholder ancestry and current net worth of members of the United States Congress. PLoS ONE 19(8): e0308351. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0308351
Author Countries: USA
Funding: The author(s) received no specific funding for this work.
END
US Congress members’ wealth statistically linked with ancestors’ slaveholding practices
Study provides new evidence that past slaveholding practices might continue to affect people today
2024-08-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Following a Mediterranean diet may be associated with reduced risk of COVID-19 infection, per systematic review
2024-08-21
Following a Mediterranean diet may be associated with reduced risk of COVID-19 infection, per systematic review, although it's unclear if the diet is also associated with reduced symptoms and severity of illness.
####
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0301564
Article Title: Relevance of Mediterranean diet as a nutritional strategy in diminishing COVID-19 risk: A systematic review
Author Countries: Indonesia
Funding: The author(s) received no specific funding for this work. END ...
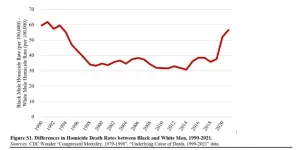
Homicide rates are a major factor in the gap between Black and White life expectancy
2024-08-21
Homicide is a major reason behind lower and more variable reduction in life expectancy for Black rather than White men in recent years, according to a new study published August 21, 2024 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Michael Light and Karl Vachuska of the University of Wisconsin-Madison, USA.
The COVID-19 pandemic precipitated a staggering drop in U.S. life expectancy and substantially widened Black-White disparities in lifespan. It also coincided with the largest one-year increase in the U.S. homicide rate in more than a century, with Black men bearing the brunt of these. Despite these trends, there has been limited research on the contribution ...
Human-wildlife overlap expected to increase across more than half of land on Earth by 2070
2024-08-21
ANN ARBOR—As the human population grows, more than half of Earth's land will experience an increasing overlap between humans and animals by 2070, according to a University of Michigan study.
Greater human-wildlife overlap could lead to more conflict between people and animals, say the U-M researchers. But understanding where the overlap is likely to occur—and which animals are likely to interact with humans in specific areas—will be crucial information for urban planners, conservationists and countries that have pledged international conservation commitments. Their findings ...
Freeze-frame: U of A researchers develop world's fastest microscope that can see electrons in motion
2024-08-21
Imagine owning a camera so powerful it can take freeze-frame photographs of a moving electron – an object traveling so fast it could circle the Earth many times in a matter of a second. Researchers at the University of Arizona have developed the world's fastest electron microscope that can do just that.
They believe their work will lead to groundbreaking advancements in physics, chemistry, bioengineering, materials sciences and more.
"When you get the latest version of a smartphone, it comes with a better camera," said Mohammed Hassan, associate professor of physics and optical sciences. "This transmission electron microscope is ...
Study finds highest prediction of sea-level rise unlikely
2024-08-21
In recent years, the news about Earth's climate—from raging wildfires and stronger hurricanes, to devastating floods and searing heat waves—has provided little good news.
A new Dartmouth-led study, however, reports that one of the very worst projections of how high the world's oceans might rise as the planet's polar ice sheets melt is highly unlikely—though it stresses that the accelerating loss of ice from Greenland and Antarctica is nonetheless dire.
The study challenges a new and alarming prediction in the latest high-profile report from the United Nations' Intergovernmental Panel on ...
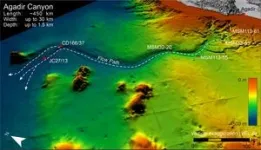
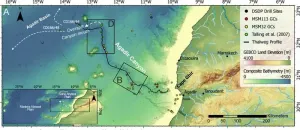
New study reveals devastating power and colossal extent of a giant underwater avalanche off the Moroccan coast
2024-08-21
New research by the University of Liverpool has revealed how an underwater avalanche grew more than 100 times in size causing a huge trail of destruction as it travelled 2000km across the Atlantic Ocean seafloor off the North West coast of Africa.
In a study publishing in the journal Science Advances (and featured on the front cover), researchers provide an unprecedented insight into the scale, force and impact of one of nature’s mysterious phenomena, underwater avalanches.
Dr Chris Stevenson, a sedimentologist from the University of Liverpool’s School of Environmental Sciences, co-led the team that for the first time has mapped a giant underwater avalanche from head ...
To kill mammoths in the Ice Age, people used planted pikes, not throwing spears, researchers say
2024-08-21
How did early humans use sharpened rocks to bring down megafauna 13,000 years ago? Did they throw spears tipped with carefully crafted, razor-sharp rocks called Clovis points? Did they surround and jab mammoths and mastadons? Or did they scavenge wounded animals, using Clovis points as a versatile tool to harvest meat and bones for food and supplies?
UC Berkeley archaeologists say the answer might be none of the above.
Instead, researchers say humans may have braced the butt of their pointed spears against the ground and angled the weapon upward in a way that would impale a charging animal. The force would have driven the spear deeper ...
Using AI to link heat waves to global warming
2024-08-21
Researchers at Stanford and Colorado State University have developed a rapid, low-cost approach for studying how individual extreme weather events have been affected by global warming. Their method, detailed in a Aug. 21 study in Science Advances, uses machine learning to determine how much global warming has contributed to heat waves in the U.S. and elsewhere in recent years. The approach proved highly accurate and could change how scientists study and predict the impact of climate change on a range of extreme weather events. The ...
The role of an energy-producing enzyme in treating Parkinson’s disease
2024-08-21
An enzyme called PGK1 has an unexpectedly critical role in the production of chemical energy in brain cells, according to a preclinical study led by researchers at Weill Cornell Medicine. The investigators found that boosting its activity may help the brain resist the energy deficits that can lead to Parkinson’s disease.
The study, published Aug. 21 in Science Advances, presented evidence that PGK1 is a “rate-limiting” enzyme in energy production in the output-signaling branches, or axons, of the dopamine neurons that are affected in Parkinson’s disease. This means that even a modest boost to PGK1 activity can have ...
Life from a drop of rain: New research suggests rainwater helped form the first protocell walls
2024-08-21
One of the major unanswered questions about the origin of life is how droplets of RNA floating around the primordial soup turned into the membrane-protected packets of life we call cells.
A new paper by engineers from the University of Chicago’s Pritzker School of Molecular Engineering (UChicago PME), the University of Houston’s Chemical Engineering Department, and biologists from the UChicago Chemistry Department, have proposed a solution.
In the paper, published today in Science Advances, UChicago PME postdoctoral researcher Aman Agrawal and his co-authors ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
[Press-News.org] US Congress members’ wealth statistically linked with ancestors’ slaveholding practicesStudy provides new evidence that past slaveholding practices might continue to affect people today